Augmented reality in Smart Homes is transforming smart home automation by overlaying digital controls directly onto physical environments, making interactions more intuitive and immersive than traditional apps or voice commands.
Over the last decade, smart home automation has evolved from gimmicky remote-controlled gadgets into robust ecosystems that manage lighting, climate, security, and entertainment. Yet most interactions still rely on smartphone apps or voice commands that can feel detached from the physical space. Augmented reality in Smart Homes bridges this gap by overlaying digital interfaces directly onto real environments, enabling users to control devices with natural gestures and on-surface holograms. In this comprehensive guide, we explore how AR is set to revolutionize smart home experiences, offering greater intuitiveness, personalization, and engagement for homeowners everywhere.
Brief History of Home Automation & the Emergence of AR
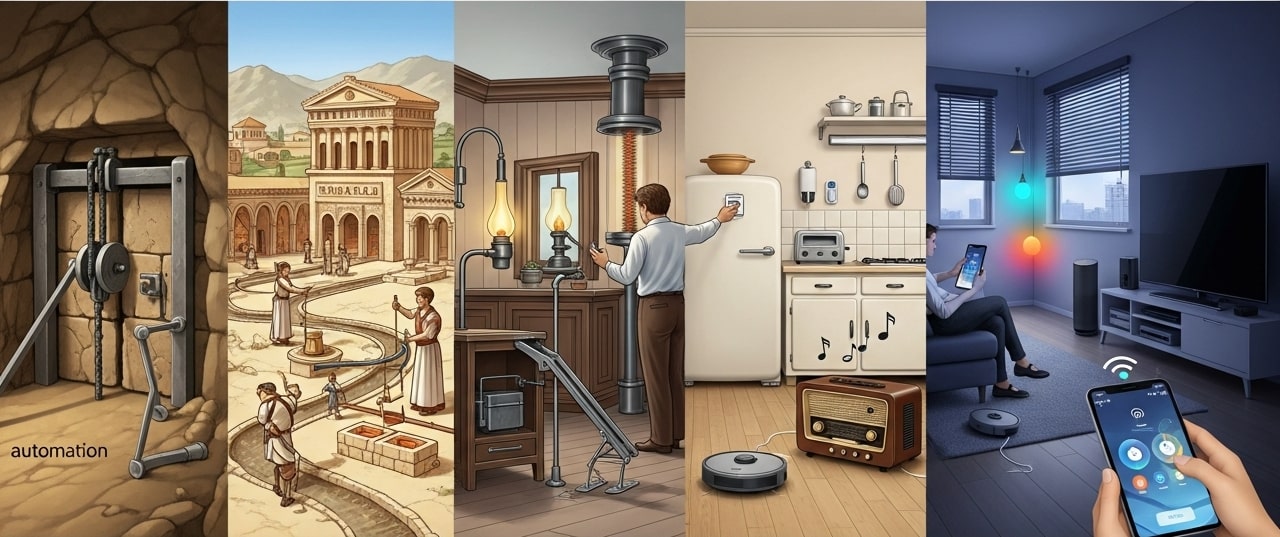
Home automation began with rudimentary timers for lights and fans in the 1970s. The 1990s saw the first programmable thermostats and basic security systems. Fast forward to the 2010s, and devices like smart bulbs, video doorbells, and voice-activated speakers became mainstream. Despite these advances, controlling a dozen or more devices often means juggling multiple apps or remembering complex voice commands. Augmented reality in Smart Homes offers a unified, spatial-first interface: instead of tapping through menus, you simply look at the object you want to control, and AR presents context-aware options right where you need them. This shift is powered by advances in computer vision, edge computing, and machine learning, which together enable real-time environment mapping and gesture recognition.
Key AR Features Enhancing Smart Home Interaction
AR-driven smart home systems combine several core technologies to deliver seamless, immersive control:
- Spatial Mapping: Devices use LiDAR, depth sensors, and stereo cameras to scan rooms in real time. This 3D map anchors digital controls—such as light dimmers, temperature sliders, or security panels—to their corresponding physical objects, ensuring holograms stay locked in place even as you move around.
- Gesture Recognition: Hand tracking and gesture libraries allow users to pinch, swipe, or tap invisible buttons in mid-air. Combined with tactile feedback from wearable devices, gestures feel intuitive and reduce dependence on screens.
- Voice Control Integration: AR platforms often integrate with existing voice assistants for hands-free commands. You can summon menus or fine-tune controls by speaking, while also seeing visual feedback in your field of view.
- Context-Aware Overlays: AR applications adjust their interface based on where you are and which devices are present. Walk into the kitchen, and recipe guidance or appliance controls appear automatically; enter the home office, and lighting and climate options take center stage.
