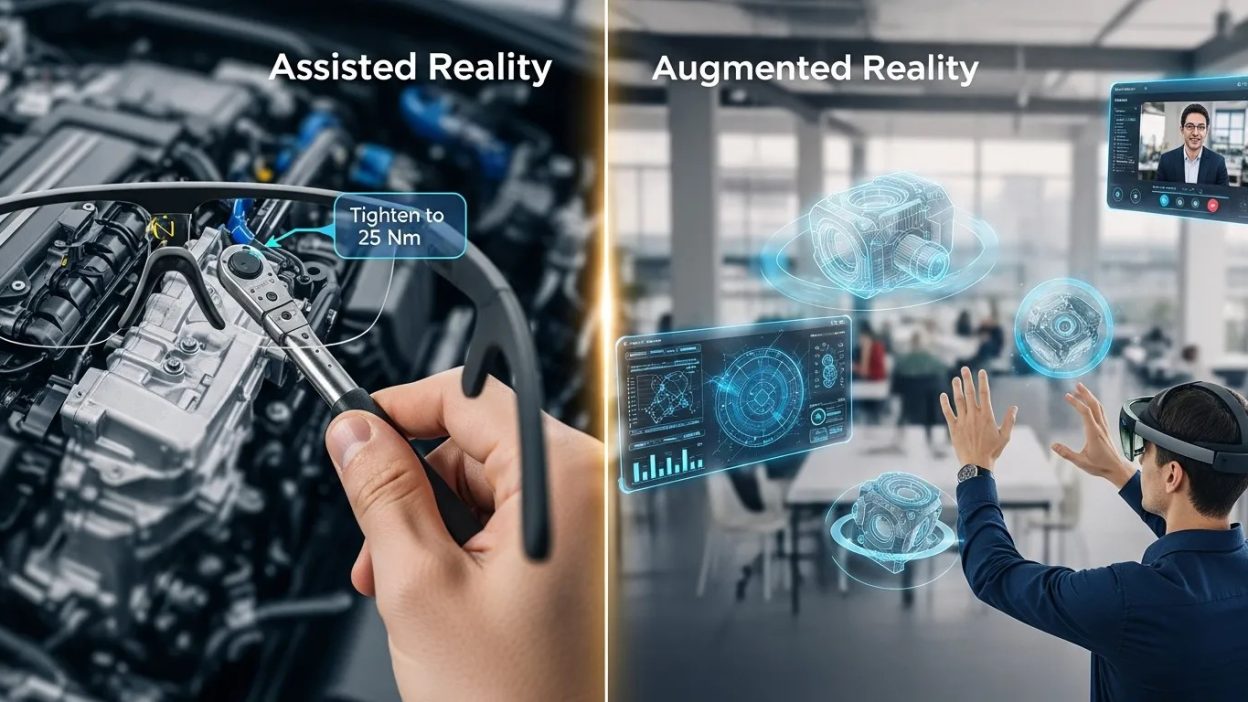
Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality enhance efficiency, training, and engagement across industries. While assisted reality focuses on practical overlays, augmented reality delivers immersive experiences, together transforming enterprise operations, customer interactions, and digital innovation.
Understanding Emerging Immersive Tools: Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technologies, Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality have emerged as transformative tools across industries. While often confused or used interchangeably, these technologies serve distinct purposes and offer unique applications. Understanding their differences is crucial for businesses, researchers, and marketers looking to leverage immersive experiences for enhanced engagement, operational efficiency, and innovation.
What is Assisted Reality?
Assisted Reality refers to a technology that overlays essential digital information onto the user’s view of the real world without fully immersing them in a digital environment. Unlike augmented reality, assisted reality focuses on providing information in a non-intrusive way. This technology often appears in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and field services, where real-time data accessibility is vital for operational efficiency.
Key Features of Assisted Reality
-
Information Overlay: Displays contextual data such as instructions, alerts, or metrics directly within the user’s field of view.
-
Non-Immersive Experience: Users remain fully aware of their physical surroundings, reducing the risk of accidents or disorientation.
-
Hands-Free Interaction: Often integrated into smart glasses or wearable devices, enabling workers to access information without using their hands.
-
Enterprise-Focused Applications: Primarily used in industrial, healthcare, and training settings where efficiency and safety are priorities.
For example, technicians can use assisted reality headsets to view repair manuals while working on machinery without stopping to consult a separate screen. This improves productivity and reduces errors significantly.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real-world environment by overlaying digital elements such as images, animations, and interactive content. Unlike assisted reality, AR is more immersive and visually engaging, often blending physical and digital objects seamlessly. AR has gained widespread adoption across entertainment, marketing, education, and research.
