AR Quantum Computing is transforming technology by merging quantum computing with augmented reality, enabling immersive experiences, adaptive systems, and industry innovation. From healthcare to marketing, education, and autonomous agents, it drives efficiency, personalization, and future-ready digital solutions.
Introduction to AR Quantum Computing
The rapid evolution of technology has brought us to a crossroads where augmented reality (AR) and quantum computing converge. AR Quantum Computing is not just a futuristic concept; it represents a tangible shift in how we perceive, interact with, and utilize digital information. By integrating quantum computing with AR systems, developers and businesses can process massive datasets in real time, enabling experiences previously thought impossible. Imagine immersive AR environments that adapt instantaneously based on user behavior, environmental conditions, and predictive modeling this is the promise of AR Quantum Computing.
In recent years, AR has seen widespread adoption across multiple industries, from gaming and education to healthcare and manufacturing. However, as the complexity of AR applications grows, the need for computational power also increases. Traditional computing methods often struggle to handle the vast amounts of data required for seamless, realistic AR experiences. Quantum computing, with its ability to perform parallel computations on enormous datasets, is emerging as the ideal solution to overcome these limitations.
Integrating quantum computing into AR platforms enables highly dynamic and responsive systems. For instance, real-time rendering of complex 3D environments can be achieved without the lag or buffering typical of conventional AR experiences. This capability unlocks new potential for virtual training simulations, real-time collaborative workspaces, and interactive entertainment experiences. The fusion of AR and quantum computing is transforming not only the technological landscape but also the way users engage with digital content.
The Science Behind AR Quantum Computing
To understand AR Quantum Computing, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental principles of quantum computing. Unlike classical computers, which rely on bits that exist as either 0 or 1, quantum computers use qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This property, known as superposition, allows quantum computers to perform numerous calculations in parallel, drastically reducing computation time for complex problems.
Entanglement, another key principle of quantum computing, allows qubits to be interconnected so that the state of one qubit directly influences the state of another, even over vast distances. When applied to AR, entanglement can enhance real-time synchronization across multiple devices, providing users with coherent, shared experiences in complex AR environments.
By leveraging these quantum properties, AR Quantum Computing can process massive streams of sensory data from cameras, motion sensors, and environmental inputs almost instantaneously. This processing speed is particularly critical for applications requiring immediate feedback, such as autonomous drones navigating dynamic landscapes, AR-guided medical procedures, or immersive virtual classrooms.
Applications of AR Quantum Computing

The potential applications of AR Quantum Computing are broad and transformative. Industries that rely on high-fidelity AR experiences are already exploring the integration of quantum technologies to enhance performance and accuracy.
Healthcare and Medical Training
In healthcare, AR is increasingly used for surgical simulations, anatomy education, and patient care visualization. By incorporating quantum computing, these AR systems can simulate complex biological processes in real time, providing highly precise, interactive models for medical professionals. Surgeons, for instance, can experience dynamic simulations of blood flow, tissue responses, or complex surgical scenarios, all powered by AR Quantum Computing.
Gaming and Entertainment
The gaming industry has long been at the forefront of AR innovation. AR Quantum Computing enables highly immersive environments where game worlds respond instantaneously to player actions. Complex physics calculations, dynamic AI behaviors, and interactive storytelling become feasible at a scale previously unattainable, creating deeply engaging experiences for users.
Industrial and Manufacturing
Manufacturing and industrial operations benefit significantly from AR applications. Quantum-enhanced AR systems can optimize real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and assembly line simulations. For example, workers equipped with AR headsets could visualize machine stress levels or production bottlenecks, with computations processed on the fly through quantum algorithms.
Addressing AR Inequality Through Quantum Advancements
While AR Quantum Computing offers enormous potential, it also raises concerns around accessibility. The term AR Inequality reflects the gap between organizations and individuals who can leverage advanced AR technologies and those who cannot. Quantum computing is still in its early stages, and high costs can limit widespread adoption.
However, research is underway to develop more cost-effective quantum solutions and cloud-based quantum AR platforms, allowing broader access. By addressing these disparities, the benefits of AR Quantum Computing can reach a more diverse set of users, from small startups to large enterprises, democratizing the transformative power of quantum-enhanced AR systems.
Enhancing Marketing with AR Quantum Computing
Businesses are exploring how AR Quantum Computing can transform marketing strategies. AR-enabled campaigns already allow customers to interact with products in virtual spaces, but quantum computing takes this a step further. Marketers can analyze vast datasets, predict consumer behavior, and deliver hyper-personalized experiences in real time.
