Augmented Reality (AR) has become one of the most exciting innovations of the 21st century, blending digital elements into our real-world environment in ways once thought impossible. From interactive gaming to remote work tools, AR is shaping industries and redefining our digital interaction. But where did it all begin? What is an early example of augmented reality, and how has it paved the way for the versatile AR experiences we enjoy today?
This article dives into the early foundations of AR technology, spotlighting one of its very first examples, and explores how this technological marvel laid the groundwork for its vast applications in modern times.
What Is Augmented Reality?
Before exploring its history, let’s briefly define what AR is. Augmented Reality overlays digital content (like images, sounds, or other data) onto the physical world in real-time. Unlike virtual reality, which immerses the user fully into a digital space, AR enhances real-world environments by integrating virtual elements, creating a seamless blend.
Think of social media filters that alter your appearance or AR apps like IKEA Place, where you can virtually position furniture in your living room before buying it. Both are perfect examples of how far the technology has come. But every remarkable innovation has its genesis, and AR is no exception.
The First Example of Augmented Reality
The roots of augmented reality can be traced back to 1968, with an invention by computer scientist Ivan Sutherland. Often referred to as the “father of computer graphics,” Sutherland developed the Sword of Damocles, which is widely recognized as the earliest example of augmented reality.
This groundbreaking device was a head-mounted display (HMD) designed to project computer-generated images directly into the user’s field of view. Named after the ancient tale of the Sword of Damocles, the device was suspended from the ceiling due to its weight and complexity, giving it an almost mythical appearance.
Although the imagery produced was rudimentary by today’s standards (think simple wireframe models), it was revolutionary for its time. The Sword of Damocles was the first attempt to merge virtual objects with the real world, establishing a foundational framework for all AR technologies to come.
How Did the Sword of Damocles Work?
The Sword of Damocles used a combination of optics, sensors, and display technology to align virtual graphics with the user’s perspective. Here’s a breakdown of its basic functionality:
- Head Tracking: The device tracked the user’s head movements via mechanical sensors. This allowed virtual objects to adjust their position based on the user’s viewing angle, creating an early sense of immersion.
- Wireframe Graphics: The system projected basic geometric shapes onto the user’s field of view. These shapes appeared to “float” in the real world when viewed through the head-mounted display.
- Ceiling Support: Due to the bulkiness of the technology at the time, the apparatus needed to be fixed to the ceiling via a mechanical arm, making it impractical for commercial use but invaluable for research.
While the Sword of Damocles itself wasn’t portable or user-friendly by today’s standards, it proved that embedding digital elements into the real world was not just science fiction but an achievable reality.
The Evolution of Augmented Reality After the Sword of Damocles
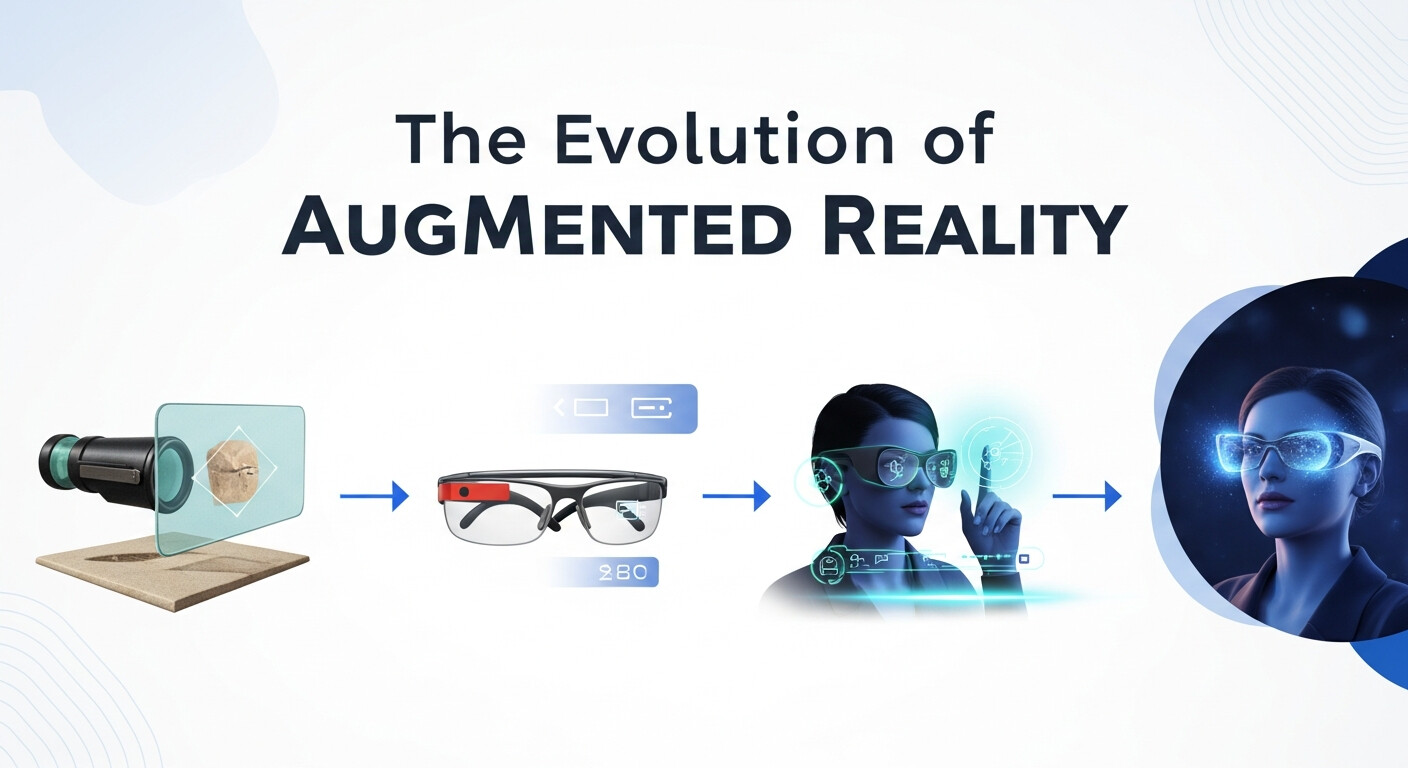
Sutherland’s invention laid the groundwork for decades of progress in the field of AR. Over the years, researchers and technologists built upon his ideas, gradually refining and expanding the capabilities of augmented reality.
1. Early Developments in AR Technology
Following the Sword of Damocles, AR research took steady strides forward:
- 1970s-1980s: Myron Krueger introduced “Videoplace,” a virtual reality environment where users could interact with digital graphics using gesture input. Although more VR-focused, it contributed concepts to AR.
