AR Autonomous Agents are revolutionizing collaborative workspaces by enhancing productivity, enabling personalized experiences, and supporting remote teams. By integrating AI, tracking ROI, and addressing AR inequality, they create adaptive, inclusive, and efficient environments for modern businesses.
How AR Autonomous Agents Are Shaping Future Workspaces
The evolution of augmented reality (AR) has transformed how teams collaborate in digital environments. One of the most promising advancements in this field is the integration of AR Autonomous Agents. These intelligent systems operate seamlessly within AR workspaces, enabling real-time assistance, task automation, and enhanced decision-making for collaborative teams. By combining spatial awareness with adaptive intelligence, these agents allow users to interact naturally with virtual elements while staying fully engaged in the physical workspace.
In today’s digital-first world, businesses are increasingly exploring how AR Autonomous Agents can streamline workflows. Whether it’s managing complex projects, coordinating remote teams, or enhancing training sessions, these agents provide valuable support by anticipating user needs and responding dynamically. Unlike traditional collaboration tools, AR agents are not passive; they act proactively, offering insights and recommendations that improve efficiency and productivity.
The Role of AR Autonomous Agents in Modern Workspaces

The integration of AR Autonomous Agents into collaborative environments creates a new paradigm for teamwork. These agents can visualize data in three dimensions, track progress across multiple projects, and offer contextual suggestions in real-time. For example, in architectural design meetings, AR agents can overlay structural models directly onto physical spaces, allowing team members to explore designs interactively. Similarly, in healthcare training, these agents can simulate complex procedures, enabling learners to practice skills safely and effectively.
Beyond operational support, AR autonomous systems also contribute to a more inclusive digital workspace. By providing adaptive interfaces and guidance, they help bridge skill gaps, making collaboration smoother for participants with varying levels of technical expertise. This approach directly addresses the challenges of AR Inequality, ensuring that everyone benefits from the same level of technological support without feeling overwhelmed or left behind.
Enhancing Team Productivity and Decision-Making
One of the key benefits of AR Autonomous Agents is their ability to enhance team productivity. By automating routine tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and progress tracking, these agents free up human participants to focus on higher-level strategic decisions. In addition, their real-time analytics capabilities support faster and more informed decision-making. For instance, sales teams can use AR dashboards powered by autonomous agents to track performance metrics and customer engagement, enabling immediate adjustments to strategy.
From a human psychology perspective, AR agents reduce cognitive load. Teams no longer need to juggle multiple software applications simultaneously, as the agents consolidate relevant information in an intuitive AR interface. This creates a more natural workflow, reducing errors and enhancing focus. The adoption of such technologies is also aligned with emerging AR Marketing Trends, where businesses leverage immersive experiences to communicate complex information more effectively to both internal teams and external audiences.
AI-Personalized Experiences in Collaborative AR
The incorporation of AI personalization within AR workspaces is another critical factor in the effectiveness of AR Autonomous Agents. These systems learn from user behavior and preferences to tailor the workspace experience. For instance, an agent might prioritize tasks based on an individual’s workflow habits, suggest collaboration partners for specific projects, or highlight critical updates that require immediate attention. This approach aligns with the growing trend of AI-Personalized VR Narratives, where immersive digital environments adapt dynamically to each user, enhancing engagement and learning outcomes.
By leveraging AI-driven personalization, teams can ensure that collaboration remains efficient even in complex or large-scale projects. The system’s ability to anticipate needs reduces friction, promotes accountability, and fosters a sense of shared purpose. Moreover, it opens opportunities for more creative problem-solving, as agents can suggest innovative approaches that human participants may not immediately consider.
ROI Tracking and Performance Metrics for AR Workspaces
For businesses adopting AR Autonomous Agents, understanding the return on investment (ROI) is crucial. Advanced AR platforms now include robust ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns, allowing teams to measure the impact of autonomous agents on productivity, collaboration efficiency, and project outcomes. By analyzing these metrics, decision-makers can identify which processes benefit most from AR integration and adjust strategies accordingly.