For example, future AR marketing campaigns could adapt dynamically to individual preferences and environments, using AR Marketing Trends insights powered by quantum processing. These campaigns can create highly engaging, tailored experiences, increasing both conversion rates and brand loyalty.
AI-Personalized VR Narratives and Quantum Computing
Another area where AR Quantum Computing intersects with emerging technology is in storytelling. By combining AR, quantum computing, and AI, developers can create AI-Personalized VR Narratives that evolve based on user choices, environmental context, and predictive modeling. These narratives offer immersive, unique experiences for each participant, from educational simulations to interactive entertainment, all while being powered by the unparalleled processing capabilities of quantum systems.
The Role of AR Autonomous Agents
Quantum computing also enables the development of AR Autonomous Agents intelligent virtual entities capable of interacting with real and virtual environments in sophisticated ways. These agents can guide users, manage complex workflows, or simulate interactive behaviors in training scenarios. When integrated with AR platforms, these agents create responsive, adaptive experiences that enhance usability and engagement.
The potential for AR Autonomous Agents extends across sectors such as retail, healthcare, logistics, and education, allowing for seamless, context-aware support in real-time scenarios. Quantum computing ensures that these agents operate efficiently even in highly complex, data-intensive environments.
Technical Innovations Driving AR Quantum Computing

The development of AR Quantum Computing is fueled by breakthroughs in both hardware and software. Quantum processors are evolving rapidly, with companies experimenting with qubits made from superconducting circuits, trapped ions, and photonic systems. These processors provide the computational power necessary for complex AR tasks such as real-time environment mapping, advanced physics simulations, and adaptive AI-driven interactions.
In addition to hardware, specialized quantum algorithms are enabling new capabilities in AR. Algorithms designed for optimization, pattern recognition, and real-time data analysis allow AR platforms to handle vast streams of information efficiently. When combined with AR sensors and IoT devices, AR Quantum Computing can deliver highly accurate, context-aware experiences to users. This technical synergy is creating a foundation for a new generation of interactive applications that blend the physical and virtual worlds seamlessly.
AR Quantum Computing in Education and Training
One of the most promising sectors for AR Quantum Computing is education and professional training. Traditional learning methods often fail to provide immersive, hands-on experiences, especially in complex fields like medicine, engineering, or scientific research. AR, enhanced by quantum computing, offers interactive simulations that adapt to individual learners’ needs.
Students and professionals can navigate detailed 3D models of chemical reactions, anatomical systems, or mechanical processes in real time. This approach goes beyond passive learning, fostering deeper comprehension and engagement. By integrating AI-Personalized VR Narratives, educational programs can dynamically adjust scenarios based on user decisions, creating a personalized and immersive learning journey powered by quantum-enhanced AR systems.
Transforming Business Operations with AR Quantum Computing
Businesses across industries are exploring the potential of AR Quantum Computing to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and improve customer experiences. In manufacturing, AR headsets can overlay real-time operational data on machinery, while quantum computing handles complex predictive maintenance algorithms to prevent failures.
Similarly, logistics companies can use quantum-enhanced AR navigation to optimize routing, inventory management, and delivery schedules. The ability to process and analyze vast datasets in real time ensures that decisions are precise, efficient, and scalable. This convergence of AR and quantum processing is redefining operational excellence and providing a competitive edge to organizations willing to adopt these technologies.
Addressing Societal Impacts: AR Inequality
As AR Quantum Computing becomes more integrated into society, concerns around AR Inequality emerge. Access to quantum-powered AR systems is still limited by high costs and technical expertise requirements. Individuals and smaller organizations may struggle to adopt these advanced tools, creating gaps in technological literacy and opportunity.
Efforts to mitigate AR Inequality include cloud-based quantum AR platforms, subscription models, and educational programs designed to familiarize users with quantum-enhanced technologies. By bridging this gap, society can ensure broader participation in the benefits of AR Quantum Computing, fostering innovation and inclusivity across sectors.
Enhancing Marketing Strategies with Quantum AR
Marketing is one of the fields experiencing rapid transformation due to AR Quantum Computing. Companies can design immersive, interactive campaigns that respond in real time to consumer behavior and environmental inputs. By analyzing massive datasets, marketers can create highly personalized experiences that increase engagement and brand loyalty.
For instance, AR campaigns informed by AR Marketing Trends can dynamically adapt visual content, promotions, or product placements based on user interactions. This level of customization was previously unattainable with conventional AR platforms. Quantum-enhanced AR allows for instantaneous adjustments, providing businesses with actionable insights while delivering a seamless customer experience.
