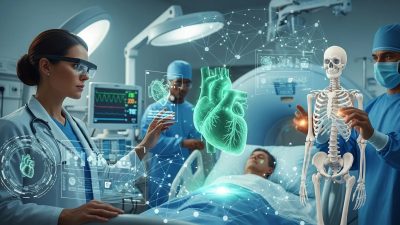
AR Hologram Technology blends digital content with the real world, enhancing education, healthcare, enterprise, and retail. AI, remote collaboration, and IoT integration make holograms intelligent and immersive, while innovations continue to expand accessibility and practical applications.
Understanding AR Hologram Technology: The Next Digital Frontier
Augmented reality (AR) has evolved far beyond simple overlays on smartphones. Among its most compelling applications is AR Hologram Technology, which seamlessly blends digital content with the physical world, creating interactive and immersive experiences. Unlike traditional AR, which often relies on screens or handheld devices, holographic AR projects three-dimensional visuals that appear as part of the real environment, giving users a sense of depth, scale, and interaction that was previously unimaginable.
The rise of AR Hologram Technology is not just about novelty—it’s about transforming how we perceive and interact with information. Industries ranging from entertainment and education to manufacturing are discovering that holographic interfaces can significantly enhance user engagement. For example, engineers can overlay a 3D model of machinery directly onto the equipment, enabling precise assembly or troubleshooting without flipping through manuals. In education, students can explore historical artifacts or anatomical structures in three dimensions, bringing learning to life in ways conventional methods cannot match.
The Core Components of AR Hologram Technology
Understanding AR Hologram Technology requires familiarity with its fundamental components:
-
Projection Systems: Holographic displays use light-field projection or laser-based systems to create realistic 3D visuals. Unlike traditional screens, these projections maintain the correct perspective as the viewer moves around them.
-
Sensors and Cameras: Depth-sensing cameras and motion detectors track the user’s environment and position. This ensures holograms interact accurately with real-world objects.
-
Processing Units: Powerful AR processors handle rendering of high-resolution holograms in real-time, allowing for fluid interaction without lag.
-
Software Platforms: Specialized AR platforms enable developers to create holographic experiences, often integrating AI for intelligent responses, interactivity, and adaptive learning.
Applications of AR Hologram Technology Across Industries
Education and Training
Holograms have revolutionized education by offering hands-on experiences virtually. Medical students, for instance, can study anatomy using 3D models that respond to touch gestures. In technical training, employees can simulate machinery repairs or safety procedures in a risk-free environment. These applications demonstrate how AR Hologram Technology bridges the gap between theory and practice.
Healthcare and Medicine
The integration of AR in Healthcare is particularly promising. Surgeons can visualize organs in three dimensions before operations, improving accuracy and reducing surgical risks. Remote consultations also benefit from holographic visualizations, allowing specialists to guide procedures from a distance. This is increasingly vital in a world where medical expertise may not always be locally accessible.
Enterprise and Remote Collaboration
Modern work relies heavily on remote collaboration. AR in Remote Work allows teams to interact with holographic models during virtual meetings. Architects, designers, and engineers can present complex prototypes in immersive formats, reducing miscommunication and accelerating decision-making. This technology is reshaping how organizations handle collaboration in distributed environments.
Holographic Experiences in Consumer Technology
AR Hologram Technology is not limited to industrial or professional applications. The entertainment and consumer sectors are exploring immersive experiences for gaming, storytelling, and brand engagement. Imagine a virtual concert where holographic performers appear on your living room stage, or a retail experience where furniture can be visualized in your own home before purchase. These experiences are highly engaging and create memorable interactions with digital content.
In marketing, brands increasingly use AI Chatbot Marketing Funnels integrated with holographic AR to personalize customer journeys. Customers can interact with holographic representatives or explore product features in a virtual setting, blending AI intelligence with immersive visualization for higher conversion rates. Similarly, Chatbots in Brand Marketing are starting to leverage AR holograms to create dynamic touchpoints that feel more like interacting with a real person than a traditional interface.