- Cross-Device Synchronization: Through cloud services and local hubs, AR interfaces stay in sync with every smart device. Holographic toggles reflect real-time status, so you never turn off a light that’s already off or set a temperature that’s already reached.
Practical Use Cases for AR-Enhanced Home Automation
Lighting and Climate Control
Picture entering a dimly lit living room and seeing floating brightness sliders next to each lamp. A simple upward swipe increases illumination, while color temperature wheels let you switch from cool white to warm amber. Over your HVAC vent, a holographic thermostat displays current and target temperatures just point and drag to adjust. These direct interactions eliminate menu diving and make fine-tuning your environment feel fluid and natural.
Home Security Management
AR can transform security monitoring by overlaying live camera feeds onto doorframes, windows, or hallways. If motion is detected outside, a small video thumbnail pops up near the entry point, complete with quick-action buttons for two-way audio or alarm activation. You can even draw virtual boundaries on the floor to define safe zones and receive visuals whenever those zones are breached.
Virtual Interior Design
Redecorating a room becomes effortless when you can preview new furniture, paint colors, or artwork in situ. Aim your Future of AR Marketing device at an empty corner, and choose a sofa model from a virtual catalog. Scale, rotate, and reposition items until they look perfect, then order directly through integrated e-commerce links. This visual approach reduces guesswork and costly returns.
Kitchen Assistance and Recipe Guidance
Cooking transforms into an interactive tutorial with AR overlays projected onto kitchen surfaces. Step-by-step instructions appear alongside ingredients, and smart appliances respond automatically—preheating ovens, measuring portion sizes, or sequencing cooking stages. Visual timers hover above pots, and safety alerts pop up if a burner is left on too long.
Senior Care and Health Monitoring
For elderly residents, AR can offer medication reminders, movement prompts, and fall-detection alerts. Holographic notifications appear near pill organizers or bathroom fixtures, guiding daily routines. Caregivers can remotely monitor vital signs and safety sensors, with real-time data displayed as unobtrusive overlays in their own AR view.
Interactive Entertainment and Gaming
Beyond utility, Augmented reality in smart homes support immersive entertainment. Virtual game boards appear on coffee tables, and multiplayer AR experiences let family members interact with shared holographic objects. Ambient lighting systems sync with on-screen action, creating dynamic light shows that deepen immersion in movies or games.
Technical Foundations of AR Smart Home Systems

Building an AR-powered smart home solution involves several interconnected layers:
- Hardware Platforms: Headsets like AR glasses offer hands-free operation, while smartphones and tablets provide handheld AR. Critical specs include field of view, resolution, weight, battery life, and sensor suite.
- Sensing and Computer Vision: Depth cameras, LiDAR modules, and stereo vision systems capture environment geometry. Computer vision algorithms perform surface detection, object recognition, and tracking, ensuring holograms align flawlessly with real objects.
- Connectivity and IoT Protocols: Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth LE, and emerging standards like Matter connect smart devices. AR apps communicate with these networks through local hubs or cloud APIs to fetch device data and send control commands.
- Edge vs. Cloud Processing: Low-latency tasks such as gesture recognition and spatial mapping run on device or edge servers. Complex AI workloads scene understanding, predictive analytics, voice transcription often leverage cloud infrastructure for scalability.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, AR smart home solutions must address several key challenges:
- Privacy and Security: Constant environment scanning raises valid privacy concerns. Encrypting sensor data, processing sensitive information locally, and providing transparent opt-in controls are critical for user trust.
- Cost Barriers: High-end AR headsets and professional installation can be expensive. Widespread adoption may depend on more affordable hardware and plug-and-play AR modules for existing smart home setups.
- Interoperability: The fragmented IoT market means AR platforms must support multiple device ecosystems. Universal standards like Matter aim to streamline integration, but legacy devices remain a hurdle.
- User Comfort and Accessibility: Wearing headsets for extended periods can fatigue users or cause motion discomfort. Designers must prioritize lightweight hardware, ergonomic interfaces, and alternative input methods for users with disabilities.
The Future of Augmented reality in Smart Homes
As AR hardware becomes more affordable and AI models grow more powerful, we can expect even richer smart home experiences:
- Predictive Personalization: AI algorithms will learn daily routines and preferences, automatically adjusting lighting, temperature, and media to match mood and schedule.
- Shared AR Environments: Multiple users will collaborate on home design or entertainment in a synced virtual layer, each seeing annotations and controls from their own perspective.
- Health and Wellness Integration: Wearable sensors will feed biometric data into AR dashboards, guiding posture correction, breathing exercises, or rehab routines within the home.
- Sustainability and Energy Awareness: AR visualizations of power usage, heat loss, and water consumption will empower homeowners to make informed conservation decisions and reduce utility costs.
