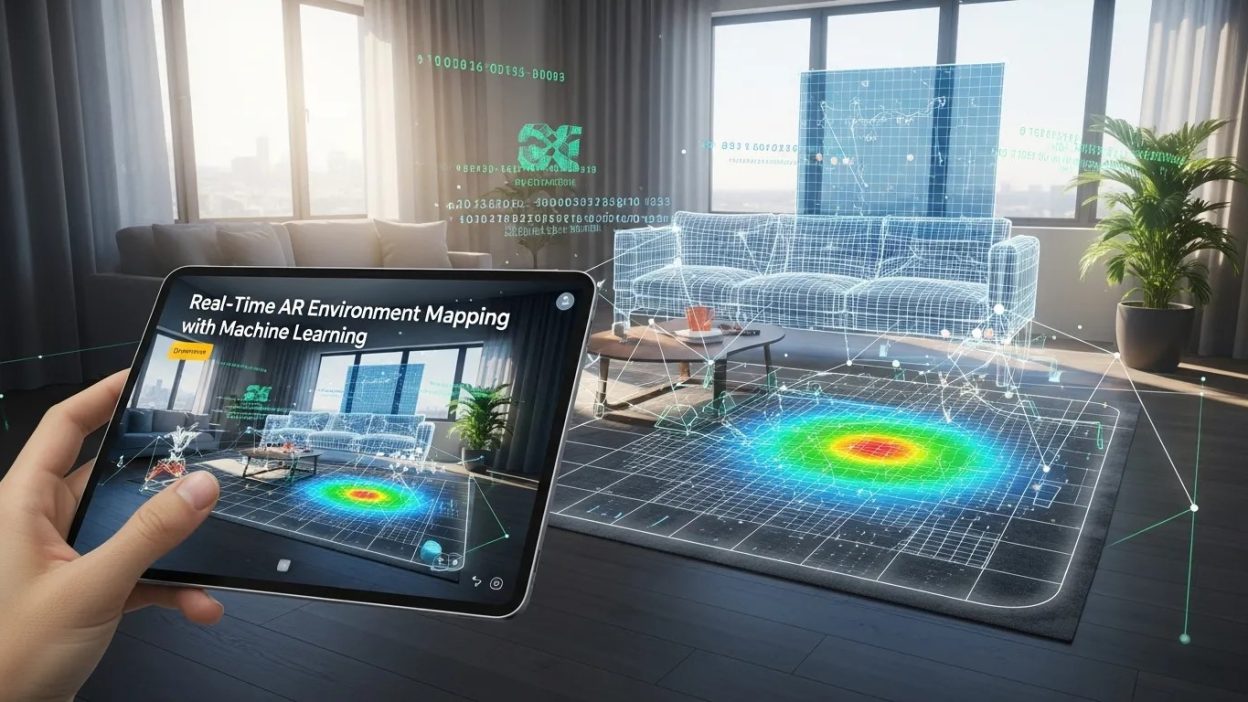
Machine learning enables real-time AR Environment Mapping, combining facial tracking, neural networks, and sensor fusion. These technologies deliver immersive, interactive experiences for gaming, retail, healthcare, and B2B applications, shaping the future of augmented reality.
Real-Time AR Environment Mapping with Machine Learning
Augmented Reality (AR) is no longer a futuristic concept; it has become an integral part of modern digital experiences. At the core of immersive AR applications lies AR Environment Mapping, a process that enables devices to understand and recreate physical spaces in real time. This capability allows digital content to interact seamlessly with the real world, creating experiences that are both engaging and functional. From interactive gaming to industrial design, the precision and reliability of environmental mapping dictate the quality of the AR experience.
The evolution of AR Environment Mapping has been largely fueled by advances in machine learning algorithms. By analyzing vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and user interactions, machine learning models can predict environmental structures, identify objects, and continuously update spatial representations. This allows AR applications to maintain accuracy even in dynamic or unpredictable environments. The combination of machine learning and AR ensures that digital overlays remain anchored correctly, enhancing realism and user trust.