Challenges Facing AR Hologram Technology
Despite its immense potential, AR Hologram Technology faces several challenges:
-
Hardware Limitations: Holographic projectors and AR-capable devices remain costly, limiting widespread adoption.
-
Processing Demands: Rendering high-resolution holograms in real-time requires significant computational power.
-
Privacy Concerns: As AR systems often rely on constant environmental scanning, AR Privacy and Security is a critical consideration. Ensuring user data is protected while maintaining a seamless experience is an ongoing challenge.
-
Content Development: Creating 3D holographic content is resource-intensive, requiring specialized skills and software.
Future Trends in AR Hologram Technology

Looking ahead, several trends are poised to drive the next wave of AR Hologram Technology adoption:
-
Integration with Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered holograms can respond intelligently to user actions, creating adaptive learning, personalized experiences, and real-time problem-solving capabilities.
-
Cloud-Based AR Solutions: Cloud computing can offload heavy processing tasks, enabling more accessible and scalable holographic experiences.
-
Wearable AR Devices: Lightweight AR glasses and headsets will make holograms more interactive and mobile, extending beyond fixed projectors or screens.
-
Cross-Industry Applications: From healthcare and education to entertainment and enterprise, holograms will become increasingly embedded in everyday workflows.
AR Hologram Technology vs. Traditional AR
| Feature | Traditional AR | AR Hologram Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Display | Screens or handheld devices | 3D holographic projections |
| Immersion | Moderate | High, interactive 3D experience |
| User Interaction | Touch-based or gesture | Gesture, spatial, and contextual |
| Application Scope | Limited visualization | Complex simulations, enterprise, and entertainment |
| Accessibility | Widely available | Emerging, device-dependent |
This table highlights how AR Hologram Technology offers enhanced immersion and interactivity compared to conventional AR, making it a disruptive force across multiple sectors.
Advanced Applications of AR Hologram Technology
As AR Hologram Technology continues to mature, industries are discovering increasingly sophisticated ways to leverage holographic experiences. Beyond simple visualizations, modern applications integrate intelligence, interactivity, and even predictive analytics to create immersive, data-driven solutions.
AR Holograms in Industrial Environments
Manufacturing and industrial operations benefit greatly from holographic overlays. Engineers can visualize machinery internals, simulate assembly sequences, and detect potential faults without dismantling equipment. By overlaying digital schematics directly onto physical machinery, workers reduce errors and improve operational efficiency.
Moreover, AR holograms allow for remote troubleshooting. Expert engineers can guide on-site personnel through complex repairs by projecting interactive holograms onto the equipment. This approach not only saves travel costs but also accelerates problem resolution, demonstrating the practical advantage of AR in Remote Work scenarios.
Transforming Healthcare Through Holograms
Healthcare professionals are embracing AR in Healthcare to improve patient outcomes. For instance, surgeons can overlay holographic representations of a patient’s anatomy onto their body during procedures, enabling precise navigation and reducing surgical risks. Beyond surgery, holographic models assist in patient education, allowing individuals to visualize complex procedures and medical conditions clearly.
Additionally, telemedicine is enhanced through AR holograms. Specialists can interact with remote teams in real-time, providing guidance using 3D visualizations. This combination of AR Hologram Technology with virtual collaboration tools ensures accurate decision-making, even across geographic barriers.
AR Intelligence: Merging AI with Holographic Experiences
The integration of AI with AR Hologram Technology opens new possibilities for intelligent and adaptive interactions. Holographic interfaces can now respond dynamically to user behavior, predict user needs, and even suggest actions based on contextual data. For example, in an industrial setting, AI-powered holograms can highlight components likely to fail or suggest maintenance procedures before problems arise.
This blend of AR Intelligence makes holograms more than just visual tools they become proactive assistants, enhancing productivity, safety, and user engagement across various sectors.