Quantum AR in Healthcare: Real-Time Decision Making
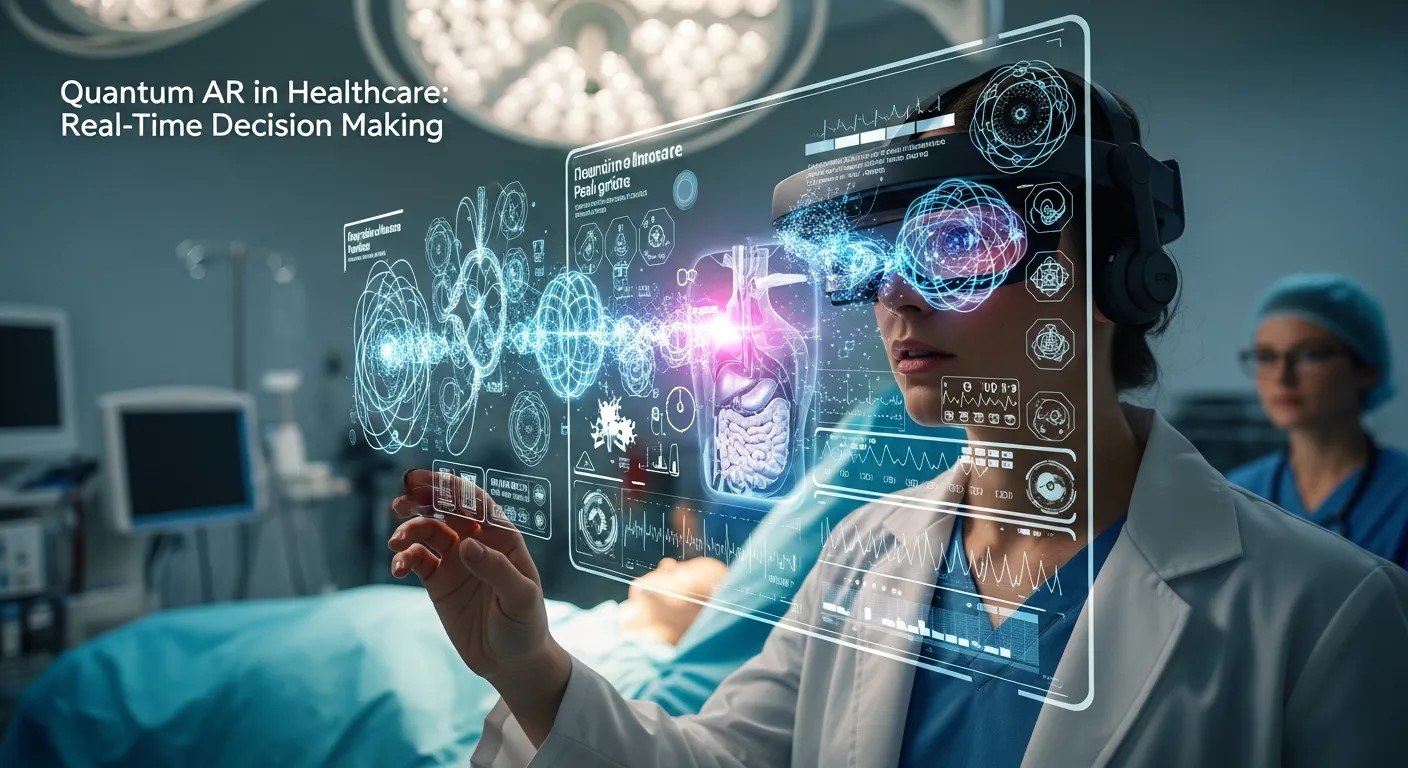

Healthcare applications benefit tremendously from AR Quantum Computing, especially in diagnostics and surgical procedures. Surgeons can use AR overlays to visualize internal organs, blood flow, and tissue interactions while quantum-powered algorithms process complex patient data in real time.
This technology allows for enhanced precision in minimally invasive surgeries, adaptive treatment planning, and personalized rehabilitation programs. By integrating AR Quantum Computing with patient-specific data, healthcare providers can deliver tailored, high-impact interventions while reducing risk and improving outcomes.
AR Autonomous Agents: The Next Frontier
One of the most exciting developments in AR Quantum Computing is the creation of AR Autonomous Agents. These intelligent virtual entities interact with users and environments in real time, providing guidance, support, and adaptive decision-making capabilities.
