AR in Healthcare enhances diagnostics, surgery, training, and patient engagement through immersive, interactive experiences. AI integration and remote capabilities improve accessibility, safety, and outcomes, establishing AR as a cornerstone of modern, technology-driven healthcare.
Introduction The Rise of AR in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is undergoing a profound transformation as technology becomes an integral part of patient care and medical training. Among the most promising innovations is AR in Healthcare, which allows practitioners to visualize complex medical data in real time, improving diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient engagement. Unlike traditional digital tools, AR in Healthcare overlays crucial information directly onto the physical world, bridging the gap between abstract data and tangible patient care.
AR technologies are now being applied across diverse areas, from surgical guidance to rehabilitation therapies. Surgeons can use AR in Healthcare to visualize anatomical structures with unprecedented clarity, reducing risks during intricate procedures. Similarly, medical students benefit from immersive learning experiences where they can explore 3D models of organs and simulate complex surgeries, enhancing comprehension and retention. The adoption of AR in Healthcare not only streamlines workflows but also fosters a safer, more interactive environment for both professionals and patients.
Transforming Medical Training with AR
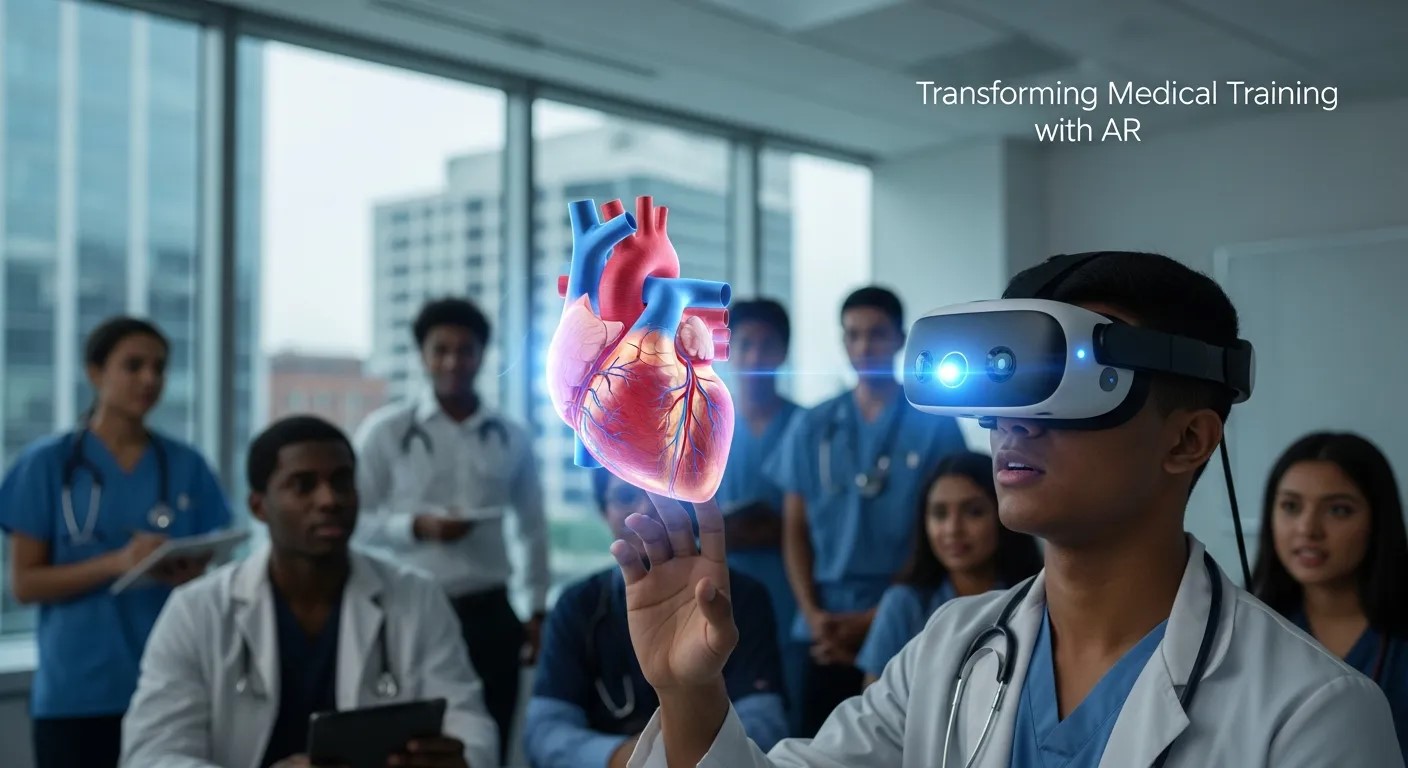

Medical education has traditionally relied on textbooks, lectures, and cadaver-based learning. While effective, these methods often lack the interactive element required to fully engage modern learners. AR in Healthcare addresses this gap by providing immersive simulations that replicate real-world scenarios. Students can interact with life-sized 3D models, practice surgical procedures in a controlled virtual environment, and receive instant feedback on their performance.