Holographic Retail and Consumer Engagement
In the retail space, AR Hologram Technology is transforming how consumers experience products. Imagine entering a store where holographic displays showcase clothing, furniture, or electronics in 3D, allowing users to visualize items in their own space before purchasing. This immersive experience enhances decision-making, reduces return rates, and strengthens brand engagement.
Brands are also combining holograms with AI Chatbot Marketing Funnels to personalize interactions. A holographic assistant can answer questions, suggest products, and guide customers through a tailored journey, making digital shopping feel more human and interactive. Similarly, Chatbots in Brand Marketing are increasingly using AR interfaces to create a seamless, immersive connection between the consumer and the product.
Education and Skill Development Through Holograms

Education is one of the most promising areas for AR Hologram Technology. Students can interact with historical figures, explore scientific phenomena, or manipulate virtual models in real-time. This level of engagement significantly improves retention and comprehension compared to traditional methods.
In corporate training, holographic simulations allow employees to practice tasks in safe, controlled environments. For example, emergency response teams can rehearse complex rescue operations with interactive 3D models, ensuring readiness without risk. The natural placement of AR Hologram Technology in these scenarios emphasizes its potential to transform learning and skill acquisition.
AR Privacy and Security Considerations
As AR Hologram Technology becomes more prevalent, AR Privacy and Security emerges as a critical concern. Holographic systems often require environmental scanning and personal data collection to function effectively. Without robust security protocols, sensitive information could be exposed, raising ethical and legal issues.
Developers are now focusing on encryption, secure cloud processing, and user consent frameworks to mitigate risks. Ensuring that holographic experiences are both immersive and secure will be crucial to building user trust and encouraging widespread adoption.
Integration of AR Hologram Technology with AI and IoT
The convergence of AR Hologram Technology, AI, and IoT devices allows for intelligent, context-aware experiences. In smart manufacturing, IoT sensors feed real-time data into holographic dashboards, enabling operators to visualize production metrics directly in their workspace. AI algorithms analyze this data, predicting maintenance needs and optimizing workflows, making the combination of holograms and intelligence a game-changer for efficiency and decision-making.
In healthcare, IoT-enabled monitoring devices combined with holographic displays provide doctors with real-time patient insights. Imagine a cardiologist reviewing a 3D hologram of a heart while receiving live biometric data this level of integration empowers informed, rapid decisions that were previously impossible.
Entertainment and Media: Redefining Storytelling
The entertainment industry is rapidly adopting AR Hologram Technology to create next-level experiences. Musicians, filmmakers, and game developers are experimenting with holographic content that interacts with audiences in real-world settings. Holographic concerts, interactive performances, and 3D storylines allow audiences to engage like never before.
Gaming is also evolving. Players can interact with holographic game elements in their physical space, merging real and virtual worlds seamlessly. By integrating AI, these experiences become adaptive, responding dynamically to player behavior and making every session unique.
Industrial and Architectural Visualization
Architects and engineers leverage holograms to visualize construction projects before they exist physically. With AR Hologram Technology, clients can walk through a building’s 3D model, assess design choices, and provide feedback in real-time. This reduces miscommunication and ensures projects align closely with expectations.
In industrial environments, large-scale machinery can be represented as holograms to plan factory layouts or simulate production processes. This level of visualization enhances planning accuracy, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, demonstrating the real-world impact of holographic AR systems.
AR Hologram Technology in Remote Collaboration
One of the most impactful applications of AR Hologram Technology is in remote collaboration. Distributed teams can interact with 3D holographic models as if they were in the same room. Engineers can review prototypes, medical teams can plan surgeries, and educators can teach students—all through holographic telepresence.
This not only increases productivity but also enhances engagement and understanding. The combination of AR in Remote Work and holographic collaboration bridges physical distances and enables a new era of virtual teamwork.
Future Innovations in AR Hologram Technology
The future of AR Hologram Technology promises even more transformative experiences as hardware, software, and AI capabilities evolve. Emerging innovations focus on enhancing immersion, interactivity, and accessibility, making holographic AR a central part of digital and physical experiences.
