Computer Vision in AR enables immersive, intelligent, and interactive experiences across gaming, education, healthcare, and enterprise. By integrating AI, edge computing, and ethical frameworks, modern AR transforms human-digital interaction while preserving privacy, efficiency, and adaptability for diverse applications.
Introduction to Computer Vision in AR
Augmented Reality (AR) has evolved rapidly over the last decade, transforming the way humans perceive and interact with digital environments. At the heart of this transformation is computer vision in AR, a technology that allows devices to interpret, understand, and respond to the physical world. From enhancing gaming experiences to enabling real-time navigation and industrial applications, computer vision acts as the bridge between digital intelligence and human perception.
The adoption of computer vision in AR is not just a technological trend; it reflects a deeper human desire for more intuitive and immersive experiences. By analyzing visual data from cameras and sensors, AR systems can identify objects, track movements, and overlay relevant information seamlessly into our surroundings. This capability enables smarter interactions and enhances the cognitive connection between humans and digital interfaces.
Key Techniques Driving Computer Vision in AR
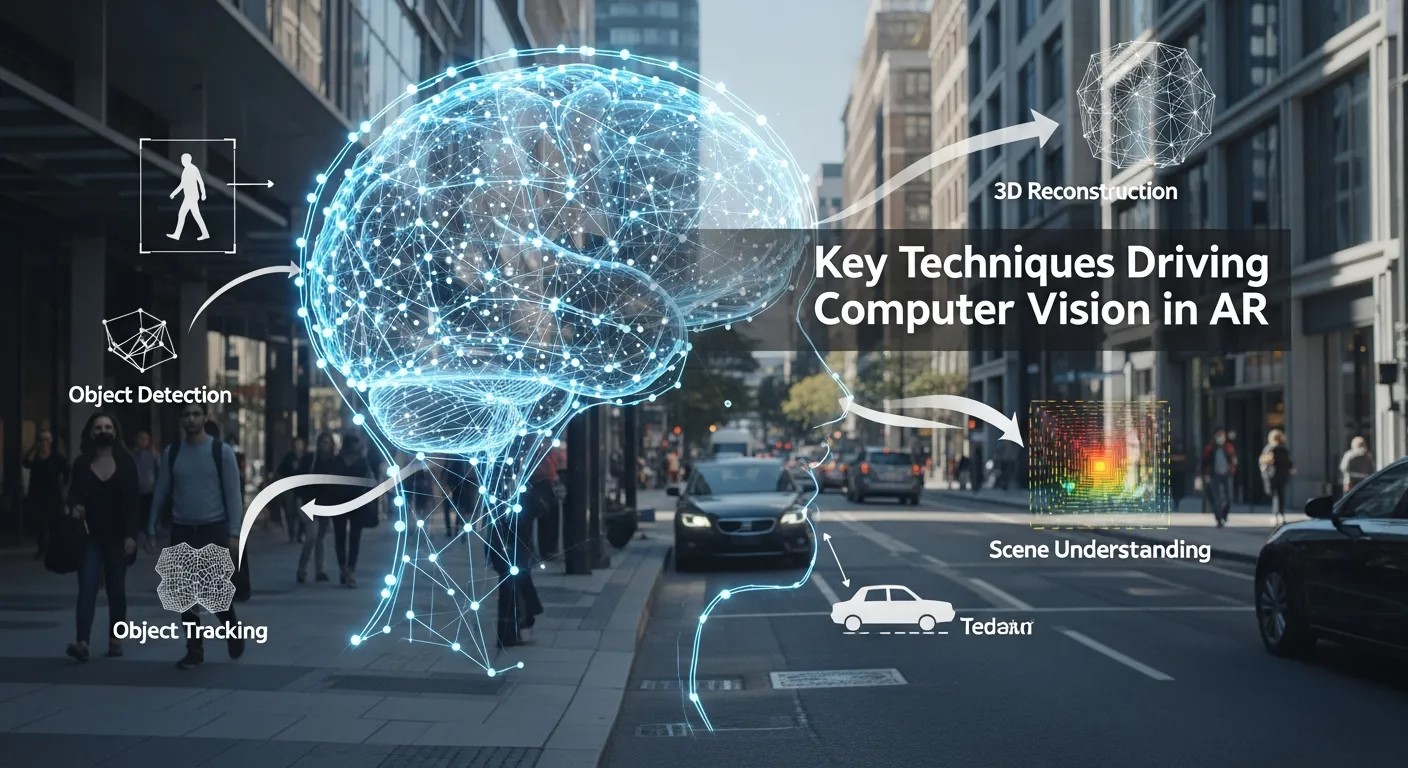
Several sophisticated techniques power modern computer vision in AR applications. Understanding these can provide insight into why AR experiences today feel more natural and responsive than ever.