For example, in anatomy labs, AR in Healthcare devices can project layers of the human body onto a mannequin or even a live patient, allowing learners to explore internal structures without invasive procedures. Beyond anatomy, AR can simulate patient interactions, giving students the opportunity to refine bedside manners and decision-making skills. This method enhances cognitive understanding while promoting muscle memory for surgical techniques, demonstrating a clear advantage over traditional methods.
Incorporating AI Adaptive AR UX in these training platforms further personalizes the learning experience. Adaptive interfaces analyze user performance, highlighting areas that need improvement and adjusting the difficulty of simulations. This creates a more efficient, tailored educational path for each student, ensuring no learner falls behind.
Enhancing Patient Care Through AR
Beyond education, AR in Healthcare is revolutionizing patient care. Clinicians now have tools to project imaging data, such as MRIs or CT scans, directly onto a patient’s body, providing precise guidance during procedures. This capability reduces errors, shortens surgery times, and enhances overall treatment outcomes. In rehabilitation, AR applications guide patients through exercises by providing visual cues, tracking progress, and offering real-time corrections.
For chronic disease management, AR in Healthcare apps can improve patient adherence to treatment plans. Patients receive interactive instructions on medication intake, exercises, or wound care, fostering engagement and reducing the likelihood of complications. This hands-on approach has proven particularly beneficial in elder care, where visualization and simplicity can significantly improve comprehension and compliance.
Interestingly, AR Privacy and Security has become a critical consideration in these applications. Handling sensitive patient data through AR in Healthcare platforms requires robust encryption and secure access controls. Healthcare providers must ensure that augmented reality solutions comply with privacy regulations such as HIPAA, safeguarding both patient trust and institutional reputation.
Surgical Precision and AR Guidance
One of the most significant impacts of AR in Healthcare is observed in surgery. Augmented reality systems allow surgeons to overlay detailed anatomical maps directly onto the operative field. These visual aids can include blood vessels, nerves, tumors, or other critical structures, giving surgeons a precise roadmap before making incisions.
Complex procedures such as neurosurgery or orthopedic interventions benefit immensely from AR in Healthcare-guided visualization. Surgeons can rehearse the operation using 3D models, anticipate potential complications, and execute procedures with enhanced accuracy. This integration of technology not only reduces operative risks but also shortens patient recovery time, improving overall outcomes.
Moreover, AR can connect remote experts to the surgical field in real time. Using AR in Remote Work, specialists can guide on-site surgeons through intricate procedures, offering expertise without physically being present. This capability is especially valuable in underserved regions or during emergency interventions where access to specialists is limited.
Patient Engagement and Rehabilitation
Augmented reality also redefines patient engagement. Traditional rehabilitation exercises can be repetitive and demotivating, leading to poor adherence. AR in Healthcare platforms transform therapy into an interactive experience. Patients can follow visual guides that illustrate correct movements, gamify exercises, and receive instant feedback, making the process more enjoyable and effective.
In pediatric care, immersive AR games can help children understand medical procedures, reducing fear and anxiety. For adults, AR in Healthcare applications provide visual progress tracking, motivating patients to continue therapy. These applications demonstrate how AR Intelligence is not just about delivering information—it’s about making healthcare experiences intuitive, personalized, and engaging.
Additionally, AR supports remote monitoring for post-operative care. Patients can perform exercises at home while sensors track performance and alert clinicians to potential issues. This reduces hospital visits, lowers costs, and maintains a high standard of care without compromising patient safety.
AR Integration with AI and Chatbots
The combination of AR in Healthcare with AI-driven tools is shaping the next generation of healthcare applications. Integrating AI Chatbot Marketing Funnels and Chatbots in Brand Marketing within AR health platforms allows providers to guide patients, answer questions, and provide educational content seamlessly. For instance, an AR interface could visualize how a treatment works while a chatbot delivers personalized instructions or reminders.