- 1990: Researcher Tom Caudell coined the term “augmented reality” while developing an AR system for assembling aircraft at Boeing.
2. AR in Commercial Applications
The 1990s saw AR making the leap from research labs to commercial industries:
- Medical Training: Physicians began using AR systems to overlay digital visuals onto a patient’s body during surgery or training simulations.
- Military Simulations: AR was employed for flight training, allowing pilots to engage with simulated environments while operating real equipment.
3. AR Goes Mainstream
By the 2010s, AR became accessible to the general public, thanks to advancements in computing power and mobile technology. Some key milestones include:
- 2010: ARToolkit allowed developers to create AR apps more easily.
- 2016: Pokémon GO took the world by storm, blending AR with mobile gaming and revolutionizing how the public viewed AR technology.
- Today: AR is everywhere, from apps and gaming to industries like retail, healthcare, and education.
AR in Everyday Living Spaces
Augmented reality is gradually becoming part of daily life inside homes, transforming how people interact with their surroundings. From visualizing wall colors before painting to seeing how new appliances fit into a kitchen layout, AR helps homeowners make smarter decisions. The concept of Augmented Reality in Smart Homes allows users to control lighting, temperature, and security systems through interactive visual interfaces. Instead of using multiple apps or switches, digital overlays provide real-time feedback directly within the physical space. This reduces complexity and improves comfort. As AR-powered devices evolve, homes are becoming more intuitive, responsive, and personalized, enhancing convenience while saving time and resources for everyday users.
Enhancing Design Visualization

One of the strongest advantages of augmented reality is its ability to bring abstract designs into real-world contexts. Architects and designers can now project digital models into physical spaces to better understand scale, depth, and placement. With Augmented Reality in Urban Planning, planners can visualize how roads, parks, and buildings will coexist before construction begins. This helps identify potential issues early and improves collaboration between stakeholders. Citizens can also engage more actively by viewing proposed developments in their actual neighborhoods. Such immersive visualization leads to better planning decisions, reduced costs, and more sustainable development outcomes.
Building More Connected Environments
Cities are becoming increasingly complex, and augmented reality plays a crucial role in managing that complexity. Through Augmented Reality for Smart Cities, city officials can overlay real-time data—such as traffic flow, energy usage, or infrastructure status—onto physical locations. This enables faster decision-making and more efficient resource management. Maintenance teams can identify underground utilities without digging, while emergency responders can access critical information instantly. For citizens, AR enhances navigation and public services by providing contextual information in real time. Overall, AR strengthens the connection between digital intelligence and physical urban environments.
AR in Education and Learning

Augmented reality is redefining education by making learning more interactive and engaging. Instead of relying solely on textbooks, students can explore 3D models, historical scenes, or scientific simulations directly in their environment. This hands-on approach improves understanding and retention, especially for complex subjects. Teachers can use AR to adapt lessons to different learning styles, making education more inclusive. As technology becomes more accessible, AR-supported learning experiences are expected to expand beyond classrooms into remote and lifelong learning environments.