Object Recognition and Tracking
One of the core functionalities of computer vision in AR is object recognition and tracking. By identifying objects in real-time and maintaining awareness of their positions in three-dimensional space, AR applications can anchor digital content accurately. For example, industrial AR systems can highlight machinery components, while educational AR apps can bring static diagrams to life.
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
SLAM is a critical algorithm that allows AR devices to map environments while tracking the device’s position simultaneously. This capability is vital for applications like navigation, indoor mapping, and AR gaming. Modern advancements in SLAM, combined with edge computing in AR, ensure faster data processing directly on devices, reducing latency and enhancing the user experience.
Depth Sensing and 3D Reconstruction
Understanding depth is essential for creating realistic AR interactions. Depth-sensing cameras capture spatial data, allowing AR systems to place digital objects convincingly in the environment. 3D reconstruction further enhances the realism, enabling users to interact with digital elements as if they existed physically. Techniques like structured light, LiDAR, and stereo vision are increasingly used to achieve high precision.
Enhancing AR with Machine Learning
Machine learning has become integral to the evolution of computer vision in AR. By training models to understand patterns and predict outcomes, AR systems can become more adaptive and context-aware. For instance, transfer learning in AR allows pre-trained models to be fine-tuned on specific AR tasks, drastically reducing development time and improving accuracy. This approach is especially valuable for niche applications, such as medical AR systems or industrial maintenance.
Additionally, integrating federated learning in AR ensures that AI models can learn from decentralized data sources while preserving user privacy. This is particularly important as AR applications increasingly rely on sensitive visual and location-based data.
AI-Enhanced Interaction in AR
The synergy of computer vision and AI in AR enables smarter interaction paradigms. Emotion recognition, gesture detection, and predictive analytics allow AR systems to respond intuitively to user behavior. By analyzing subtle cues, these systems can adapt content dynamically, improving engagement and usability. Ethical considerations, such as ethical AI in AR, are critical here to ensure these technologies respect user privacy and avoid biases in real-time decision-making.
AR in Industry and Enterprise
Computer vision in AR is no longer limited to entertainment or consumer apps. Enterprises are leveraging AR for operational efficiency, training, and collaboration. For example, AR-enabled maintenance apps overlay instructions onto machinery, reducing errors and downtime. In manufacturing, AR can visualize complex assemblies before production, improving accuracy and resource planning.
In addition, AI conversational commerce and chatbots in B2B marketing are being integrated with AR systems to create interactive client experiences. Imagine a virtual showroom where users can ask questions and receive instant responses while visualizing products in real space. This convergence of technologies exemplifies the potential of AR beyond traditional interfaces.
Edge Computing Meets AR
Processing visual data locally is becoming increasingly important for AR applications. Edge computing in AR ensures that high-volume data from cameras and sensors is analyzed near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth dependency. This local processing is crucial for real-time applications like AR navigation, gaming, and industrial inspection, where delays can disrupt user experience or operational efficiency.
Advanced Applications of Computer Vision in AR

The evolution of computer vision in AR has enabled applications that were once considered science fiction. From interactive gaming to professional enterprise solutions, modern AR leverages computer vision to create experiences that are not only immersive but also highly intelligent. By analyzing live visual input, AR systems can interpret complex environments and dynamically adapt content, giving users a sense of true interactivity.
Immersive Gaming Experiences
Gaming has been one of the earliest adopters of computer vision in AR. By using object recognition, depth sensing, and gesture tracking, AR games can overlay digital elements onto real-world environments seamlessly. Players can interact with virtual objects as if they physically exist, creating experiences that are engaging and physically intuitive. Moreover, edge computing in AR allows these complex computations to occur locally, reducing lag and enhancing responsiveness—critical factors for immersive gaming.
Modern AR games also benefit from transfer learning in AR, where pre-trained models are adapted to understand player movements or predict gameplay patterns. This technique allows developers to bring sophisticated AI capabilities to mobile AR games without extensive on-device training.