- Voice-Free Interfaces: Advanced gesture vocabularies and eye-tracking may reduce reliance on voice control, offering silent, private interaction modes in shared living spaces.
AR for Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
As Augmented reality in smart homes grow more complex, energy awareness becomes increasingly important. AR provides intuitive, real-time visualizations that help homeowners understand and reduce their environmental footprint.
Real-Time Energy Overlays
Point your AR device at any appliance, and a floating energy meter appears showing current power consumption. Color-coded indicators highlight inefficient devices, while predictive graphs estimate monthly usage based on patterns. This makes energy management tangible and immediate instead of abstract and hidden in utility dashboards.
Heat Mapping and Insulation Insights
Advanced thermal sensors paired with AR and VR Marketing can reveal hotspots, drafts, or insulation gaps. Homeowners can literally see where heat escapes in the winter or where cooling inefficiencies appear in the summer. These visual cues guide smarter decisions about window sealing, insulation upgrades, or HVAC adjustments.
Water Usage Visualization
Bathrooms and kitchens can feature AR water-flow indicators that display real-time consumption while faucets or showers run. Overlays offer suggestions like switching to eco mode or adjusting temperature to reduce waste without sacrificing comfort.
Automated Eco-Modes
By combining AR with AI-driven automation, homes can suggest or automatically activate energy-saving modes. For example, if AR detects that sunlight fills the living room, it may recommend turning off overhead lighting and adjusting smart blinds for optimal brightness.
Benefits at a Glance:
- Lower utility costs
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Better understanding of home energy patterns
- Simplified decision-making through visual guidance
AR for Home Maintenance and Repairs
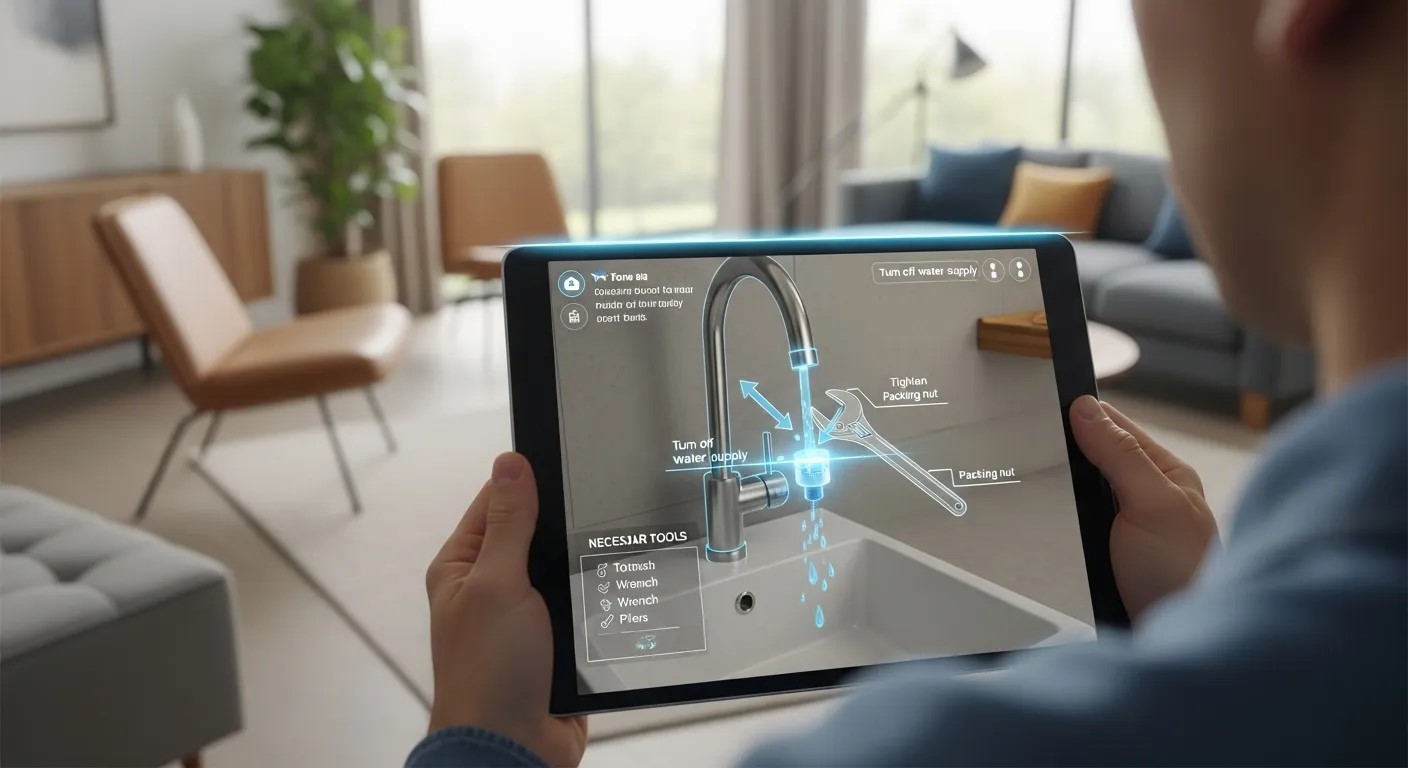
Beyond convenience and entertainment, augmented reality in Smart Homes is poised to transform everyday home maintenance by making repairs simpler, safer, and more accessible. Instead of searching through instruction manuals or online tutorials, homeowners can point their AR device at a malfunctioning appliance or fixture and instantly receive step-by-step visual guidance overlaid directly onto the real object. Pipes, electrical panels, and HVAC components can be highlighted with interactive markers that show which parts to inspect, tighten, or replace. Complex tasks—such as troubleshooting wiring or diagnosing water leaks—become far less intimidating when AR diagrams reveal hidden structures behind walls or beneath floors. This immersive approach not only empowers homeowners to solve minor issues independently but also reduces the likelihood of costly mistakes.