Key Features of Augmented Reality
-
Immersive Visuals: Digital objects or data are integrated with the real environment in a visually rich manner.
-
Interactivity: Users can interact with AR elements through gestures, touch, or voice commands.
-
Cross-Platform Use: AR applications are available on mobile devices, tablets, smart glasses, and AR-specific hardware.
-
Versatility: From gaming to training simulations, AR offers diverse applications across industries.
Table: Assisted Reality vs Augmented Reality
| Feature | Assisted Reality | Augmented Reality |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Non-immersive | Immersive |
| Use Cases | Industrial, Healthcare | Marketing, Education, Entertainment |
| Device Type | Smart Glasses, Wearables | Smartphones, AR Glasses, Tablets |
| Interaction | Minimal, Hands-Free | Interactive, Gestures & Touch |
| Data Presentation | Contextual, Practical | Visual, Engaging |
Core Differences Between Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality
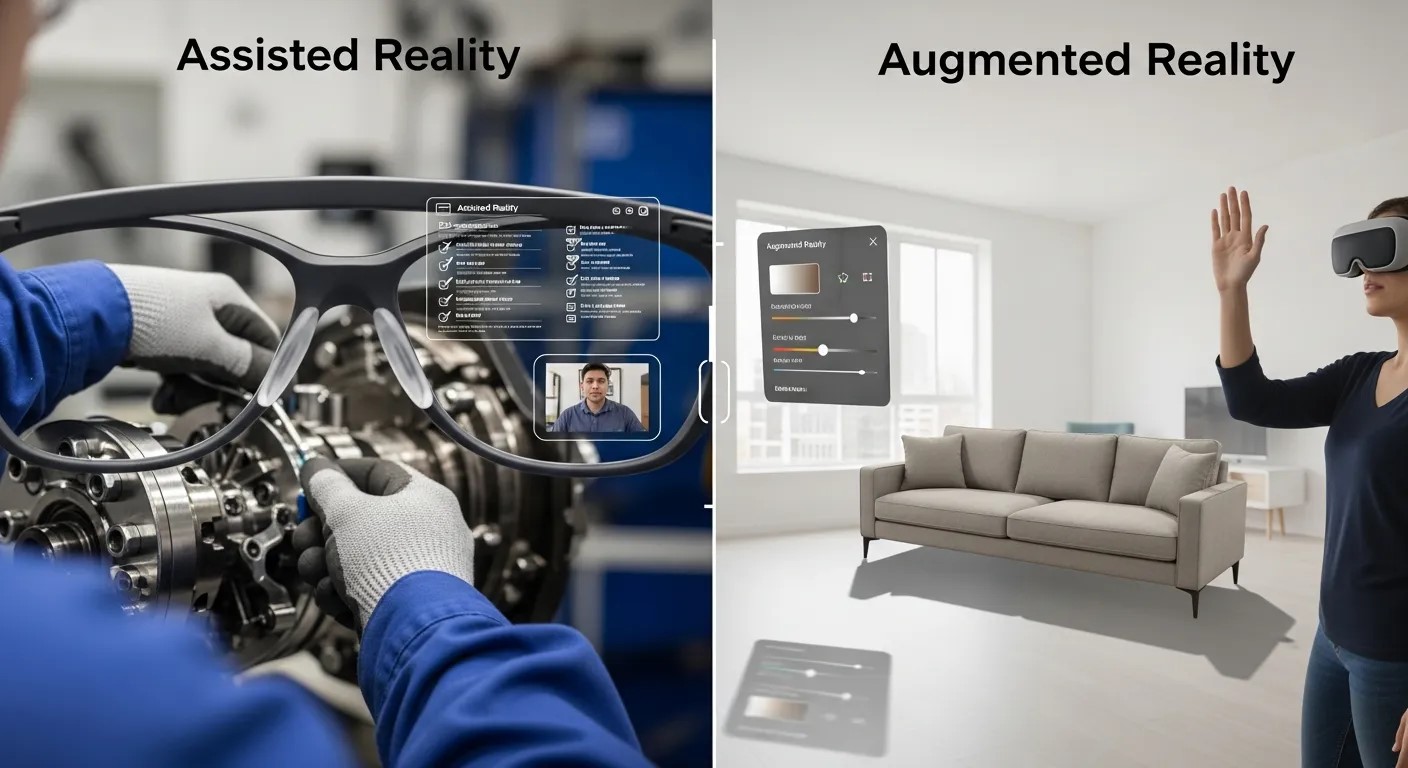

While Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality share the concept of overlaying digital information on the real world, the execution and purpose differ significantly.