Next-Generation Holographic Displays

Advances in projection technology are enabling more realistic, high-resolution holograms that can be viewed from multiple angles without special glasses. Light-field displays, volumetric projection, and holographic waveguides are pushing the boundaries of visual fidelity. These developments allow AR Hologram Technology to become more portable, energy-efficient, and scalable, expanding its reach beyond specialized laboratories to homes, offices, and public spaces.
AI-Driven Holographic Experiences
Artificial intelligence continues to enhance holographic AR by creating adaptive, context-aware interactions. AI algorithms can analyze user behavior, environmental factors, and historical patterns to modify holographic content dynamically. For instance, in retail, a holographic assistant can suggest products based on a shopper’s past preferences. In education, holographic tutors can adjust difficulty levels in real-time, ensuring personalized learning paths. This integration of AR Intelligence makes experiences smarter and more engaging.
AR Holograms in Environmental Monitoring
Environmental scientists are leveraging AR Hologram Technology to visualize ecological data in intuitive ways. Holographic projections of climate models, pollution patterns, and natural resource flows allow researchers and policymakers to better understand complex systems. By combining real-time data feeds with predictive simulations, stakeholders can make informed decisions about conservation, urban planning, and disaster preparedness.
Government and Enterprise Adoption
Governments and large enterprises are increasingly exploring AR Hologram Technology for operational efficiency and public services. Military and defense applications include training simulations using interactive holograms for mission planning and equipment handling. Public safety departments are experimenting with AR holographic maps to manage crowd control and emergency response more effectively.
Enterprises use holographic dashboards to monitor logistics, manufacturing pipelines, and product lifecycle management. These applications demonstrate how holographic AR goes beyond entertainment, becoming a core tool in decision-making and strategic planning.
Holographic AR and Remote Work Evolution
The post-pandemic world has accelerated the need for effective remote collaboration. AR in Remote Work is now a strategic advantage, allowing employees to interact with holographic project models, architectural layouts, and product prototypes in real-time. Virtual meetings become immersive experiences, where participants can manipulate 3D content together. This improves comprehension, reduces errors, and increases engagement compared to traditional video conferencing.
Moreover, companies are integrating AI Chatbot Marketing Funnels and holographic interfaces into remote workflows, allowing automated support for employees and clients alike. For example, a holographic assistant can provide step-by-step guidance for complex technical tasks, reducing dependency on manual supervision.
AR Privacy and Security in Emerging Applications
As adoption expands, AR Privacy and Security remains a pivotal consideration. Holographic AR devices often collect environmental, behavioral, and biometric data to function effectively. Protecting this information through encryption, secure cloud storage, and user consent mechanisms is critical.
Future standards are likely to enforce stringent guidelines, ensuring that AR Hologram Technology is deployed responsibly. Companies that prioritize privacy and security in their AR solutions will gain a competitive edge, as consumers and enterprises increasingly demand transparent and safe digital experiences.
Industrial and Architectural Innovation
In manufacturing, AR Hologram Technology enables virtual prototyping and digital twins. Engineers can simulate entire production lines with holographic overlays, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing workflows before physical implementation. This reduces costs, minimizes downtime, and ensures better resource management.
Architects and construction firms benefit similarly. Holographic models allow clients and stakeholders to explore buildings before construction begins. By walking through interactive 3D representations, teams can identify design flaws early and improve collaboration between architects, contractors, and clients.
Entertainment, Gaming, and Immersive Storytelling
The entertainment sector continues to push boundaries with AR Hologram Technology. Holographic storytelling allows creators to blend real-world environments with virtual narratives. Audiences can interact with holographic characters, explore 3D environments, and experience content that adapts to their actions.
In gaming, holograms enhance spatial awareness, interaction, and immersion. Players can see game elements in their physical environment, creating a unique blend of virtual and real-world experiences. AI-driven holograms can adjust gameplay dynamically, offering challenges and rewards tailored to the player’s skill level, making each session distinctive.