AR can also enhance professional repairs by giving technicians real-time support. Remote experts can annotate the technician’s field of view, indicating precise actions or confirming diagnoses without needing to be on-site. This minimizes downtime, improves service accuracy, and cuts travel-related emissions. Over time, AR-based maintenance systems may even integrate predictive diagnostics, alerting homeowners to emerging problems before they escalate. By blending visual guidance with intelligent monitoring, AR helps create homes that are not just smart but also resilient, self-aware, and easier to care for.
Conclusion
Augmented reality in Smart Homes represents the next frontier in smart home automation, merging the digital and physical worlds to create intuitive, immersive experiences. By overlaying controls directly onto household objects, AR eliminates the friction of app hopping and voice frustrations, delivering seamless, context-aware interactions. While challenges around privacy, cost, and hardware comfort remain, industry momentum and evolving standards promise a future where managing your home feels as natural as living in it. Now is the time to explore AR solutions and envision how this technology can transform your living space into a truly intelligent environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Augmented Reality in Smart Homes?
Augmented Reality in Smart Homes refers to using AR technology to overlay digital controls, data, and interactive interfaces directly onto physical home environments for intuitive device management.
Do I need expensive AR glasses to use Augmented Reality in Smart Homes?
Not necessarily. While premium AR glasses provide a more immersive experience, many Augmented Reality in Smart Homes features work on smartphones or tablets. As hardware prices decrease, affordable options are becoming more accessible.
Will Augmented Reality in Smart Homes slow down my system?
Modern AR applications are optimized with edge processing and efficient connectivity. As long as your home network is stable, AR overlays and commands should respond instantly without disrupting other smart devices.
Is my home data safe when using Augmented Reality in Smart Homes?
Security depends on the platform. Trusted Augmented Reality in Smart Homes systems use end-to-end encryption, local data processing, and transparent privacy controls to protect user information.
Can Augmented Reality in Smart Homes work with existing smart devices?
Yes. Many AR solutions integrate with common IoT protocols like Matter, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi. Compatibility depends on your device ecosystem and may require a hub for older systems.
What happens if multiple people use Augmented Reality in Smart Homes?
Shared AR environments allow multiple users to view synchronized overlays and controls. Each person can have personalized dashboards without interfering with others.
Is Augmented Reality in Smart Homes useful beyond device control?
Absolutely. It supports entertainment, gaming, guided cooking, fitness tracking, education, maintenance assistance, and eldercare monitoring, making it far more versatile than basic automation.
Will Augmented Reality in Smart Homes replace mobile apps?
Not entirely. Augmented Reality in Smart Homes enhances apps by providing spatial, immersive controls. Many systems will likely combine AR, mobile apps, and voice assistants for maximum flexibility.
How does Augmented Reality in Smart Homes improve energy efficiency?
AR can display real-time energy usage overlays, highlight inefficiencies, visualize heat loss, and suggest eco-friendly adjustments, helping homeowners reduce costs and carbon footprints.
Is Augmented Reality in Smart Homes difficult to set up?
Basic AR features are relatively easy to configure through compatible apps. Advanced systems with spatial mapping and AI personalization may require professional setup.
Does Augmented Reality in Smart Homes require constant internet access?
Some features rely on cloud processing, but many AR interactions use local edge processing. Core automation functions can still work even with limited connectivity.
Is Augmented Reality in Smart Homes the future of home automation?
Industry trends suggest yes. As AR hardware becomes more affordable and AI grows more advanced, Augmented Reality in Smart Homes is expected to become a mainstream interface for managing intelligent living spaces.