User Immersion
-
Assisted reality keeps the user grounded in the real world, providing only essential information.
-
Augmented reality aims to immerse the user by integrating digital objects that interact with the environment.
Industry Applications
-
Assisted reality is prevalent in industrial operations, field services, and healthcare where safety and efficiency are critical.
-
Augmented reality is common in marketing campaigns, retail, education, and entertainment for engagement and visualization.
Device Requirements
-
Assisted reality devices are usually lightweight, hands-free headsets.
-
AR can run on consumer devices such as smartphones or specialized AR glasses with advanced graphics processing.
Interaction Level
-
Assisted reality allows limited interaction—primarily for viewing or simple commands.
-
AR is highly interactive, often requiring gestures, touch, or voice input.
Practical Applications of Assisted Reality
Assisted reality is increasingly being adopted in enterprise settings due to its efficiency and simplicity. Some notable applications include:
-
Field Service Support: Technicians can access schematics, manuals, or real-time instructions while performing maintenance.
-
Healthcare Assistance: Surgeons can view patient vitals or imaging data during operations without looking away.
-
Training and Onboarding: New employees can receive contextual instructions while performing tasks, enhancing learning and retention.
-
Manufacturing Efficiency: Workers can monitor assembly instructions or safety alerts in real-time.
Practical Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality Use Cases span multiple sectors and continue to expand as technology advances. Some examples include:
-
Retail and E-Commerce: AR allows customers to virtually try products, such as furniture or clothing, before purchasing.
-
Education and Training: Students interact with 3D models to better understand complex subjects.
-
Marketing Campaigns: Brands create immersive experiences to attract and retain audience attention.
-
Research and Development: Scientists and engineers use AR to visualize data and prototypes interactively.
By integrating Software Used for Augmented Reality, developers can create applications that are both scalable and highly engaging. Popular software solutions include ARKit, ARCore, Unity, and Vuforia.
How Businesses Leverage Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality
Boosting Operational Efficiency
Companies using assisted reality can provide workers with instant access to information, reducing downtime and mistakes. For example, a logistics company might equip warehouse employees with smart glasses that display pick-and-pack instructions, thereby increasing throughput.
Enhancing Customer Engagement
Augmented reality has revolutionized Augmented Reality Marketing Strategy. Retailers can offer AR experiences that allow customers to visualize products in real-world settings. This not only increases purchase confidence but also improves brand loyalty.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Both assisted and augmented reality can integrate with analytics platforms. By tracking interactions, companies gain insights into workflow efficiency, user behavior, and customer engagement. Advanced Audience Segmentation becomes possible when AR interactions reveal preferences, demographics, and behavioral patterns.
Optimizing Advertising Campaigns
Digital marketers use AR experiences alongside traditional channels to enhance CPC Advertising performance. For instance, interactive AR ads can increase click-through rates by engaging users more effectively than static content.
Research and Innovation in Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality
Assisted Reality in Research
Researchers are exploring how assisted reality can improve cognitive load management and enhance workplace safety. By overlaying critical information selectively, users can maintain focus and efficiency. Industries such as aviation and construction are increasingly incorporating these technologies in research studies.
Augmented Reality in Research
Augmented Reality in Research focuses on immersive simulations, training modules, and visualization of complex datasets. Medical schools, for instance, use AR to visualize anatomy and surgical procedures, offering students an interactive learning environment that traditional textbooks cannot provide.
Implementation Challenges
While both technologies offer significant advantages, there are challenges in deployment:
-
Hardware Limitations: Lightweight, comfortable, and durable devices are essential for long-term use.
-
Software Integration: Ensuring AR/assisted reality platforms integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise systems is critical.
-
User Adaptation: Employees or customers may require time and training to use these technologies effectively.
-
Cost Considerations: Initial investment in devices, software, and training can be substantial, though ROI is often justified by efficiency gains or engagement metrics.
Future Trends in Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality

-
Wearable Device Advancements: Smarter, more ergonomic headsets will enhance user experience.
-
AI Integration: Artificial intelligence will improve context-aware displays, predictive analytics, and personalization.
-
Expanded Enterprise Use: Sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics will continue to adopt assisted reality for operational optimization.
-
Enhanced Marketing Campaigns: Augmented reality will become increasingly critical for brand engagement and digital advertising.
Comparative Insights for Decision-Makers
When deciding between assisted reality and augmented reality, companies should evaluate objectives, context, and desired user experience.
| Consideration | Assisted Reality | Augmented Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Efficiency and productivity | Engagement and immersion |
| User Focus | Workers and professionals | Consumers and learners |
| Interaction | Minimal, information-focused | Highly interactive |
| ROI Measurement | Operational metrics | Engagement metrics, conversions |
| Best For | Enterprise and industrial use | Marketing, research, and education |
Industry-Specific Examples
Manufacturing
- Assisted Reality: Real-time instructions on assembly lines reduce errors.