These integrations enhance both operational efficiency and patient experience. Patients receive consistent, on-demand support, reducing dependency on direct clinician interaction for routine queries. Healthcare brands benefit from higher engagement, as interactive AR content paired with conversational AI creates a memorable and informative user experience.
Furthermore, the fusion of AI and AR enables predictive analytics. By analyzing patient interactions within AR in Healthcare environments, AI can recommend tailored care plans, anticipate complications, or identify learning gaps in medical training. This synergy demonstrates the vast potential of combining immersive technology with intelligent systems.
Overcoming Challenges in AR Healthcare Implementation

Despite its promising advantages, implementing AR in Healthcare comes with challenges. High initial costs, technical complexity, and clinician training requirements can hinder adoption. Integration with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems must be seamless to avoid workflow disruptions. Additionally, device ergonomics and user comfort play a significant role in the acceptance of AR in Healthcare in daily clinical practice.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between technology developers, healthcare institutions, and regulatory bodies. Continuous feedback from end users helps refine interfaces, optimize performance, and ensure that AR tools are not only technologically advanced but also practical and intuitive for clinical use.
AR in Diagnostics: Precision Meets Speed
One of the most transformative applications of AR in Healthcare is in diagnostics. Traditional diagnostic procedures often rely on multiple imaging scans and manual interpretation, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. AR in Healthcare streamlines this process by overlaying imaging results—such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs—directly onto a patient’s body, allowing physicians to pinpoint abnormalities with remarkable precision.
For instance, radiologists can use AR in Healthcare to compare past and present scans in real time, detecting subtle changes that might otherwise go unnoticed. This enhanced visualization not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also reduces the time required for analysis, enabling faster treatment decisions. Early detection of conditions such as tumors or vascular anomalies is now more feasible, thanks to AR-driven insights.
Additionally, integrating AI Adaptive AR UX within diagnostic platforms allows systems to analyze patterns across patient data, highlighting critical areas that require immediate attention. This intelligent interface tailors diagnostic workflows to the needs of individual clinicians, improving efficiency without sacrificing accuracy.
Remote Consultations and Telemedicine
The rise of telemedicine has reshaped patient care, and AR in Healthcare plays a crucial role in enhancing these remote interactions. Patients can now share real-time views of their symptoms with clinicians, who can overlay digital annotations, instructions, or treatment visualizations onto the patient’s environment.
For example, a dermatologist can guide a patient in capturing detailed images of skin lesions, using AR in Healthcare tools to highlight areas of concern. Similarly, physical therapists can remotely demonstrate exercises using AR overlays, ensuring patients maintain proper form and avoid injury. These applications not only expand access to medical expertise but also enhance the quality of remote care.
Interestingly, AR in Remote Work has further accelerated this trend. Healthcare professionals can collaborate across locations, sharing AR visualizations during consultations, surgical planning, or team briefings. This fosters knowledge sharing, reduces travel time, and ensures that even patients in remote regions receive top-quality care.
Patient Safety and Risk Reduction
Patient safety is a paramount concern in every healthcare setting, and AR in Healthcare offers innovative solutions to minimize risk. In surgical procedures, AR overlays provide precise anatomical guidance, helping surgeons avoid critical structures and reduce complications. In emergency care, AR-enabled devices can assist paramedics by displaying patient vitals, procedural steps, or drug dosages directly in their line of sight, speeding up decision-making during critical moments.
AR-based training also improves safety outcomes. By simulating high-risk scenarios in a virtual environment, medical professionals can practice responses to emergencies without endangering patients. AR in Healthcare ensures that new staff members gain experience and confidence before handling real-life cases, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
Furthermore, integrating AR Privacy and Security safeguards patient information across these immersive experiences. Encrypted AR platforms protect sensitive medical records while maintaining accessibility for authorized personnel. This balance between innovation and compliance is essential for fostering trust in emerging healthcare technologies.
Advanced Imaging and 3D Visualization
Imaging is at the heart of modern healthcare, and AR in Healthcare elevates it to a new level. Traditional 2D scans can be difficult to interpret, but AR allows clinicians to visualize organs, blood vessels, and tumors in 3D. Surgeons can rotate models, zoom into areas of interest, and simulate interventions before stepping into the operating room.