Key Technologies Behind AR Environment Mapping
Several technologies work together to make AR Environment Mapping effective. One of the most crucial is Computer Vision in AR, which enables devices to detect edges, surfaces, and textures in their surroundings. Through computer vision, AR systems can convert raw visual data into actionable spatial information, allowing virtual objects to interact convincingly with physical elements. This capability is essential for applications like virtual interior design, where accurate surface detection ensures furniture and decor are placed realistically.
Another critical component is the use of neural networks in processing complex environmental data. Neural Networks in AR help identify patterns and predict spatial relationships, improving mapping accuracy and reducing latency. For instance, a neural network can recognize recurring structures, such as walls or furniture, and anticipate user movement to adjust the AR overlay accordingly. This predictive ability is vital for maintaining a smooth and immersive AR experience, particularly in real-time applications where any delay can disrupt the user’s sense of presence.
Sensor fusion further enhances mapping precision. By combining inputs from cameras, LiDAR, and motion sensors, AR systems can generate comprehensive environmental models. Machine learning algorithms analyze these inputs, filtering out noise and optimizing the spatial representation. This integrated approach ensures that AR content remains stable, even when users move quickly or the lighting conditions change.
Applications Across Industries
The potential applications of AR Environment Mapping span multiple industries. In healthcare, real-time mapping supports surgical procedures by overlaying critical anatomical data directly onto the patient. Surgeons can view virtual guides while keeping their hands free, improving accuracy and reducing risk. Similarly, in architecture and construction, AR mapping allows designers and engineers to visualize structures before they are built. They can detect spatial conflicts, simulate lighting conditions, and make informed decisions without physical prototypes.
The gaming industry has also benefited significantly from advanced AR mapping. Players can interact with virtual characters and objects as if they exist in the real world. Games leverage real-time environmental data to create dynamic experiences that respond to user movement and surrounding features. Marketing is another area where AR Environment Mapping is proving transformative. Brands use AR to engage consumers interactively, allowing them to visualize products in their own space before purchase. These applications highlight how accurate environment mapping enhances both functionality and engagement.
Challenges in Real-Time AR Mapping
Despite its advantages, AR Environment Mapping faces several challenges. Real-time processing requires significant computational power, particularly for complex environments with multiple moving objects. Maintaining low latency is critical; any lag can break immersion and reduce the effectiveness of the AR experience. Additionally, environmental changes such as lighting variations, moving obstacles, and reflective surfaces can complicate mapping accuracy. Machine learning models must be robust enough to adapt to these conditions while still providing precise spatial representations.
Another challenge lies in device limitations. AR-capable devices range from smartphones to specialized headsets, each with different sensor capabilities and processing power. Developing algorithms that perform well across multiple hardware platforms requires careful optimization. Ensuring privacy and security is also essential, as AR systems often capture sensitive environmental and personal data during mapping.
Future Trends in AR Environment Mapping
Looking ahead, the integration of AI Interfaces for AR Experiences promises to further enhance environment mapping. These interfaces will allow users to interact more intuitively with AR content, using voice commands, gestures, and predictive behaviors to manipulate digital elements in real time. The combination of machine learning and AI-driven interfaces will make AR applications more adaptive, personalized, and context-aware.
In the B2B space, Chatbots in B2B Marketing and AI Conversational Commerce can leverage real-time AR mapping to create interactive client experiences. Imagine virtual showrooms where clients explore products in a realistic AR environment while interacting with AI-powered sales assistants. Such innovations demonstrate the expanding possibilities when AR Environment Mapping converges with intelligent, conversational technologies.
Enhancing AR Experiences with Facial Tracking and Neural Analysis
![]()
While environmental mapping forms the backbone of immersive AR, integrating user-specific data has become equally critical for personalized experiences. AR Facial Tracking enables devices to recognize and track facial features in real time, creating highly interactive and responsive AR applications. By monitoring expressions, gaze, and head movements, AR systems can adapt virtual elements to user behavior, ensuring more natural interactions.
Facial tracking relies heavily on machine learning models trained on vast datasets of human faces. These models detect key landmarks such as eyes, nose, and mouth and predict their movement in three-dimensional space. When combined with AR Environment Mapping, these insights allow digital overlays to maintain alignment not only with the environment but also with user expressions. For example, in virtual try-on applications for makeup or eyewear, AR Facial Tracking ensures that products fit accurately and move naturally as the user interacts.