- Augmented Reality: Virtual prototyping helps engineers visualize new product designs.
Healthcare
- Assisted Reality: Surgeons view patient vitals during procedures without distraction.
- Augmented Reality: Medical students practice surgery in immersive simulations.
Retail
- Assisted Reality: Employees receive stock or inventory updates via wearable devices.
- Augmented Reality: Customers visualize furniture or apparel in real-life settings.
Marketing
- Assisted Reality: Limited use in workflow optimization.
- Augmented Reality: Interactive campaigns improve brand awareness and CPC Advertising efficiency.
Integrating Software and Tools
Successful deployment of Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality relies on selecting the right software tools:
-
AR Software: Unity, Vuforia, ARKit, ARCore
-
Assisted Reality Platforms: RealWear, Vuzix, Epson Moverio
-
Analytics and Segmentation Tools: Platforms enabling Advanced Audience Segmentation help companies optimize campaigns and operational workflows.
Proper integration ensures seamless user experiences, actionable insights, and scalability.
Emerging Applications
-
Remote Assistance: Technicians guided by experts remotely using assisted reality devices.
-
Immersive Product Demos: AR enables interactive exploration of products without physical prototypes.
-
Gamified Learning Experiences: Educational AR apps make learning interactive and memorable.
-
Interactive Advertising: AR-based ads improve conversion rates and CPC Advertising ROI.
Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality in Enterprise Digital Transformation
The role of Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality in enterprise digital transformation is growing rapidly. Organizations are leveraging these technologies to streamline workflows, enhance productivity, and reduce operational risks. By embedding assisted reality solutions into everyday tasks, businesses enable employees to access real-time data without interrupting their workflow.
Augmented reality complements this by providing immersive experiences for training, simulation, and visualization of complex processes. Together, Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality create a hybrid digital ecosystem where practical efficiency meets interactive engagement. Companies adopting these technologies report faster onboarding, lower error rates, and improved decision-making, proving their strategic value in digital transformation initiatives.
Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality for Workforce Training
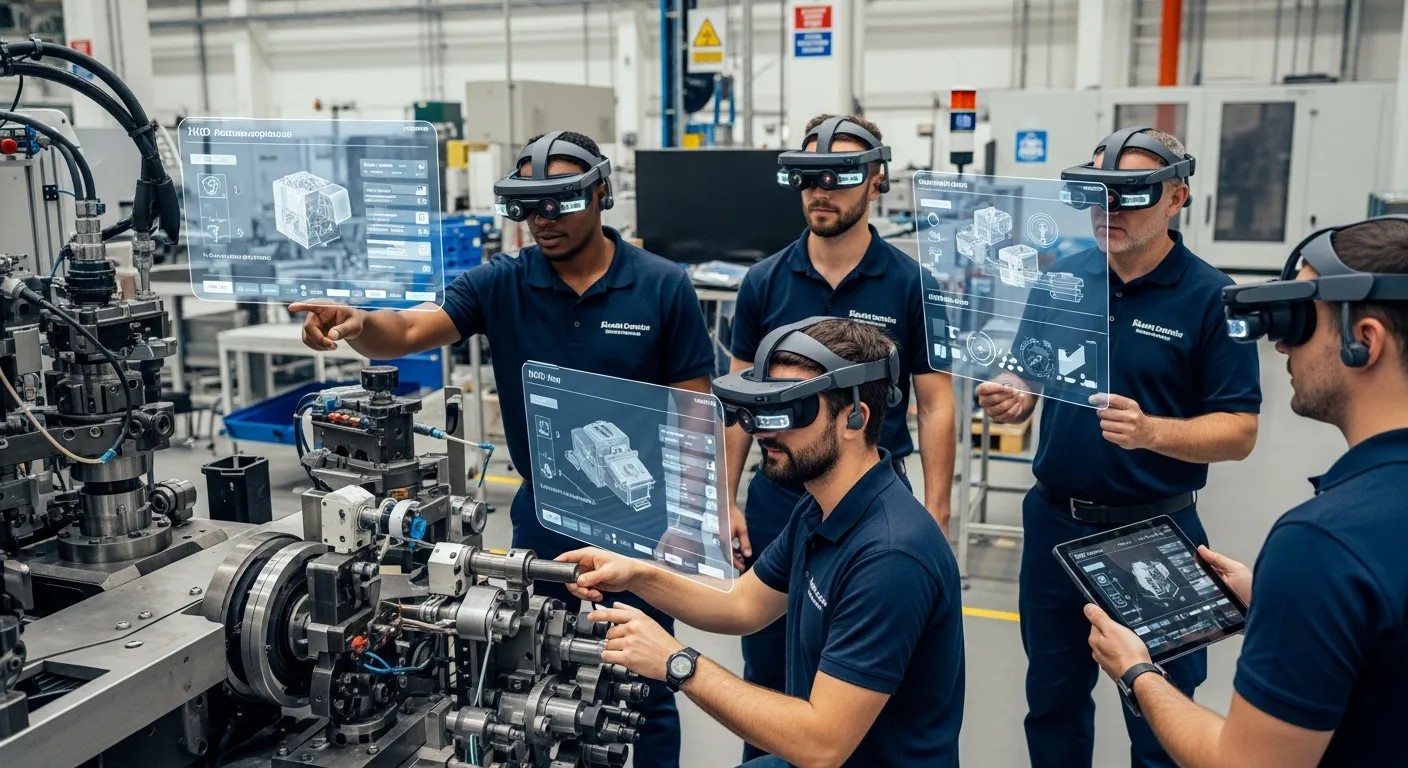

One of the most impactful applications of Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality is workforce training. Employees can engage with digital overlays while performing tasks or participate in fully immersive simulations to learn new skills. Assisted reality devices display step-by-step instructions or contextual alerts directly in the user’s field of view, reducing mistakes and enhancing retention.
Meanwhile, augmented reality allows trainees to interact with virtual equipment, explore detailed 3D models, or practice high-risk procedures in a safe environment. By combining both approaches, organizations can create blended training programs that maximize learning outcomes and minimize downtime. The adoption of Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality in corporate learning strategies is transforming traditional training into a dynamic, measurable, and scalable process.
Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality in Customer Engagement
Customer experience is another domain where Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality offer significant advantages. While assisted reality provides staff with real-time insights to improve service delivery, augmented reality engages customers directly by enabling interactive product demonstrations, virtual try-ons, and immersive brand experiences.
