How Augmented Reality Technology Works: Concepts, Systems, and Real-World Use

Augmented Reality Technology has quietly shifted from a futuristic novelty into a daily digital experience that reshapes how people see, decide, and interact with information. From social media filters and virtual try-ons to advanced industrial training and immersive marketing, AR Technology is now deeply woven into modern human behavior. This evolution is not accidental—it aligns perfectly with new‑generation psychology, where users crave speed, visual clarity, interactivity, and emotional connection before making decisions.
In this in‑depth guide, we’ll explore how AR Technology works, the core systems behind it, why the human brain responds so strongly to it, and how brands, creators, and platforms are leveraging it to influence perception, trust, and engagement.
Understanding Augmented Reality Technology at Its Core
Augmented Reality Technology refers to a system that overlays digital elements—such as images, 3D objects, sounds, or data—onto the real‑world environment in real time. Unlike Virtual Reality, which replaces reality entirely, AR Technology enhances what users already see.
At its core, AR Technology blends three fundamental layers:
- The physical world (captured through a camera or sensor)
- Digital augmentation (computer‑generated content)
- Real‑time interaction (user movement and response)
The true power of AR Technology lies in its ability to merge digital intelligence with physical presence, creating an experience that feels intuitive rather than artificial.
Why the Human Brain Responds So Strongly to Augmented Reality Technology
Modern digital psychology explains why AR Technology is so effective. The human brain processes visuals nearly 60,000 times faster than text. When digital content is placed directly into a real‑world context, comprehension and memory retention increase dramatically.
Augmented Reality Technology triggers:
- Spatial awareness – the brain understands where an object exists
- Embodied cognition – users feel involved, not just informed
- Emotional validation – seeing is believing
This explains why users trust AR‑powered previews more than static images or videos. The experience feels personal, controlled, and authentic—key traits modern users demand.
Core Components That Power Augmented Reality Technology
To understand how AR Technology works, it’s essential to break down the technologies that make it possible.
Computer Vision
Computer vision allows AR Technology to interpret the physical environment. Cameras capture real‑world data, while algorithms detect surfaces, edges, lighting, and depth. This ensures digital objects appear grounded and realistic.
Sensors and Tracking