In industrial settings, autonomous agents can monitor machinery, predict maintenance needs, and guide workers through complex procedures. In retail, these agents can assist customers, recommend products, and provide interactive demonstrations, all powered by quantum-level computation. The responsiveness and adaptability of these agents are made possible by the computational efficiency of quantum systems, setting a new standard for immersive AR experiences.
Security and Privacy Considerations
As AR Quantum Computing becomes more widespread, security and privacy are critical concerns. AR systems collect vast amounts of personal and environmental data, and quantum computing enables processing at unprecedented speeds. Ensuring that sensitive information remains secure is essential for user trust.
Quantum encryption and secure quantum communication protocols are being developed to protect data integrity in AR applications. These protocols will allow for encrypted transmissions between AR devices, cloud servers, and autonomous agents, maintaining confidentiality while supporting the advanced computational needs of AR Quantum Computing applications.
Future Trends in AR Quantum Computing
The trajectory of AR Quantum Computing points toward increasingly immersive and intelligent systems. Emerging trends include:
-
Hybrid Quantum-Classical Systems: Combining classical computing with quantum processors to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
-
Scalable Cloud-Based AR Quantum Services: Making high-powered AR experiences accessible without requiring expensive hardware.
-
Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing predictive capabilities, personalization, and adaptive behaviors in AR environments.
-
Cross-Industry Collaboration: Healthcare, entertainment, education, and manufacturing working together to push AR Quantum Computing applications forward.
These trends indicate that AR Quantum Computing will continue to expand its influence, creating opportunities for innovation, enhanced user experiences, and business transformation.
Cross-Industry Applications of AR Quantum Computing
AR Quantum Computing is no longer limited to theoretical research; real-world applications are expanding across industries. Businesses are leveraging quantum-enhanced AR to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and create immersive experiences.
Manufacturing and Industrial Optimization
In manufacturing, AR-powered systems can overlay operational data directly onto machinery, allowing workers to visualize processes in real time. Quantum computing enables rapid analysis of complex variables, such as supply chain logistics, machine performance, and workflow optimization. Companies adopting AR Quantum Computing can simulate different production scenarios almost instantaneously, identifying bottlenecks and improving efficiency.
Additionally, these technologies facilitate predictive maintenance. Sensors collect real-time operational data, which quantum processors analyze to forecast equipment failures before they occur. This reduces downtime, enhances productivity, and optimizes resource allocation. By merging AR with quantum computing, manufacturers gain a strategic advantage that combines human intuition with high-speed computational power.
Retail and Customer Engagement
Retailers are exploring AR Quantum Computing to revolutionize customer experiences. Interactive AR shopping experiences can now adapt in real time based on customer preferences, purchase history, and environmental context. By integrating insights from AR Marketing Trends, businesses can deliver hyper-personalized experiences.
For example, virtual showrooms allow customers to visualize products in their homes or workplaces. Quantum-enhanced AR systems process massive datasets to adjust visualizations, recommendations, and interactive elements instantly. This creates an immersive, customized shopping journey that fosters loyalty and increases conversion rates.
Healthcare: Precision and Personalized Care
Healthcare continues to benefit from AR Quantum Computing, particularly in diagnostics, treatment planning, and remote care. Hospitals are using AR overlays to provide surgeons with real-time guidance during complex procedures, while quantum algorithms process patient data to recommend optimal surgical strategies.
In rehabilitation and therapy, AR systems track patient progress and adapt exercises dynamically. The inclusion of AI-Personalized VR Narratives ensures that treatment plans are engaging, interactive, and tailored to each patient’s needs. The computational power of quantum systems enables precise, context-aware responses, enhancing the quality and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Education and Research
Educational institutions are adopting AR Quantum Computing to create immersive learning environments. Students can explore complex subjects, such as molecular chemistry, physics simulations, or historical reconstructions, through interactive AR experiences. Quantum computing allows real-time processing of dynamic models, enabling personalized exploration based on student actions.
For research purposes, AR environments integrated with quantum computing facilitate simulation of scenarios that are otherwise impossible to replicate physically. For instance, climate modeling, astrophysics simulations, and material science experiments benefit from the ability to visualize and manipulate complex datasets in an interactive manner.
Addressing AR Inequality on a Global Scale
While AR Quantum Computing offers transformative potential, AR Inequality remains a critical concern. Access to quantum-enhanced AR systems is currently limited to high-budget enterprises, research institutions, and technologically advanced nations.