Neural Networks and Predictive Modeling in AR
To manage the computational complexity of real-time tracking, Neural Networks in AR play a central role. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), for instance, analyze image data efficiently, detecting patterns and facial landmarks with high precision. These networks are trained to adapt to different lighting conditions, angles, and user behaviors, providing consistent tracking even in dynamic or uncontrolled environments.
Predictive modeling further enhances AR responsiveness. Machine learning algorithms can anticipate user movements and adjust AR elements proactively. This is especially important in gaming or training simulations, where even slight lag or misalignment can disrupt immersion. By leveraging neural networks for predictive analysis, AR systems maintain seamless interaction between the physical world, the user, and digital overlays.
Advanced Applications in Retail and Marketing
AI Interfaces for AR Experiences are transforming how businesses engage with consumers. Retailers use AR to create interactive showrooms, allowing customers to visualize products in their own spaces. By combining AR Environment Mapping with facial tracking and AI interfaces, these applications can adjust visualizations according to user behavior and preferences. For instance, an AI interface can recommend complementary products based on a user’s interactions or facial reactions, creating a personalized shopping experience.
Marketing campaigns are also evolving with AR technologies. Brands deploy immersive AR experiences at events or via mobile apps, where users can explore digital content embedded in real-world environments. The integration of Chatbots in B2B Marketing further elevates this experience. Conversational AI can guide users, answer questions, and provide real-time support while they interact with AR displays, creating an engaging, information-rich environment. Combining AI Conversational Commerce with AR mapping ensures that customer interactions are seamless and intuitive, driving engagement and conversion rates.
Technical Challenges in Facial Tracking and Mapping Integration
Despite these advancements, integrating AR Facial Tracking with environmental mapping is not without challenges. Real-time processing of multiple data streams—environmental scans, facial recognition, and sensor inputs—demands high computational efficiency. Machine learning models must be optimized to handle noise, occlusions, and varying lighting conditions while maintaining low latency.
Another challenge lies in privacy and data security. Facial tracking involves sensitive biometric data, and AR systems must implement strict protocols to protect user information. This includes secure data storage, anonymization, and compliance with regional regulations. Balancing technical performance with ethical considerations is crucial for widespread adoption of these technologies.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the fusion of AR Environment Mapping, facial tracking, and AI interfaces is expected to redefine human-computer interaction. We are moving toward systems that understand context, emotion, and intent, enabling AR applications to respond dynamically to user behavior. In professional settings, this could include virtual collaboration environments where participants’ expressions and movements influence real-time shared content.
In education and training, predictive AR systems can adapt lessons or simulations based on learner engagement. For example, an AI interface can detect confusion through subtle facial cues and adjust instruction accordingly. The combination of environmental mapping, facial tracking, and AI-driven interfaces creates opportunities for highly adaptive, personalized experiences that were previously impossible.