Accelerometers, gyroscopes, GPS, and depth sensors track device movement and orientation. AR Technology relies on these inputs to adjust digital overlays instantly as users move.
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
SLAM enables AR Technology to map unknown environments while tracking position in real time. This is critical for stable object placement and realistic interaction.
Rendering Engines
Rendering engines generate 3D models, lighting, shadows, and textures. High‑quality rendering enhances realism, which directly impacts user trust and engagement.
AI and Machine Learning
Modern AR Technology increasingly uses AI to recognize objects, faces, gestures, and behavior patterns making experiences more adaptive and personalized.
Types of Augmented Reality Technology Explained
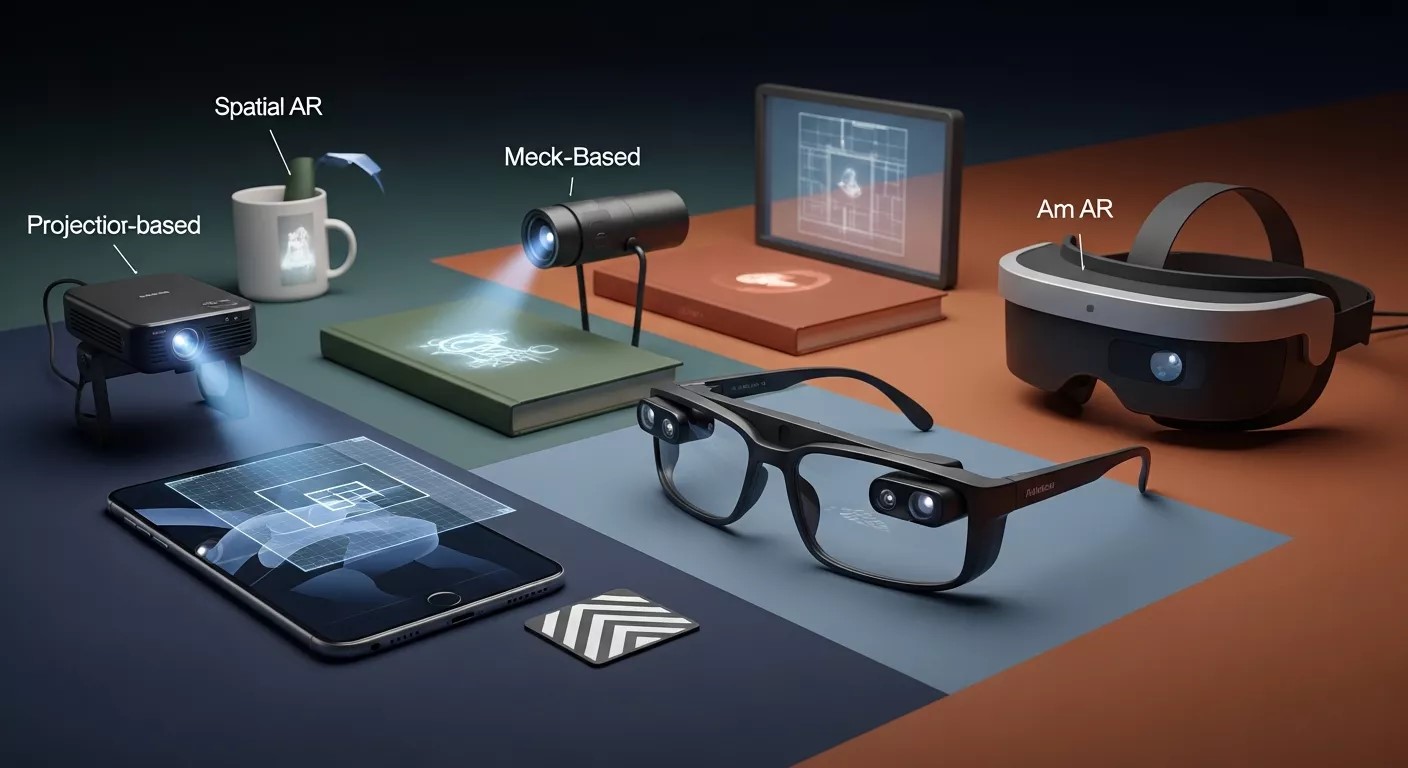
Augmented Reality Technology is not a single approach. It exists in multiple forms, each serving different use cases.
Marker‑Based Augmented Reality
This type uses visual markers such as QR codes or images to trigger digital content. When scanned, Augmented Reality Technology overlays predefined assets onto the marker.
Markerless Augmented Reality
Also known as location‑based AR, this approach uses GPS, sensors, and SLAM. It’s commonly used in navigation, gaming, and retail experiences.
Projection‑Based Augmented Reality
Digital content is projected onto physical surfaces. This version of Augmented Reality Technology is popular in industrial training and interactive displays.
Superimposition‑Based Augmented Reality
Here, the original view is partially or fully replaced with an augmented version. Medical imaging and product visualization often use this method.
How Augmented Reality Technology Works Step by Step
To simplify a complex system, here’s how Augmented Reality Technology typically functions in real time:
- The camera captures the physical environment
- Sensors detect movement and spatial orientation
- Computer vision analyzes surfaces and depth
- The AR engine selects relevant digital content
- Rendering engines generate realistic visuals
- The system overlays digital elements instantly
- User interactions adjust the experience dynamically
This entire process happens within milliseconds, creating a seamless illusion that feels natural to the user.
Augmented Reality Technology in Consumer Behavior
Augmented Reality Technology plays a growing role in shaping how consumers evaluate products and services. Today’s users want confidence before committing and AR delivers it visually.
When users interact with products through AR:
- Uncertainty drops
- Decision time shortens
- Emotional attachment increases
This is why brands increasingly focus on Enhancing Product Marketing with Augmented Reality because it bridges the gap between curiosity and conversion.