Education and Workforce Development

The combination of AR Hologram Technology and AI opens new avenues for education and workforce development. Holographic tutors, interactive 3D models, and immersive simulations provide learners with practical, hands-on experience without physical constraints.
Industries such as aviation, healthcare, and engineering benefit from virtual training modules where mistakes are risk-free but lessons are impactful. For example, medical residents can practice procedures on holographic patients, while technicians can simulate complex machinery assembly. This approach increases skill retention and ensures safer, more confident professionals.
Retail, Marketing, and Consumer Engagement
Retailers are experimenting with AR Hologram Technology to create next-level shopping experiences. Holographic displays allow customers to visualize products in their own space, interact with virtual merchandise, and receive personalized recommendations.
Marketing campaigns increasingly integrate Chatbots in Brand Marketing with holographic experiences. Customers can interact with digital brand ambassadors in three dimensions, receiving personalized guidance while exploring products. This seamless integration of AI, holography, and marketing funnels enhances engagement, drives conversions, and fosters long-term brand loyalty.
Challenges in Scaling AR Hologram Technology
Despite its promise, AR Hologram Technology faces challenges in mass adoption:
-
High Cost of Hardware: Advanced holographic displays and AR-capable devices remain expensive, limiting accessibility.
-
Complex Content Creation: Developing high-quality holograms requires specialized skills and software.
-
Data Security and Privacy: Collecting environmental and biometric data raises ethical and legal considerations.
-
User Comfort: Prolonged use of AR holograms may cause fatigue or discomfort, requiring ergonomic design considerations.
Addressing these challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of AR Hologram Technology across industries and consumer markets.
Comparative Insights: AR vs. VR vs. Holographic AR
| Feature | Virtual Reality (VR) | Traditional AR | AR Hologram Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immersion | Fully virtual | Partial overlay | High, interactive 3D in real-world space |
| Devices | Headsets | Smartphones/Tablets | Holographic displays, AR glasses |
| User Interaction | Controller/gestures | Touch or gesture | Gesture, spatial, and contextual |
| Applications | Gaming, simulations | Navigation, info overlays | Education, healthcare, enterprise, entertainment |
| Accessibility | Moderate | High | Emerging, device-dependent |
This comparison shows how AR Hologram Technology combines the immersive qualities of VR with the contextual integration of AR, positioning it as a hybrid solution for diverse applications.
Conclusion
AR Hologram Technology is transforming how we perceive, interact with, and utilize digital information across industries. From healthcare and education to retail and enterprise operations, holographic AR provides immersive, interactive experiences that enhance decision-making, training, and consumer engagement. By integrating AI intelligence, remote collaboration tools, and IoT data, these holograms become proactive, context-aware tools that improve efficiency and productivity. While challenges like hardware costs, content creation, and data privacy remain, ongoing innovations in AI, cloud computing, and wearable AR devices promise to make holographic experiences more accessible, secure, and impactful in the years ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is AR Hologram Technology?
AR Hologram Technology projects three-dimensional digital visuals into real-world environments, creating interactive and immersive experiences beyond traditional AR.
How is AR used in healthcare?
It enables surgeons to visualize anatomy in 3D, assists in patient education, and supports remote consultations through interactive holographic models.
Can holographic AR work in remote work?
Yes, teams can interact with 3D models, prototypes, or simulations in real-time, enhancing collaboration and reducing miscommunication.
What are the privacy concerns with AR holograms?
AR systems often collect environmental and biometric data, requiring secure storage, encryption, and transparent consent frameworks to protect users.
How does AI enhance AR holograms?
AI adds intelligence, enabling holograms to adapt dynamically to user behavior, provide predictive insights, and personalize experiences across industries.
What industries benefit most from AR Hologram Technology?
Healthcare, education, retail, enterprise operations, manufacturing, and entertainment are among the primary beneficiaries.
What challenges does AR Hologram Technology face?
High hardware costs, complex content creation, user comfort, and privacy/security concerns remain key adoption challenges.