Technical Insights into Real-Time AR Environment Mapping
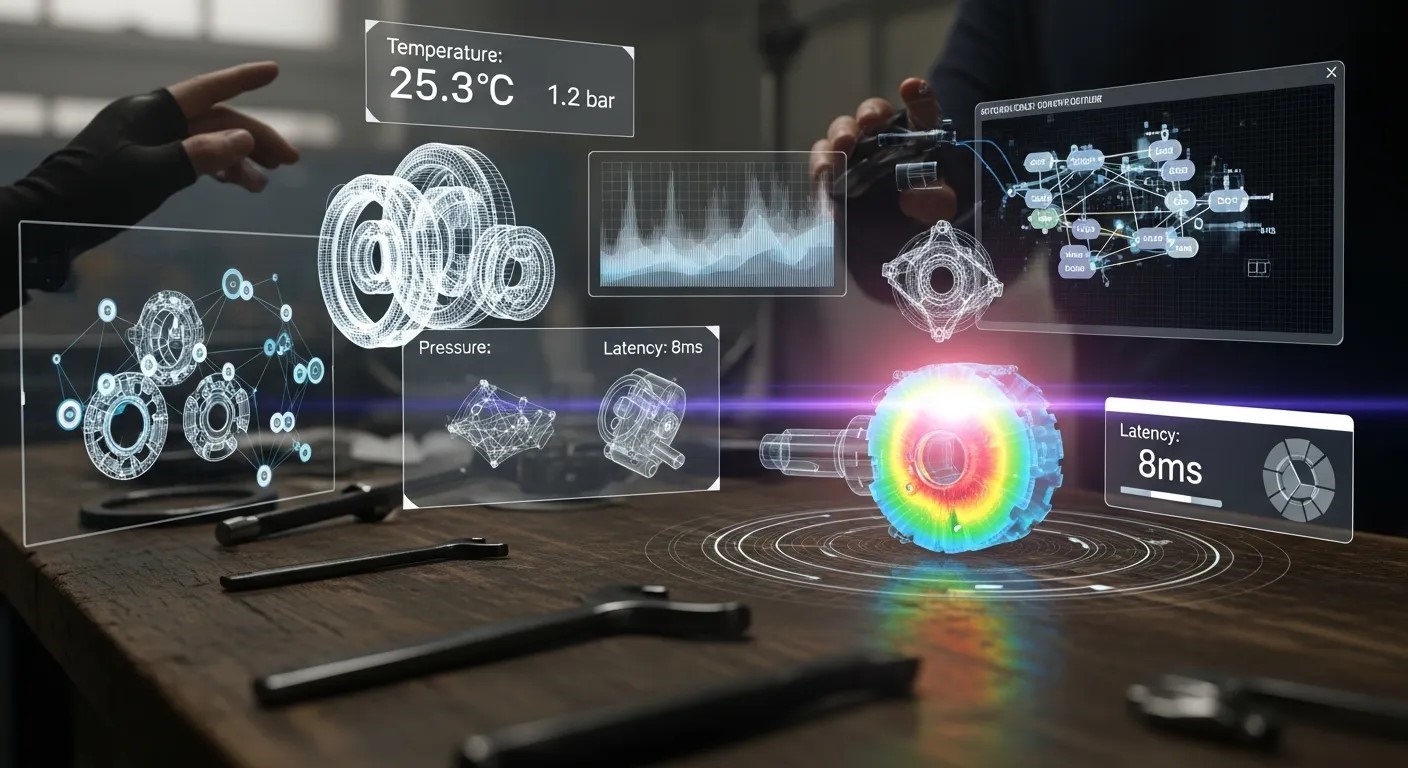
Creating accurate and responsive AR Environment Mapping in real time requires a deep understanding of both hardware capabilities and software algorithms. Modern AR systems rely on a combination of computer vision, neural networks, and sensor integration to generate a dynamic, interactive representation of the user’s environment. Each component contributes to spatial awareness, latency reduction, and immersive user experiences.
Sensor Fusion: The Backbone of Real-Time Mapping
A critical factor in effective AR Environment Mapping is sensor fusion. AR devices combine data from multiple sources such as RGB cameras, depth sensors, LiDAR scanners, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) to construct precise 3D models. Machine learning algorithms analyze this diverse data to detect surfaces, edges, and textures while filtering out noise.
| Sensor Type | Function | Benefits in AR Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| RGB Camera | Captures visual data | Color, texture, object detection |
| Depth Sensor | Measures distance to surfaces | Accurate spatial positioning |
| LiDAR Scanner | 3D mapping of surroundings | High precision in low-light conditions |
| IMU | Detects motion and orientation | Stabilizes virtual overlays |
By fusing data from these sensors, AR applications achieve high fidelity environmental mapping. The system predicts spatial relationships, enabling AI interfaces for AR experiences to overlay content accurately.
Algorithmic Strategies for Low-Latency Mapping
Latency is a significant challenge in real-time AR Environment Mapping. Even minor delays can disrupt immersion. To address this, developers use optimization techniques such as:
-
Predictive Modeling: Neural networks anticipate user movement and environmental changes, updating virtual overlays proactively.
-
Spatial Hierarchies: Segmentation of the environment into priority zones ensures critical objects are processed first.
-
Edge Computing: Processing data locally on the device reduces reliance on cloud latency.