Augmented Reality Technology in Marketing Ecosystems
Marketing has evolved from persuasion to experience. Augmented Reality Technology enables brands to move beyond messaging into participation.
One emerging strategy is to Build an Augmented Reality Marketing Campaign That Converts by allowing users to test, explore, and personalize products in real time. This approach aligns with intent‑based marketing, where relevance matters more than reach.
The Role of Augmented Reality Technology in Trust Building

Trust is the currency of the digital economy. Augmented Reality Technology reduces perceived risk by showing users exactly what they’ll get.
Instead of imagining outcomes, users experience them. This transparency builds confidence and lowers return rates, complaints, and dissatisfaction.
Psychologically, AR satisfies the brain’s demand for control—an essential factor in modern decision‑making.
Augmented Reality Technology Across Industries
Augmented Reality Technology is not limited to marketing. Its influence spans multiple sectors:
- Retail – virtual try‑ons and store navigation
- Education – immersive learning and visualization
- Healthcare – surgical guidance and diagnostics
- Manufacturing – maintenance and training
- Real estate – virtual walkthroughs
Each application reinforces the same principle: information becomes more valuable when it’s contextual and interactive.
Human‑Centered Design in Augmented Reality Technology
Modern AR systems are built with user psychology in mind. Interfaces prioritize simplicity, responsiveness, and minimal friction.
Designers focus on:
- Natural gestures
- Visual clarity
- Low cognitive load
- Emotional comfort
This human‑centered approach ensures Augmented Reality Technology feels helpful rather than overwhelming.
Over time, Augmented Reality Marketing Impacts Your Online Reputation by signaling innovation, transparency, and customer‑centric thinking. Brands using AR are often perceived as more trustworthy and forward‑thinking.
Performance, Latency, and User Experience
For Augmented Reality Technology to feel believable, performance matters. Even slight delays can break immersion.
Key performance factors include:
- Low latency rendering
- Accurate tracking
- Stable object anchoring
- Realistic lighting adaptation
As hardware improves, these limitations continue to fade—opening doors for more complex AR experiences.
Privacy, Ethics, and Data Awareness
As Augmented Reality Technology becomes more personalized, concerns around data usage and privacy grow. Cameras, location tracking, and behavioral data must be handled responsibly.
Future‑ready AR platforms balance innovation with ethical safeguards to maintain long‑term trust.
The Future Direction of Augmented Reality Technology

Augmented Reality Technology is moving toward:
- Wearable AR glasses
- AI‑driven personalization
- Cross‑platform experiences
- Persistent digital layers in physical spaces
These trends suggest a future where digital information seamlessly coexists with reality—always available, yet unobtrusive.
Another fast‑growing use case is Augmented Reality in Email Marketing Campaigns, where interactive previews embedded in emails increase open rates, dwell time, and click‑through behavior. Users no longer just read emails they interact with them.
Why Augmented Reality Technology Is a Long‑Term Digital Shift
This technology is not a trend it’s an interface evolution. Just as touchscreens replaced buttons, Augmented Reality Technology is redefining how humans interact with information.
By aligning with human psychology, real‑world context, and emotional engagement, AR creates experiences that feel meaningful rather than promotional.
Cognitive Science Behind Augmented Reality Technology
Augmented Reality Technology works so effectively because it aligns with how the human brain naturally learns and interprets information. Cognitive science shows that humans understand concepts faster when abstract data is visualized within familiar environments. AR does exactly that it removes the mental gap between information and experience.
When users interact with AR Technology, multiple sensory channels activate simultaneously. Vision, spatial reasoning, and motor response work together, creating deeper neural connections. This is why AR-based learning, product exploration, and brand experiences are remembered longer than traditional digital content.
Augmented Reality Technology and Decision-Making Psychology
Modern consumers rarely make decisions instantly. They evaluate, compare, hesitate, and seek reassurance. Augmented Reality Technology reduces this friction by answering unspoken questions visually.