Transforming Retail Experiences
Retailers are using augmented reality to bridge the gap between online and in-store shopping. Customers can virtually try products, preview items in real spaces, and receive personalized recommendations through AR interfaces. This reduces uncertainty and increases buyer confidence. For businesses, AR helps lower return rates and improve customer satisfaction. Interactive product displays also create memorable shopping experiences that strengthen brand loyalty. As consumer expectations evolve, AR is becoming a key differentiator in competitive retail markets.
AR in Healthcare Innovation
In healthcare, augmented reality supports both training and real-world medical procedures. Surgeons can view critical data overlaid onto a patient’s body during operations, improving accuracy and safety. Medical students benefit from realistic simulations that enhance skill development without risk. AR also assists in patient education by visually explaining diagnoses and treatment plans. These applications reduce errors, improve outcomes, and make complex medical information easier to understand for both professionals and patients.
How the Sword of Damocles Shaped the Future of AR
Sutherland’s Sword of Damocles was a trailblazer, proving that AR was not just a concept but an achievable innovation. It introduced key principles still fundamental to AR today, such as head tracking, field-of-view alignment, and real-time interaction. More importantly, it inspired a generation of researchers and engineers to expand the possibilities of AR.
Without the Sword of Damocles, we likely wouldn’t have AR-powered technologies like modern AR glasses (e.g., Microsoft HoloLens) or even mobile AR applications. Though crude in appearance, Sutherland’s invention marked the starting point for a technological revolution.
Why Augmented Reality Matters
Augmented reality is not just about fun filters and immersive gaming. It’s a powerful tool reshaping how we interact with the digital and physical worlds. Businesses are leveraging AR to provide better customer experiences, streamline operations, and gain new insights through data visualization. Students are learning in AR-enhanced classrooms where complex concepts are brought to life. Urban planners are using AR to visualize new buildings in existing cityscapes before laying a single brick.
AR is no longer just a novelty; it’s a necessity for many industries looking to innovate and stay competitive.
Take the Next Step into AR Innovation

The early example of the Sword of Damocles serves as a reminder of how far technology has come and how much potential lies ahead for augmented reality. From its humble beginnings to the sophisticated AR applications of today, the evolution of augmented reality highlights the importance of curiosity, experimentation, and vision.
If you’re eager to explore the possibilities of AR for your business or personal projects, consider staying up to date with the latest AR advancements or experimenting with AR tools to enhance your delivery.
Who knows? The next big leap in AR might be closer than you think.
The Future Potential of AR
The future of augmented reality holds immense promise across industries. As hardware becomes lighter and software more intelligent, AR experiences will feel increasingly natural and seamless. Integration with artificial intelligence and real-time data will further enhance its capabilities. From personalized digital assistants to immersive collaboration tools, AR will continue to blur the line between physical and digital worlds. Its long-term impact lies not just in innovation, but in how it fundamentally changes the way humans perceive, interact with, and shape their environment.
FAQ – Augmented Reality (AR)
1. What is augmented reality (AR)?
Augmented reality is a technology that overlays digital elements like images, text, or sounds onto the real world in real time. It enhances physical environments rather than replacing them.
2. What is the earliest example of augmented reality?
The earliest example of augmented reality is the Sword of Damocles, developed in 1968 by computer scientist Ivan Sutherland. It is considered the foundation of modern AR systems.
3. Why is the Sword of Damocles important in AR history?
It was the first system to combine computer-generated graphics with real-world viewing using head tracking. This innovation introduced core AR principles still used today.
4. How did the Sword of Damocles work?
It used a head-mounted display with mechanical sensors to track head movement and display wireframe graphics. The system adjusted visuals based on the user’s perspective.
5. Was the Sword of Damocles suitable for everyday use?
No, it was large, heavy, and suspended from the ceiling, making it impractical for regular users. However, it was extremely valuable for research and experimentation.
6. Who is considered the father of augmented reality?
Ivan Sutherland is regarded as the father of augmented reality and computer graphics. His early work laid the foundation for AR and VR technologies.
7. How is augmented reality different from virtual reality?
Augmented reality adds digital elements to the real world, while virtual reality completely immerses users in a digital environment. AR keeps users connected to their physical surroundings.
8. When did augmented reality become popular?
AR became popular in the 2010s due to smartphones and improved computing power. Games like Pokémon GO helped bring AR to the mainstream.
9. What are common uses of augmented reality today?
AR is used in gaming, healthcare, education, retail, manufacturing, and architecture. It helps visualize data, train professionals, and enhance user experiences.
10. Why is augmented reality important today?
Augmented reality improves learning, productivity, and decision-making across industries. It bridges the gap between digital information and the real world.