-
Dynamic Level of Detail (LOD): Complex areas are rendered in higher detail, while less important regions are simplified.
These strategies ensure AR applications remain responsive, even in complex or changing environments.
Facial Interaction and User Adaptation
Integrating AR Facial Tracking into real-time mapping enhances personalization. Facial landmark detection allows AR systems to align overlays with user expressions, improving the realism of virtual try-on experiences, gaming avatars, or interactive educational tools. Neural networks process subtle facial cues, predicting movements and ensuring overlays remain consistent with user behavior.
Additionally, machine learning enables adaptive interactions. For example, AI conversational commerce systems can adjust recommendations based on detected expressions or attention levels. This convergence of facial tracking and environmental mapping results in AR experiences that feel more intuitive, responsive, and engaging.
Advanced Neural Network Applications
Neural networks in AR extend beyond facial recognition and surface mapping. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) analyze sequential environmental data, allowing AR systems to track moving objects and predict user interactions. Reinforcement learning techniques can also be applied, enabling AR models to improve over time based on real-world feedback.
In practical applications, neural networks:
-
Detect occlusions and maintain accurate overlay alignment
-
Predict environmental changes for dynamic AR content
-
Enable object recognition to enhance interactive learning and gaming
This layer of intelligence significantly increases both the realism and functionality of AR applications, making AR Environment Mapping a core differentiator in the market.
Optimizing AR for Diverse Hardware
Real-time AR experiences must operate across a range of devices, from smartphones to AR headsets. Performance optimization strategies include:
-
Hardware-aware modeling: Tailoring neural networks to utilize device GPUs or AI accelerators efficiently
-
Memory management: Streaming environmental data to avoid bottlenecks
-
Battery-efficient algorithms: Reducing computational load without sacrificing mapping accuracy
These optimizations ensure that AR Environment Mapping remains consistent, immersive, and accessible across platforms.
Future Technical Trends
The next frontier for AR Environment Mapping lies in combining AI interfaces for AR experiences with predictive environmental modeling. As AR devices become smarter, they will not only map environments but also anticipate user intentions, dynamically adapting content. In B2B contexts, chatbots in B2B marketing integrated with AR can provide interactive demonstrations, product walkthroughs, or client support directly in real-world environments.
Emerging trends include:
-
Real-time multi-user environmental mapping for collaborative AR
-