AR in Education and Training
The integration of computer vision in AR has redefined education and professional training. Students can visualize complex concepts in 3D, enhancing comprehension and retention. For instance, AR anatomy applications allow medical students to explore human organs in interactive, lifelike 3D models.
In professional training, AR applications equipped with computer vision provide real-time feedback. For example, assembly line workers can receive visual instructions overlaid on machinery, ensuring accuracy and safety. Additionally, federated learning in AR ensures that these educational AR platforms improve over time while keeping user data private, a critical consideration in institutional environments.
Healthcare Applications
Healthcare has emerged as a transformative field for computer vision in AR. Surgeons can use AR overlays during operations to visualize internal anatomy, while remote consultation tools allow specialists to guide procedures in real-time. By integrating AI, these AR systems can predict potential complications or highlight areas of interest, making interventions safer and more precise.
Ethical considerations remain paramount, and ethical AI in AR is applied to ensure that patient data is protected and AI-driven suggestions do not introduce bias. The combination of computer vision, AI, and AR is enabling unprecedented levels of precision in medical practice.
AR in Retail and Marketing
Retailers and marketers are increasingly turning to computer vision in AR to create interactive shopping experiences. Customers can visualize products in their own space using AR apps, such as placing furniture in a room or trying on virtual clothing.
Integrating AI conversational commerce and chatbots in B2B marketing enhances this experience, allowing consumers to ask questions and receive immediate, personalized responses while interacting with products. By combining computer vision with AI-driven conversational tools, businesses are creating highly engaging, efficient, and personalized customer journeys.
Industrial and Enterprise Use Cases
Industries ranging from manufacturing to logistics are leveraging computer vision in AR to improve operational efficiency. AR applications can highlight components for assembly, overlay repair instructions on machinery, or guide warehouse staff to locate items faster. These tools often rely on edge computing in AR to process visual data locally, ensuring real-time performance without cloud dependency.
The integration of federated learning in AR further enhances these systems, allowing multiple factories or branches to contribute to a shared learning model without compromising sensitive operational data. The result is an adaptive AR ecosystem that continuously improves across locations while maintaining data security.
Future of Immersive Experiences
The trajectory of computer vision in AR points toward increasingly immersive and intelligent environments. With advancements in 3D reconstruction, AI-driven predictive modeling, and ethical AI frameworks, AR applications will become even more context-aware. Future applications may seamlessly blend digital and physical worlds, offering interactions that are indistinguishable from reality.
Moreover, combining computer vision with emerging AR hardware, such as smart glasses and wearable sensors, will allow users to navigate and interact with complex digital environments effortlessly. This next generation of AR will benefit from ongoing research in transfer learning in AR, ensuring rapid adaptability of AI models for new environments and scenarios.
AR Hardware Innovations Powered by Computer Vision
The evolution of computer vision in AR is tightly coupled with advancements in hardware. Modern AR experiences are made possible through high-resolution cameras, depth sensors, LiDAR scanners, and AR-capable processors. These components allow AR systems to accurately capture and interpret real-world environments, laying the groundwork for immersive applications.
Smart Glasses and Wearables
Smart glasses equipped with AR capabilities rely heavily on computer vision in AR to overlay digital content onto the user’s field of view. By detecting objects, tracking motion, and mapping surroundings, these devices enable hands-free interactions in professional and consumer settings alike. In enterprise environments, workers can receive step-by-step instructions overlaid on machinery, while consumers can enjoy AR games and interactive shopping experiences.
Wearables such as AR headsets also benefit from edge computing in AR, which reduces latency by processing visual data locally rather than relying on cloud servers. This ensures seamless, real-time interaction and preserves a natural user experience even in resource-intensive scenarios.
Mobile Devices
The widespread availability of AR-enabled smartphones and tablets has democratized computer vision in AR. With multiple cameras, depth sensors, and AI accelerators, mobile devices can recognize objects, track motion, and overlay content accurately. AR apps can now transform everyday environments into interactive spaces, whether for education, gaming, or retail.
Developers often leverage transfer learning in AR to adapt pre-trained computer vision models for mobile applications. This approach accelerates development while maintaining high performance, allowing AR experiences to scale quickly across diverse devices.
LiDAR and 3D Mapping
LiDAR sensors provide precise depth perception for computer vision in AR systems. By emitting laser pulses and measuring reflections, LiDAR can reconstruct detailed 3D maps of an environment in real time. This capability is critical for applications like autonomous navigation, industrial inspections, and architectural visualization.