For cardiology, AR in Healthcare facilitates the mapping of complex vascular networks, helping specialists plan interventions with greater confidence. Orthopedic surgeons can overlay skeletal structures to design precise surgical strategies for joint replacements or fracture repairs. This interactive visualization reduces guesswork, increases procedural accuracy, and ultimately improves patient outcomes.
Moreover, these AR systems often incorporate AR Intelligence, which processes imaging data and highlights potential risks or anomalies. By combining real-time visualization with intelligent analytics, clinicians can make faster, more informed decisions, translating into better care for patients.
Data-Driven Insights for Personalized Care
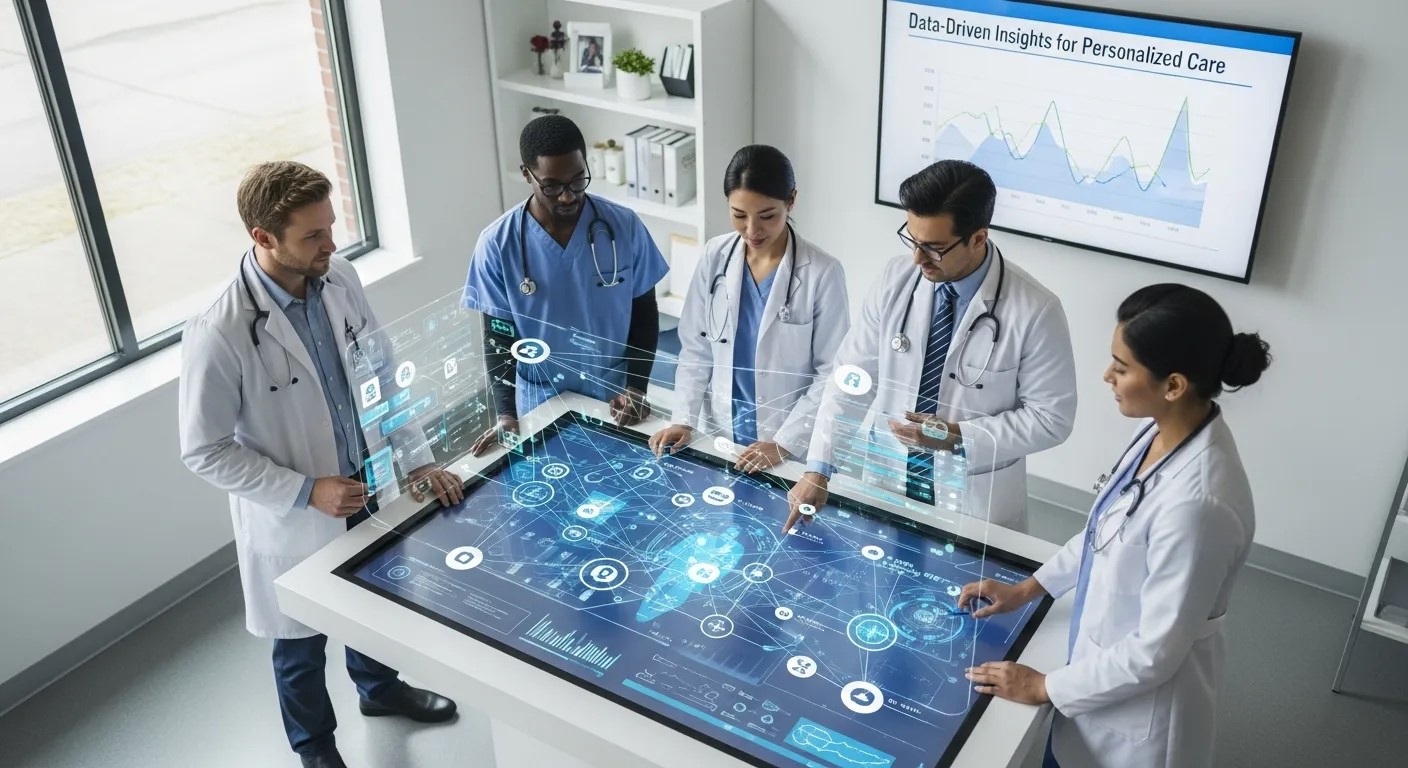

The integration of data analytics with AR in Healthcare enables highly personalized patient care. Sensors embedded in AR devices track patient movements, physiological responses, and adherence to prescribed exercises, generating valuable insights. Clinicians can monitor trends, adjust treatments, and intervene proactively when necessary.