ROI tracking also helps quantify the value of real-time insights provided by AR agents. For example, in manufacturing or logistics environments, autonomous agents can monitor workflow bottlenecks and provide immediate recommendations. The insights generated not only improve efficiency but also reduce operational costs by identifying redundancies or potential errors before they escalate. This data-driven approach ensures that investments in AR technology are both measurable and meaningful.
Integrating AR Autonomous Agents into Existing Workflows
Seamless integration is essential for the success of AR Autonomous Agents. Companies must ensure that their AR solutions complement existing collaboration tools rather than disrupt established workflows. This often involves training sessions, pilot programs, and continuous feedback loops to optimize the agent’s behavior. When implemented thoughtfully, these agents can enhance communication, reduce misunderstandings, and foster more cohesive teamwork.
In practice, AR agents can serve as mediators during virtual meetings, automatically highlighting agenda points, tracking task completion, and providing contextual annotations in real time. By doing so, they minimize the need for constant manual oversight, allowing teams to focus on creative problem-solving. Additionally, the agents’ ability to adapt to different user preferences ensures that participants at all skill levels can interact comfortably with the system.
Overcoming Challenges in Collaborative AR Environments

Despite their many advantages, deploying AR Autonomous Agents comes with challenges. Technical barriers, such as device compatibility, network latency, and system scalability, must be addressed to ensure smooth operation. Human factors, such as user adaptability and trust in autonomous systems, also play a significant role in adoption. Companies should prioritize user-centric design and iterative testing to overcome these obstacles.
Another critical consideration is accessibility. Addressing AR Inequality requires that AR tools and autonomous agents are designed inclusively, ensuring equitable participation for all users. By offering customizable interfaces, adjustable guidance levels, and adaptive feedback, organizations can create an environment where technology empowers rather than alienates team members.
Future Prospects of AR Autonomous Agents
Looking ahead, the potential of AR Autonomous Agents in collaborative workspaces is immense. As AI and AR technologies continue to advance, agents will become increasingly capable of understanding complex human interactions, predicting project needs, and offering context-aware suggestions. This evolution will enable richer, more immersive collaboration experiences, where virtual and physical workspaces blend seamlessly.
Emerging trends also point toward integration with AI-Personalized VR Narratives, allowing agents to deliver tailored guidance and training within AR environments. For instance, onboarding new team members could involve immersive, agent-guided experiences that adapt to each individual’s learning style. Similarly, creative teams could leverage AR agents to simulate multiple design iterations quickly, accelerating innovation while reducing resource waste.
Real-World Case Studies of AR Autonomous Agents
Many industries are already reaping the benefits of AR Autonomous Agents in collaborative workspaces. In manufacturing, autonomous agfents assist teams by overlaying assembly instructions directly onto physical components. Workers can follow step-by-step guidance while the agent monitors progress, reducing errors and increasing output efficiency. Similarly, in architecture and engineering, AR agents allow teams to interact with 3D models in real-time, adjusting designs collaboratively without relying solely on traditional CAD tools.
Healthcare is another sector embracing AR agents. Surgical teams can use AR Autonomous Agents to visualize patient anatomy during procedures, receive automated recommendations, and access critical data without diverting attention from the operation. These applications demonstrate that the agents not only enhance productivity but also improve safety and accuracy in high-stakes environments.
Across these case studies, organizations also observe measurable outcomes through ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns, highlighting improvements in task completion rates, error reduction, and team efficiency. This evidence reinforces the value of autonomous agents beyond theoretical benefits, showing tangible business impact.
Cross-Industry Applications
AR Autonomous Agents are versatile and applicable across numerous industries. In retail, they can create interactive shopping experiences, guiding staff through inventory management or assisting customers in navigating complex stores. Marketing teams leverage these agents to develop immersive campaigns aligned with AR Marketing Trends, where virtual elements enhance consumer engagement and storytelling.
Education and training sectors also benefit greatly. Agents can deliver personalized instruction, adapting to individual learning speeds and preferences. This aligns closely with AI-Personalized VR Narratives, allowing learners to explore immersive content tailored to their knowledge gaps, thereby improving retention and engagement.
Even remote collaboration benefits significantly. Teams dispersed across locations can share the same AR workspace, with autonomous agents facilitating communication, tracking project milestones, and offering contextual insights. This creates a unified workspace experience, overcoming the limitations of physical distance.