Instead of asking, “Will this fit my space?” or “Will this suit me?”, users see the answer instantly. This visual confirmation lowers cognitive stress and creates emotional comfort. From a psychological perspective, this sense of control dramatically increases decision confidence.
This is one of the core reasons brands are investing heavily in AR-powered experiences across digital touchpoints.
The Role of Augmented Reality Technology in Micro-Moment Marketing
Micro-moments define modern digital behavior. Users want immediate answers, not long explanations. Augmented Reality Technology fits perfectly into these moments by delivering instant, contextual value.
Whether it’s scanning a product, previewing a feature, or visualizing a result, AR compresses the journey from curiosity to clarity. This makes it especially powerful in mobile-first ecosystems, where attention spans are limited but intent is high.
Augmented Reality Technology and Personalization at Scale

Personalization is no longer optional it’s expected. Augmented Reality Technology enables dynamic personalization by adapting experiences based on user behavior, environment, and preferences.
For example, AR systems can adjust product size, color, lighting, or placement based on real-world surroundings. This level of customization makes users feel understood rather than targeted, which strengthens brand relationships over time.
Augmented Reality Technology in Omnichannel Experiences
Today’s user journey is not linear. Users move between apps, websites, emails, physical stores, and social platforms. Augmented Reality Technology acts as a unifying layer across these channels.
By integrating AR consistently, brands create seamless transitions between online and offline experiences. This continuity improves recall, satisfaction, and long-term engagement.
Technical Challenges in Augmented Reality Technology
Despite its advantages, AR Technology faces technical challenges. Environmental lighting variations, hardware limitations, and device compatibility can affect experience quality.
Developers continuously optimize algorithms to improve object stability, reduce latency, and enhance realism. As processing power increases and AR frameworks mature, these barriers are gradually diminishing.
Augmented Reality Technology and User Adoption Barriers
While adoption is growing, some users still hesitate due to unfamiliarity or perceived complexity. Successful AR experiences prioritize simplicity, guided interaction, and intuitive onboarding.
When AR Technology feels effortless, users are more likely to explore and engage without resistance.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Augmented Reality Technology
Understanding performance is crucial. Metrics such as engagement duration, interaction depth, repeat usage, and conversion lift help evaluate AR success.
Unlike traditional metrics, AR analytics focus on experiential quality rather than passive views. This shift reflects the interactive nature of AR Technology.
Augmented Reality Technology as a Competitive Differentiator
In crowded digital markets, differentiation is difficult. AR Technology provides a tangible way to stand out by offering value beyond information.
Brands that adopt AR early often position themselves as innovators, earning stronger emotional loyalty and higher brand recall.
Augmented Reality Technology and the Evolution of Interfaces

Interfaces are evolving from screens to spaces. AR Technology represents a transition toward spatial computing, where digital content exists within the physical world.
This evolution changes how users search, learn, and interact. Instead of navigating menus, users engage directly with information around them.
Conclusion
Augmented experiences are redefining how people interact with digital information by making it more visual, contextual, and intuitive. As user expectations evolve, immersive technologies will continue to shape learning, marketing, and decision-making across industries in more human-centric ways.
Frequency Asked Question (FAQ)
What is the main purpose of augmented reality?
The primary purpose is to enhance real-world experiences by adding digital information that improves understanding, interaction, and decision-making in real time.
How is augmented reality different from virtual reality?
Augmented reality adds digital elements to the real environment, while virtual reality fully replaces the physical world with a simulated one.
Which devices support augmented experiences?
Smartphones, tablets, AR-enabled headsets, smart glasses, and some wearable devices support augmented experiences using cameras and sensors.
Is augmented reality only used for marketing?
No. It is widely used in education, healthcare, manufacturing, navigation, training, and entertainment, in addition to marketing.
Does augmented reality require an internet connection?
Some experiences work offline, but advanced features like cloud recognition, real-time updates, and personalization usually require internet access.
Why is augmented reality becoming more popular now?
Improved hardware, faster processors, better cameras, and rising demand for interactive, visual experiences have accelerated adoption.