For example, in rehabilitation, AR-based systems measure joint angles and movement speed, alerting therapists if exercises are performed incorrectly. Patients receive personalized feedback, while healthcare providers gain objective data to guide therapy progression. This combination of AR visualization and data analytics represents a major step forward in evidence-based medicine.
Additionally, AR platforms incorporating AI Chatbot Marketing Funnels can guide patients through their treatment journey, offering reminders, educational content, and progress updates. This seamless interaction keeps patients engaged and informed, enhancing adherence and outcomes.
Streamlining Clinical Workflows
AR in Healthcare also improves operational efficiency. Clinicians can access patient records, imaging, and procedural instructions without diverting attention away from the patient. This hands-free access minimizes errors, reduces administrative burden, and allows healthcare professionals to focus on direct patient care.
Moreover, AR systems can integrate with hospital management platforms, scheduling tools, and inventory tracking. For instance, surgical teams can visualize available instruments in real time, reducing delays caused by missing equipment. By streamlining workflows, AR in Healthcare not only improves care quality but also optimizes resource utilization.
Patient Education and Engagement
Engaging patients in their care is another area where AR in Healthcare excels. Interactive AR applications educate patients about conditions, procedures, and lifestyle modifications. Instead of relying on abstract explanations, patients can visualize treatment effects, understand surgical steps, or practice post-operative exercises in a virtual environment.
Pediatric patients, in particular, benefit from gamified AR experiences, which reduce anxiety and improve cooperation. Adults can also visualize long-term health consequences or rehabilitation progress, fostering motivation and adherence. Integrating these features with Chatbots in Brand Marketing enables healthcare providers to maintain consistent, informative communication while building trust and credibility.
AR in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Surgical Procedures
Surgical interventions are among the most critical areas in modern medicine, and AR in Healthcare is transforming how surgeries are planned and executed. Surgeons can now overlay 3D anatomical models directly onto a patient’s body, providing precise guidance during complex procedures. This not only enhances accuracy but also reduces the risk of complications and shortens recovery times.
Using AR in Healthcare, neurosurgeons and orthopedic specialists can visualize critical structures like blood vessels or nerves in real time. These immersive views allow for more confident decision-making, especially in high-risk surgeries. The combination of AR visualization with advanced imaging ensures that every incision is guided by the most accurate data available.
Enhancing Rehabilitation with AR
Beyond surgery, AR in Healthcare is revolutionizing rehabilitation therapy. Patients recovering from injuries or surgeries benefit from interactive exercises where AR overlays provide real-time feedback on posture, range of motion, and exercise completion. This approach improves adherence to therapy plans and accelerates recovery.