The combination of LiDAR with federated learning in AR allows multiple devices to contribute to improved 3D mapping models without sharing sensitive environmental data. This approach balances technological progress with privacy concerns, enabling smarter AR systems across industries.
Consumer Experiences Enhanced by Computer Vision in AR
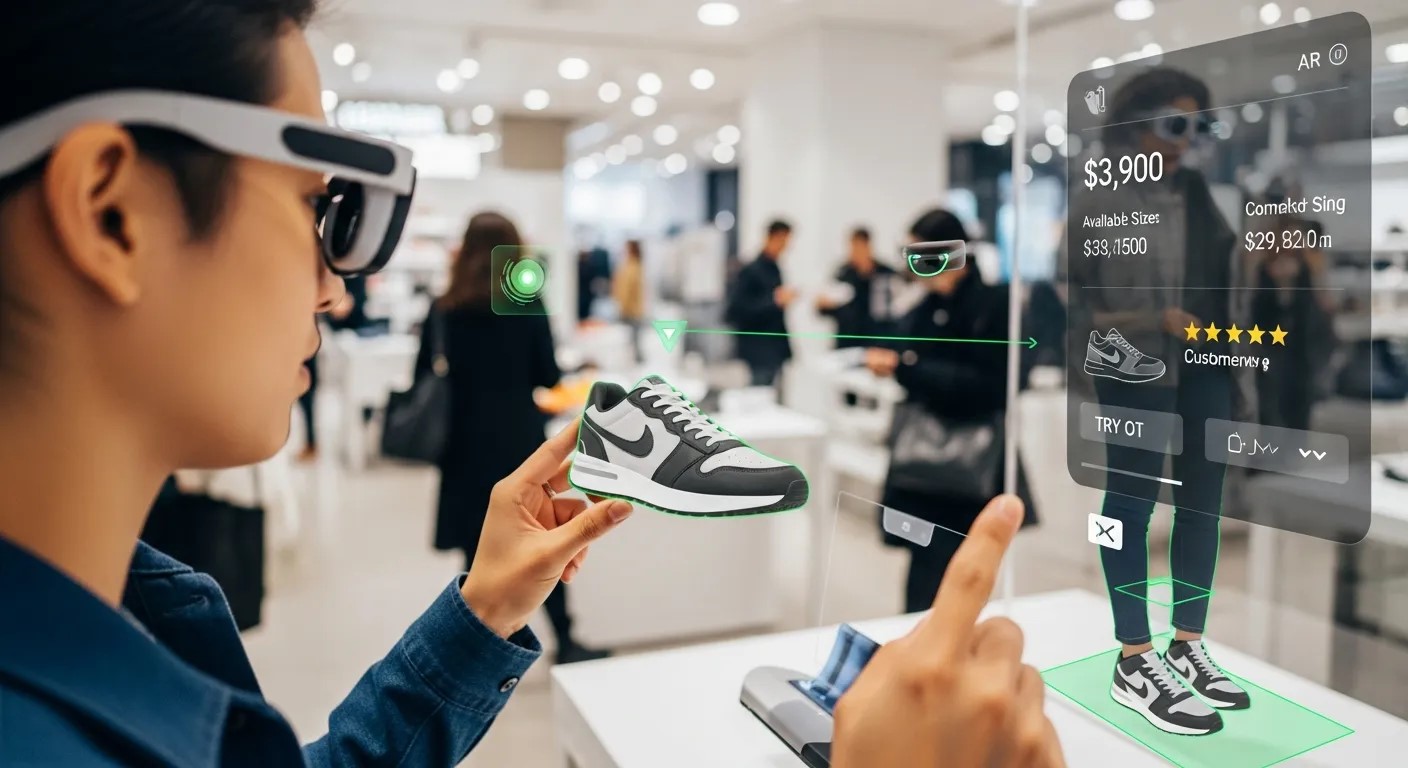

Computer vision in AR is reshaping the way consumers interact with products, media, and entertainment.
Retail and E-Commerce
AR applications now allow shoppers to virtually place furniture, try on clothing, or preview products in their homes. Integrating AI conversational commerce into these experiences enables real-time assistance, personalized recommendations, and interactive engagement. Additionally, chatbots in B2B marketing are being paired with AR for virtual product demonstrations, creating immersive sales and marketing tools that are transforming the retail landscape.