Integration of cloud AI for complex predictive analytics
-
Adaptive AR environments responding to both user behavior and environmental changes
Real-Time AR Mapping in Everyday Applications
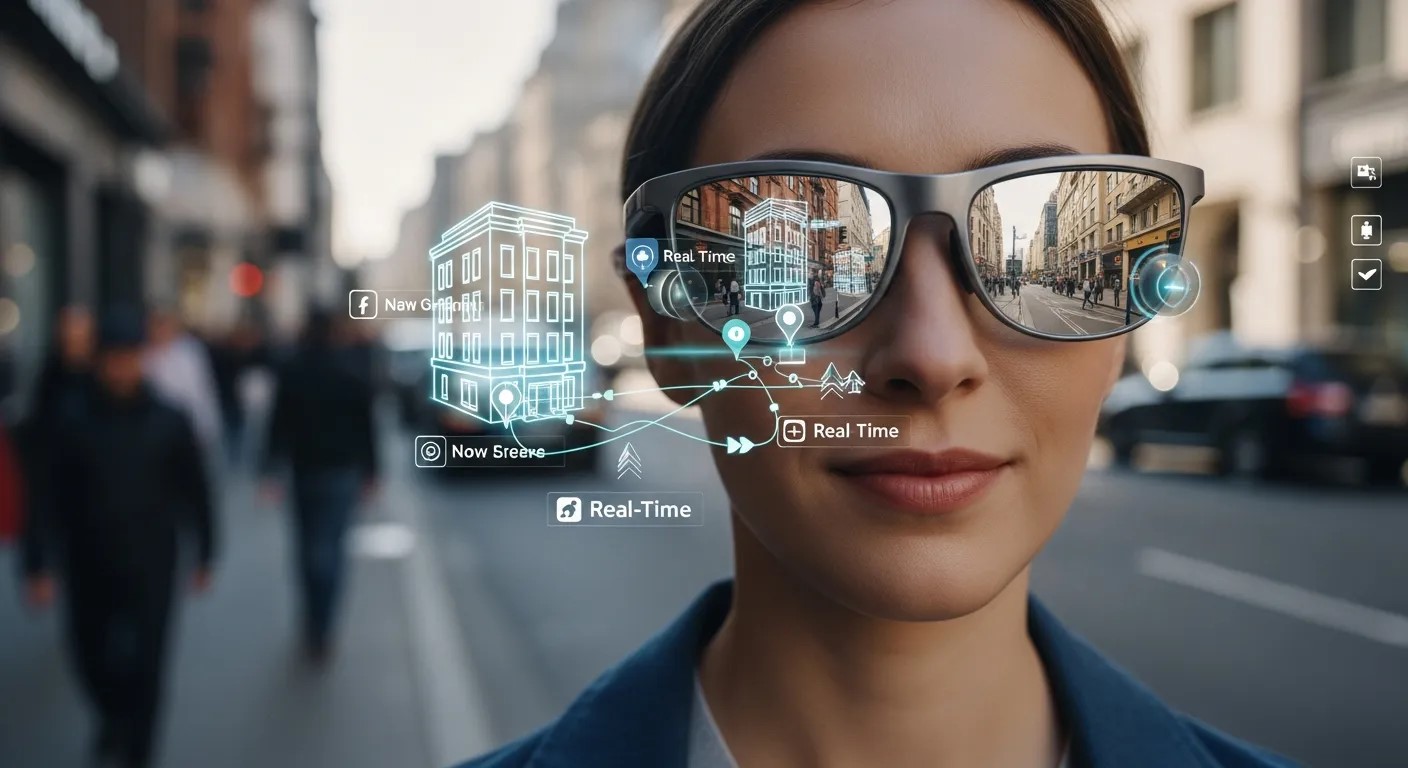

Real-time AR Environment Mapping is not limited to gaming or industrial use; it’s increasingly present in everyday applications. Smartphones use mapping to overlay navigation cues onto streets, while retail apps let users virtually place furniture or try on products at home. Social media filters rely on AR Facial Tracking to adapt effects dynamically, enhancing user engagement. Meanwhile, AI Interfaces for AR Experiences provide intuitive controls and interactions, making augmented reality more accessible. By combining machine learning with environmental data, AR applications deliver seamless, personalized, and interactive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds effortlessly.
Conclusion
Real-time AR Environment Mapping powered by machine learning is revolutionizing how we interact with digital and physical spaces. By integrating technologies like Computer Vision in AR, AR Facial Tracking, and neural networks, AR applications deliver precise, immersive, and interactive experiences across industries. From gaming and retail to healthcare and architecture, mapping environments accurately enhances usability, personalization, and engagement. Coupled with AI Interfaces for AR Experiences and AI Conversational Commerce, these systems are driving innovation in both consumer and B2B applications. As algorithms advance and hardware improves, AR will become even more intuitive, responsive, and integral to our daily lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is AR Environment Mapping?
AR Environment Mapping is the process of scanning, analyzing, and replicating physical spaces digitally to enable interactive AR experiences.
How does machine learning improve AR mapping?
Machine learning predicts spatial relationships, filters sensor noise, and optimizes overlays, ensuring accurate real-time AR interactions.
What role does AR Facial Tracking play in AR experiences?
Facial tracking detects expressions and movements, allowing virtual content to align naturally with user behavior for personalization.
Which industries benefit most from AR Environment Mapping?
Gaming, retail, healthcare, architecture, and marketing leverage AR mapping for immersive, interactive, and data-driven experiences.
How do AI interfaces enhance AR applications?
AI interfaces allow dynamic interaction with AR content, including voice commands, gestures, and adaptive recommendations.
What are the challenges in real-time AR mapping?
Challenges include latency, sensor limitations, dynamic environments, computational demands, and data privacy concerns.
Can AR mapping integrate with B2B chatbots?
Yes, Chatbots in B2B Marketing and AI Conversational Commerce can interact within mapped AR spaces to guide users or clients.