Efforts to bridge this gap include cloud-based quantum AR services, subscription models, and partnerships between private and public organizations. By making these technologies more accessible, smaller businesses, educational institutions, and underserved communities can leverage the benefits of AR Quantum Computing, fostering inclusivity and democratizing innovation worldwide.
Innovations in AR Autonomous Agents
One of the most exciting frontiers in AR Quantum Computing is the development of AR Autonomous Agents. These intelligent systems can operate independently within AR environments, assisting users, monitoring conditions, or providing guidance without constant human input.
For instance, in smart factories, autonomous agents analyze machinery data and offer real-time operational recommendations. In retail, these agents help customers navigate stores, recommend products, and provide interactive demonstrations. Quantum computing ensures these agents operate efficiently, even when processing large, complex datasets in real time.
Global Adoption and Future Outlook
Countries and corporations around the world are investing heavily in AR Quantum Computing. Tech giants are establishing quantum research labs focused on AR applications, while startups experiment with niche use cases. As quantum hardware becomes more powerful and cost-effective, adoption is expected to accelerate across healthcare, education, entertainment, and manufacturing.
The global outlook for AR Quantum Computing is promising. By 2030, experts predict widespread integration of quantum-enhanced AR in consumer applications, professional training, and enterprise solutions. This trajectory suggests not only technological advancement but also economic growth and innovation across industries.
Challenges Facing AR Quantum Computing

Despite the immense potential, several challenges must be addressed:
-
Technical Complexity: Developing quantum algorithms for AR applications requires specialized knowledge in both quantum computing and AR system design.
-
Hardware Limitations: Qubit stability, error correction, and environmental sensitivity remain major technical hurdles.
-
Cost Barriers: Quantum hardware and advanced AR devices are expensive, contributing to AR Inequality.
-
Data Privacy and Security: Quantum-enhanced AR collects massive amounts of sensitive data, necessitating robust encryption and security measures.
-
User Adoption: Integrating complex quantum-enhanced AR systems into daily workflows requires training and adaptation.
Addressing these challenges is critical for realizing the full potential of AR Quantum Computing. Collaboration between governments, corporations, and educational institutions will accelerate solutions and broaden adoption.
Conclusion
AR Quantum Computing is reshaping the technological landscape, bridging the gap between augmented reality and unprecedented computational power. By combining quantum algorithms with AR systems, industries are now able to deliver highly immersive, real-time, and adaptive experiences that were once unimaginable. From healthcare and education to retail, manufacturing, and entertainment, the integration of quantum computing is unlocking innovative solutions, streamlining operations, and enhancing decision-making.
While challenges such as technical complexity, hardware limitations, and AR Inequality remain, ongoing advancements in quantum research, cloud-based platforms, and cross-industry collaboration are steadily addressing these obstacles. Emerging trends, including AR Autonomous Agents, AI-Personalized VR Narratives, and quantum-powered data analysis, point to a future where AR experiences are smarter, more interactive, and universally accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is AR Quantum Computing?
AR Quantum Computing is the integration of quantum computing technologies with augmented reality systems. It enables real-time processing of complex data, creating immersive, adaptive, and highly responsive AR experiences across industries.
How does AR Quantum Computing benefit healthcare?
In healthcare, AR Quantum Computing allows for real-time visualization of patient data, interactive surgical simulations, and personalized treatment planning. Combined with AI-Personalized VR Narratives, it enhances precision, engagement, and efficiency in medical procedures.
What industries are adopting AR Quantum Computing?
Industries such as education, retail, manufacturing, entertainment, and logistics are exploring AR Quantum Computing. These applications improve immersive learning, customer experiences, operational efficiency, and decision-making processes.
What is AR Inequality and how does it relate to quantum AR?
AR Inequality refers to the gap between those who can access advanced AR technologies and those who cannot. High costs and technical requirements of AR Quantum Computing can exacerbate this, but cloud-based platforms and research initiatives are helping bridge the divide.
What are AR Autonomous Agents?
AR Autonomous Agents are intelligent virtual entities powered by quantum computing that interact with AR environments independently. They assist users, guide workflows, and provide real-time decision-making support in complex systems.
How does AR Quantum Computing influence marketing?
Marketers leverage AR Quantum Computing to deliver hyper-personalized campaigns. Insights from AR Marketing Trends enable dynamic, real-time adjustments to AR experiences, increasing engagement, conversion rates, and customer loyalty.
What challenges does AR Quantum Computing face?
Challenges include technical complexity, expensive hardware, security and privacy concerns, and ensuring broad accessibility. Overcoming these hurdles is key to unlocking the full potential of AR Quantum Computing globally.