Gamified AR experiences also increase motivation, making repetitive exercises more engaging. For example, stroke patients can practice hand coordination by following AR-guided tasks that track progress and adjust difficulty automatically. Integrating AR Intelligence ensures these systems respond dynamically to patient performance, creating a highly personalized rehabilitation experience.
AR in Remote Consultations
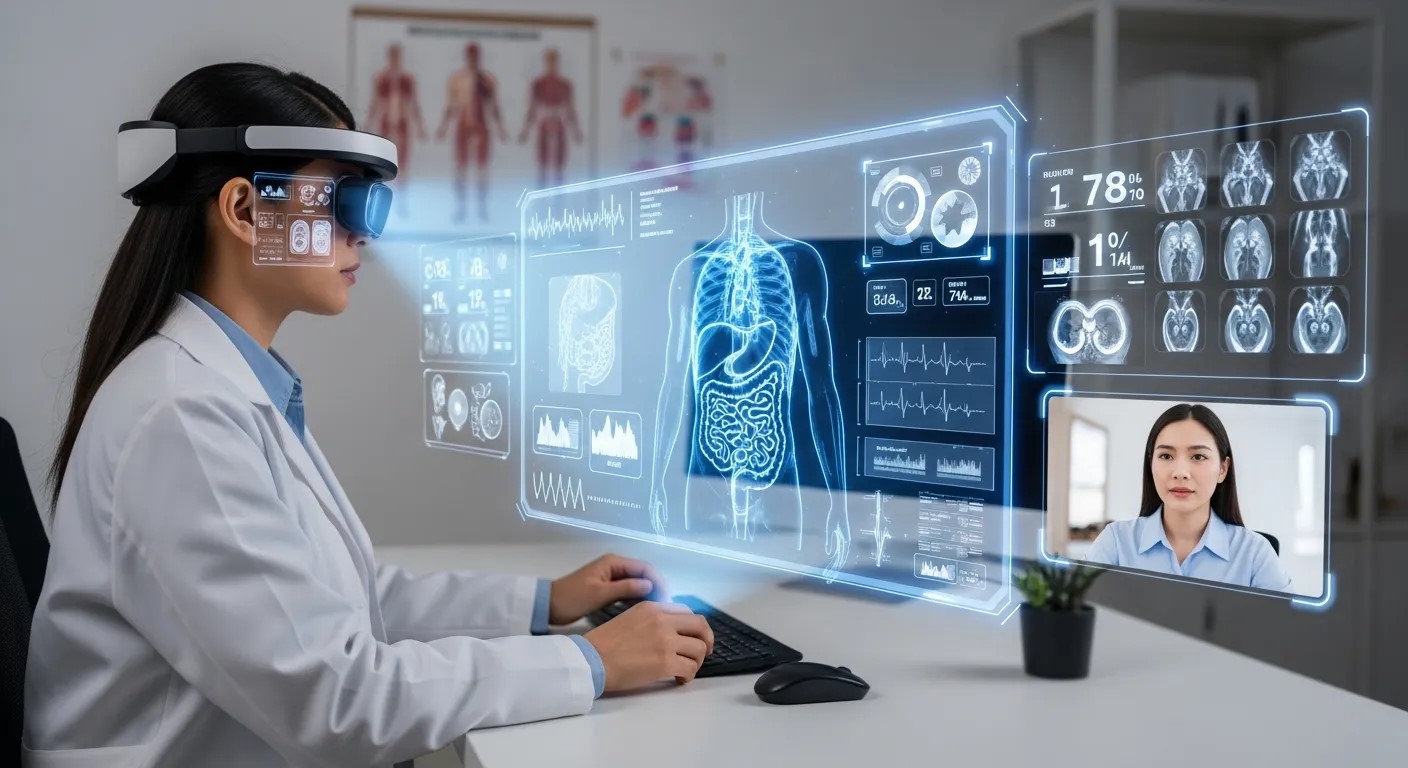

Telemedicine is evolving with the support of AR in Healthcare. Remote consultations now allow physicians to guide patients interactively, overlaying instructions and highlighting key areas of concern during virtual visits. This capability is especially useful for managing chronic conditions or post-operative follow-ups, where patients can receive expert guidance without traveling to a clinic.
Moreover, AR in Remote Work enables specialists in different locations to collaborate on complex cases, sharing visual insights and live annotations in real time. This global connectivity expands access to medical expertise, particularly in underserved regions.
Improving Patient Education
Educating patients about their conditions and treatments is another strong advantage of AR in Healthcare. Instead of abstract explanations, AR provides interactive 3D visualizations, helping patients understand procedures, anatomy, or lifestyle changes. In pediatrics, AR applications reduce fear and anxiety by making medical experiences more interactive, while adult patients gain a clear understanding of treatment plans, boosting engagement and adherence.
Conclusion
AR in Healthcare is transforming patient care, medical training, and surgical precision. From immersive simulations to real-time surgical overlays, augmented reality enables faster, safer, and more effective healthcare delivery. Integrating AR Intelligence, adaptive user experiences, and AI-powered monitoring ensures personalized care and improved outcomes. Remote consultations and rehabilitation programs further extend the reach of healthcare services, enhancing accessibility and engagement. As privacy, security, and workflow integration advance, the potential of AR in Healthcare continues to grow. By bridging technology and medicine, AR empowers clinicians, educates patients, and sets a new standard for modern healthcare innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is AR in Healthcare?
AR in Healthcare uses augmented reality technology to overlay digital information onto the physical world, improving patient care, medical training, and clinical procedures.
How does AR improve medical training?
AR enables immersive simulations, 3D anatomical visualization, and interactive practice, allowing students to gain hands-on experience without risk to patients.
Can AR assist in remote consultations?
Yes, AR allows clinicians to guide patients interactively, highlight key areas, and collaborate with remote specialists in real time.
Is patient data secure in AR systems?
Properly implemented AR platforms incorporate robust AR Privacy and Security measures to protect sensitive health information.
What are future trends in AR Healthcare?
Future developments include AI-driven personalization, predictive analytics, enhanced surgical guidance, and broader integration in rehabilitation, diagnostics, and patient education.