Best Practices for Implementing AR Autonomous Agents
Successfully integrating AR Autonomous Agents requires a combination of strategic planning, user-centered design, and continuous optimization. Organizations should begin with a clear understanding of workflows and collaboration bottlenecks. Identifying areas where autonomous agents can add measurable value ensures that their deployment supports business objectives rather than adding unnecessary complexity.
Training and onboarding are critical. Even the most advanced AR Autonomous Agents require users to understand their capabilities and limitations. Providing interactive tutorials, simulations, and gradual adoption paths helps teams embrace these technologies effectively.
Privacy and security considerations must also be addressed. AR workspaces often involve sensitive data, and autonomous agents may access or process this information. Organizations should implement robust security protocols, including data encryption, user access controls, and activity monitoring.
Finally, iterative feedback loops ensure continuous improvement. By collecting user feedback, analyzing usage patterns, and refining agent behaviors, companies can maintain high levels of engagement and productivity over time.
Technical Architecture of AR Autonomous Agents
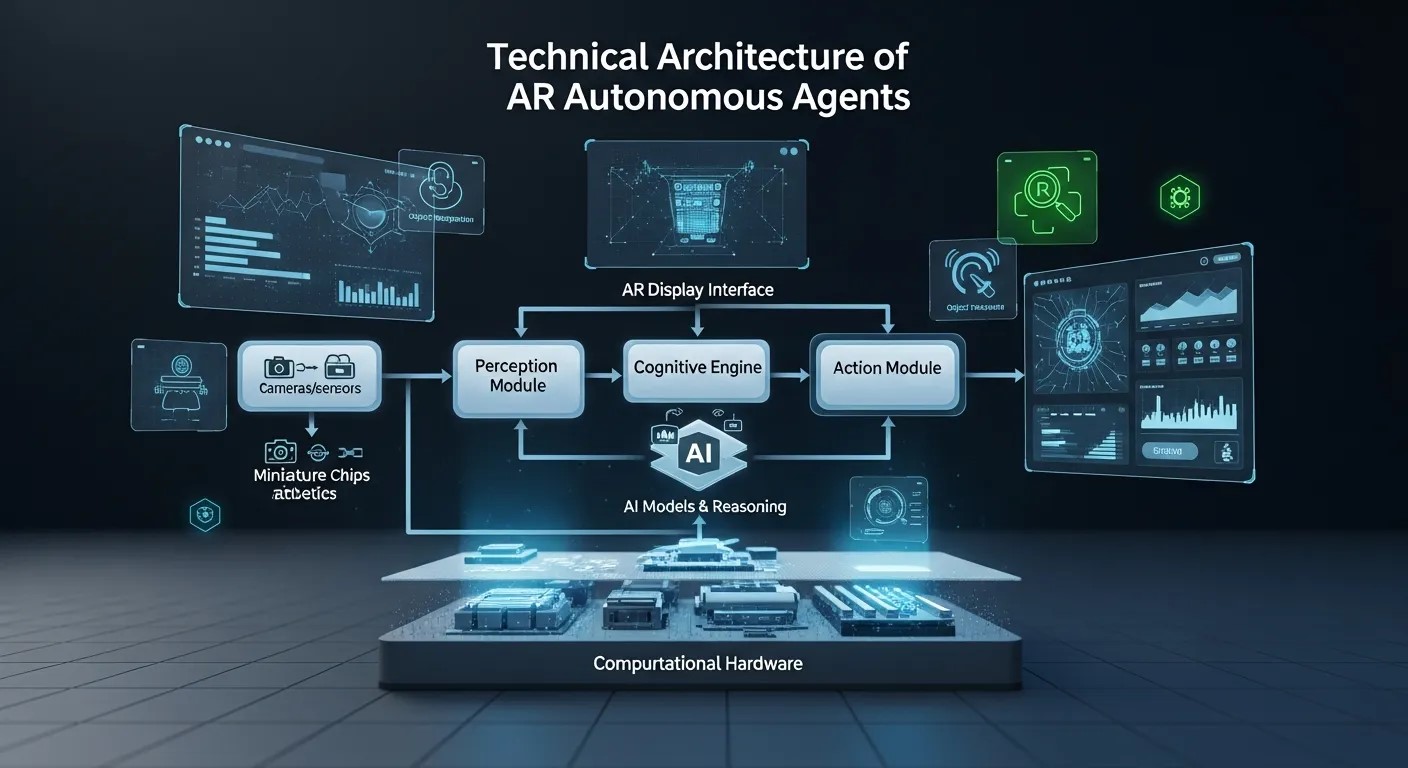
Understanding the technical foundation of AR Autonomous Agents helps organizations design and implement effective collaborative workspaces. These agents are built on a combination of AR frameworks, AI algorithms, and real-time data processing systems. The AR layer provides spatial awareness, mapping the physical environment and overlaying digital information seamlessly. The AI layer enables intelligent decision-making, pattern recognition, and predictive recommendations. Finally, data processing and cloud connectivity ensure that agents operate efficiently, even in complex, multi-user environments.