Gaming and Entertainment
AR games that utilize computer vision in AR create highly interactive experiences. Gesture recognition, motion tracking, and object detection allow players to interact with digital elements in ways that mimic real-world physics. Gamers can physically navigate spaces while the AR system adapts in real-time, offering a level of immersion previously unattainable.
Education and Training
AR educational platforms leverage computer vision in AR to make learning more intuitive. Students can manipulate 3D models, conduct virtual experiments, and explore complex concepts visually. In professional training, AR systems provide real-time feedback and guidance, improving safety, efficiency, and skill acquisition. The use of ethical AI in AR ensures that these platforms respect user privacy and provide unbiased learning experiences.
Challenges in Implementing Computer Vision in AR
Despite rapid advancements, several challenges remain in deploying computer vision in AR at scale:
-
Processing Power and Latency – High-resolution image analysis requires significant computational resources. Edge computing in AR helps mitigate this by processing data locally, but hardware limitations can still restrict performance.
-
Data Privacy and Security – AR applications often rely on sensitive visual data. Implementing federated learning in AR and ethical AI in AR frameworks is essential to maintain user trust and compliance with privacy regulations.
-
Environmental Variability – Lighting conditions, occlusions, and cluttered environments can affect object recognition accuracy. Advanced algorithms and continuous model training using transfer learning in AR help address these issues.
-
Integration with AI Systems – Combining computer vision in AR with AI conversational tools like AI conversational commerce or chatbots in B2B marketing requires seamless interoperability to ensure smooth user experiences.
Future Trends of Computer Vision in AR

The future of computer vision in AR is bright, with several emerging trends shaping the next generation of experiences:
-
Adaptive AR Interfaces: Systems that learn from user behavior to personalize content dynamically.
-
Collaborative AR: Multi-user AR experiences where federated learning in AR ensures adaptive performance without compromising privacy.
-
AI-Powered Predictive AR: Applications that anticipate user actions and environmental changes for smoother interactions.
-
Integration with IoT: Smart environments will leverage edge computing in AR to provide context-aware digital overlays in real-time.
By continuing to refine object recognition, SLAM algorithms, and depth perception, AR systems will become increasingly intelligent, intuitive, and integrated into daily life. Computer vision in AR will remain the cornerstone technology enabling these innovations.
Transforming Enterprise Operations with Computer Vision in AR
Modern enterprises are increasingly leveraging computer vision in AR to optimize operations and enhance decision-making. From real-time machinery guidance to immersive training programs, AR systems enable workers to interact with complex environments effortlessly. By integrating edge computing in AR, organizations ensure faster data processing and low-latency experiences, while federated learning in AR allows AI models to improve collaboratively without compromising sensitive information. Additionally, combining AR with AI conversational commerce or chatbots in B2B marketing creates interactive client solutions that drive engagement and efficiency, illustrating the transformative potential of augmented reality across industries.
Conclusion
Computer Vision in AR is revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with digital environments. From immersive gaming to enterprise efficiency, healthcare precision, and interactive education, AR applications now seamlessly merge the physical and digital worlds. By leveraging edge computing, transfer learning, and federated learning, AR systems deliver real-time, adaptive, and intelligent experiences while ensuring privacy and ethical AI usage. As hardware advances and AI integration deepens, future AR solutions promise even more personalized and context-aware interactions. Businesses and developers adopting these technologies stand to redefine engagement, efficiency, and innovation in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is computer vision in AR?
Computer vision in AR allows devices to interpret visual data from the real world, enabling digital overlays, object recognition, motion tracking, and interactive experiences in augmented reality applications.
How does AI enhance AR experiences?
AI improves AR by enabling predictive modeling, gesture recognition, adaptive interfaces, and personalized interactions, enhancing usability and immersion across education, gaming, retail, and enterprise applications.
What are the privacy considerations in AR?
Privacy is critical as AR systems process visual and location data. Techniques like federated learning in AR and ethical AI in AR ensure user data is analyzed securely and responsibly.
What industries benefit from computer vision in AR?
Healthcare, education, retail, enterprise operations, manufacturing, and gaming are major beneficiaries, leveraging AR to improve efficiency, engagement, and interactive experiences.
How is edge computing relevant to AR?
Edge computing in AR processes visual data locally on devices, reducing latency, enhancing real-time performance, and enabling smoother, more immersive AR experiences.