For example, retail and e-commerce companies implement AR to let customers visualize products in their environment before purchase. Integrating assisted reality tools behind the scenes ensures sales staff can provide informed recommendations seamlessly. By using Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality together, businesses enhance customer satisfaction, boost loyalty, and improve overall conversion rates in a measurable way.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality
Looking ahead, the landscape of Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality is poised for significant innovation. Emerging technologies, such as AI-powered context recognition, 5G connectivity, and advanced sensor integration, will make these experiences more intuitive, responsive, and adaptive to user needs.
Businesses investing in Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality today will benefit from improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer interactions, and new avenues for research and development. The synergy between assisted and augmented reality enables organizations to create holistic digital environments where productivity, learning, and engagement converge seamlessly.
Conclusion
In summary, Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality offer distinct yet complementary benefits for modern businesses and industries. Assisted reality enhances efficiency and safety through practical, hands-free information overlays, while augmented reality drives engagement, training, and immersive experiences. Leveraging both technologies strategically enables organizations to optimize operations, improve customer interactions, and stay ahead in the digital landscape. Understanding and adopting Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality is essential for enterprises aiming to innovate, increase productivity, and deliver meaningful user experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between Assisted Reality and Augmented Reality?
Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality differ mainly in immersion and purpose. Assisted reality provides hands-free, practical information overlays, keeping users grounded in the real world, while augmented reality delivers immersive, interactive digital experiences integrated with physical surroundings.
Where is Assisted Reality commonly used?
Assisted reality is widely used in industrial operations, field service, manufacturing, and healthcare. It enables real-time access to instructions, alerts, or data, improving efficiency, safety, and productivity.
What are common use cases of Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality has diverse applications including retail product visualization, immersive training simulations, marketing campaigns, and research. It enhances user engagement by overlaying interactive digital elements onto the real world.
Can Assisted Reality and Augmented Reality be used together?
Yes. Combining Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality allows enterprises to optimize both operational efficiency and immersive engagement. For example, staff can use assisted reality for task instructions while customers experience augmented reality product demos.
Which industries benefit most from Assisted Reality And Augmented Reality?
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, education, and marketing gain the most. Assisted reality improves workforce efficiency and safety, while augmented reality drives engagement, learning, and innovation.
How can businesses measure the impact of these technologies?
Impact can be measured through KPIs like productivity improvement, error reduction, user engagement, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction. Integrating analytics and advanced audience segmentation helps optimize ROI for both assisted and augmented reality deployments.