For instance, in a collaborative design session, AR agents can render 3D models that respond to user interactions, automatically adjusting layouts or suggesting optimizations. These capabilities rely on advanced algorithms capable of analyzing multiple inputs simultaneously, from user gestures to project data, ensuring that the workspace remains dynamic and context-aware.
Collaboration Features Enabled by AR Autonomous Agents
AR Autonomous Agents significantly enhance collaboration through features such as real-time annotations, automated task tracking, and contextual reminders. Teams can communicate more effectively as agents provide a shared, interactive visual workspace. By minimizing misunderstandings and aligning team members on the same page, productivity increases substantially.
Agents can also support multi-user sessions across different geographic locations. In such scenarios, participants experience the same AR environment, with autonomous agents facilitating communication, highlighting key information, and tracking contributions. This ensures that remote teams can collaborate as effectively as co-located teams, bridging gaps in distance and time zones.
Agent Intelligence and Adaptive Behavior
The intelligence of AR Autonomous Agents lies in their ability to learn and adapt to user behaviors. Machine learning models enable agents to recognize patterns in task execution, communication styles, and user preferences. Over time, this allows agents to predict needs, offer relevant suggestions, and automate repetitive tasks without explicit instructions.
For example, a project management agent can detect recurring bottlenecks in workflow and proactively suggest adjustments, such as reassigning tasks or reallocating resources. Similarly, agents in training environments can adapt content delivery based on learner progress, aligning with trends in AI-Personalized VR Narratives to provide a truly customized experience.
Scalability Considerations for AR Workspaces
As organizations expand their use of AR Autonomous Agents, scalability becomes a crucial factor. The system architecture must support multiple concurrent users, handle large volumes of data, and maintain low latency for real-time interactions. Cloud-based infrastructure and distributed computing models often provide the necessary flexibility.
Scalable AR solutions ensure that collaboration remains smooth, regardless of team size or project complexity. By monitoring usage metrics and applying ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns, companies can make informed decisions about resource allocation, system upgrades, and future expansion. Scalable solutions also allow integration with emerging technologies, such as advanced gesture recognition and haptic feedback, further enhancing the immersive experience.
Future Innovations in AR Autonomous Agents
The future of AR Autonomous Agents is poised for transformative growth. Advances in AI, machine learning, and AR hardware will enable agents to interact even more intuitively with humans, bridging the gap between digital and physical collaboration. Predictive intelligence will allow agents to anticipate user needs before they are explicitly stated, providing proactive suggestions that enhance productivity and creativity.
Moreover, integration with AI-Personalized VR Narratives will allow autonomous agents to create individualized experiences within collaborative AR environments. Teams will benefit from dynamic, adaptive workspaces that adjust based on project complexity, team composition, and individual skill levels. For example, a software development team could have agents dynamically reorganize workflows and suggest optimizations tailored to each programmer’s strengths, streamlining project delivery.
AR Marketing Trends and Business Opportunities

As AR Autonomous Agents become mainstream, businesses are exploring innovative ways to leverage them for marketing and brand engagement. Immersive campaigns facilitated by autonomous agents allow brands to create interactive experiences that capture attention and communicate complex concepts effortlessly. Companies aligning with emerging AR Marketing Trends can differentiate themselves in crowded markets, offering customers unique and memorable experiences that blend real and virtual worlds.
Beyond customer engagement, AR agents can provide internal value by optimizing workflows, tracking campaign performance, and providing insights for strategic planning. ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns ensures that organizations can quantify benefits, demonstrating tangible returns on investment from these immersive technologies. By combining marketing strategy with intelligent AR systems, businesses gain a competitive edge while improving team collaboration.
Human Factors and Adoption Strategies
Despite the technological promise of AR Autonomous Agents, successful adoption depends heavily on human factors. Teams need training, clear guidance, and confidence in the system to integrate AR agents into daily workflows. Addressing user concerns, such as ease of use, accessibility, and trust, is critical to maximize the technology’s potential.
Reducing AR Inequality is another important aspect. Organizations must ensure equitable access to AR tools and adaptive guidance for all participants, regardless of technical skill levels. By designing inclusive systems and providing customizable interfaces, autonomous agents can empower teams rather than create dependency or frustration.
Adoption strategies often include pilot programs, iterative feedback loops, and phased rollouts. These methods allow teams to adapt gradually while optimizing the agents’ behaviors based on real-world usage. Over time, users become more confident and proficient, unlocking the full collaborative potential of AR environments.
Practical Implementation Examples
Practical examples of AR Autonomous Agents in action highlight their versatility. In project management, agents can monitor task completion, provide deadline reminders, and offer contextual recommendations for resource allocation. In design studios, agents help visualize multiple iterations of a product simultaneously, allowing teams to make informed creative decisions without switching between multiple tools.
Remote teams benefit immensely as well. Agents ensure all members, regardless of location, experience the same workspace, track contributions, and highlight important updates. By integrating these functionalities with ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns, organizations can measure efficiency improvements, cost reductions, and enhanced collaboration outcomes.
Conclusion
AR Autonomous Agents are transforming the way teams collaborate in modern workspaces. By combining augmented reality with intelligent, adaptive behaviors, these agents streamline workflows, enhance decision-making, and foster more engaging, productive interactions. From improving remote collaboration to enabling personalized learning and training experiences, their potential spans across industries, including healthcare, education, design, and marketing.
As businesses adopt these agents, addressing human factors, accessibility, and inclusivity becomes crucial. Reducing AR Inequality and implementing structured adoption strategies ensure that teams can leverage AR technology effectively without disruption. Additionally, integrating tools like ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns and aligning with AR Marketing Trends helps organizations measure impact and optimize their strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are AR Autonomous Agents?
AR Autonomous Agents are intelligent systems that operate within augmented reality workspaces to assist teams, automate tasks, provide real-time insights, and enhance collaboration across physical and virtual environments.
How do AR Autonomous Agents improve team productivity?
They reduce cognitive load by consolidating information, automating routine tasks, and offering context-aware recommendations. This allows team members to focus on strategic decisions, creativity, and problem-solving, improving overall efficiency.
Which industries benefit most from AR Autonomous Agents?
AR Autonomous Agents are used in healthcare, education, design, architecture, manufacturing, and marketing. They support training, project management, immersive campaigns, and collaborative workflows, delivering measurable outcomes across sectors.
How do AR Autonomous Agents support remote teams?
By creating shared virtual workspaces, tracking contributions, highlighting updates, and facilitating real-time collaboration, AR agents ensure remote participants experience the same level of engagement as co-located teams.
What role does AI personalization play in AR Autonomous Agents?
AI personalization allows agents to adapt to user behavior, preferences, and workflow patterns. This ensures individualized guidance, dynamic task prioritization, and immersive experiences aligned with trends like AI-Personalized VR Narratives.
How can organizations measure the impact of AR Autonomous Agents?
Through ROI Tracking for AR Campaigns, organizations can quantify improvements in productivity, efficiency, error reduction, and overall collaboration, making the benefits of AR agents measurable and actionable.
How do AR Autonomous Agents address AR inequality?
Inclusive design, customizable interfaces, and adaptive guidance help ensure equitable participation for users with varying technical skills, bridging gaps and enabling a productive, accessible collaborative environment.
What are the challenges of implementing AR Autonomous Agents?
Challenges include technical integration, device compatibility, user adoption, and security. Effective training, phased rollouts, and iterative feedback loops help mitigate these issues.





