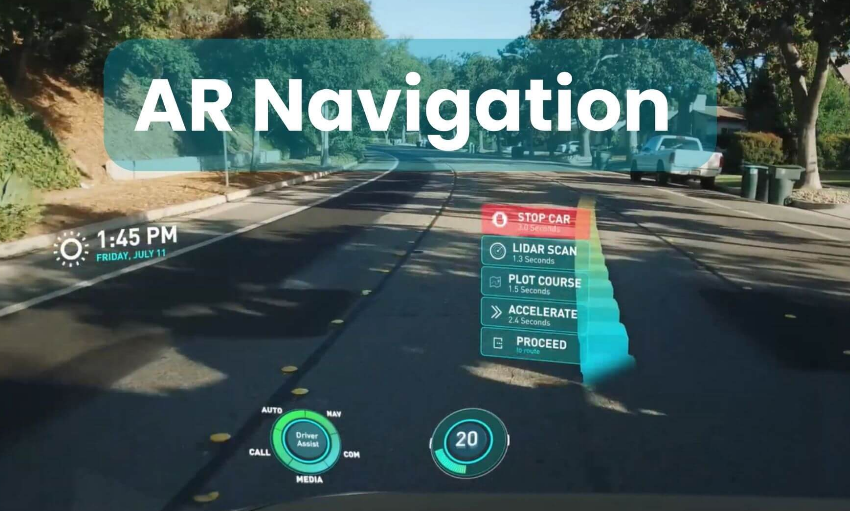
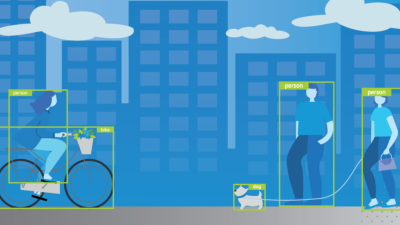
Remember paper maps? Those unwieldy sheets we awkwardly folded while trying to find our way in unfamiliar places? We’ve come a long way.
GPS devices changed everything, giving us turn-by-turn directions. Then smartphone apps brought navigation to our pockets, making dedicated GPS units largely obsolete.
Now we stand at the next frontier: augmented reality navigation. This technology doesn’t just tell you where to go – it shows you, blending digital directional cues with your real-world view.
How AR Navigation Works
AR navigation overlays digital information onto your actual surroundings through your smartphone camera or specialized glasses.
Digital arrows appear to float above streets. Building information pops up as you look at storefronts. Warning signals highlight potential hazards ahead.
The magic happens through a combination of GPS, computer vision, and spatial mapping technologies. Your device constantly analyzes what you’re seeing and positions digital elements accordingly.
Unlike traditional map apps, AR navigation eliminates the mental translation between a 2D map and your 3D surroundings. The guidance exists in your actual field of vision.
Transforming Urban Exploration
Getting lost becomes nearly impossible with AR navigation. Virtual breadcrumbs can mark your path, while highlighted routes show exactly which street to take.
Tourism transforms entirely. Visitors can discover hidden gems and historical information without constantly checking guidebooks or phone screens.
Language barriers diminish when street signs and business information appear translated in your preferred language through AR overlays.
Accessibility improves dramatically for people with cognitive disabilities who struggle with traditional maps. Visual cues directly in their environment provide clearer guidance.
Indoor Navigation Breakthroughs
While GPS works well outdoors, indoor navigation presents unique challenges. AR is solving this problem through visual positioning systems.
Shopping malls become navigable with virtual paths guiding shoppers directly to specific stores or facilities. Product locations within stores appear as floating markers.
Hospitals implement AR wayfinding to guide patients and visitors through complex layouts. This reduces stress and improves the patient experience significantly.
Conference centers and large venues use AR to direct attendees to specific rooms or exhibits. Personalized schedules appear with directional guides to each event.
Real-World Implementation Examples
Mapbox has pioneered AR navigation experiences that blend precise mapping with augmented reality. Their technology powers numerous commercial applications used daily by millions.
Major cities like Singapore have begun implementing AR-enhanced tourist maps that reveal hidden stories about landmarks and neighborhoods as visitors explore.
Transportation hubs increasingly offer AR navigation assistance. Some airports guide travelers with virtual lines leading to gates, while highlighting amenities along the way.
At AR Marketing Tips, we’ve documented how businesses integrating AR navigation into their customer experience see increased foot traffic and engagement.
Challenges and Considerations
Battery drain remains a concern when using AR navigation continuously. The constant camera use and processing demands significant power.
Privacy questions arise when systems need to “see” and analyze surroundings. Clear consent frameworks and data policies must evolve alongside the technology.
Accuracy varies depending on environmental conditions. Crowded spaces, weather, and unusual architectural features can sometimes confuse AR positioning systems.
Social norms are still developing around AR navigation use. Walking while focusing on AR displays raises similar concerns to texting while walking.
AR Navigation for Businesses
Retail establishments increasingly offer custom AR navigation experiences within their spaces. This creates opportunities for contextual promotions and improved customer service.
Office complexes implement AR systems to help visitors find specific rooms or staff members without assistance. This reduces reception workload and improves visitor experiences.
CityGuide AR offers development tools specifically for businesses wanting to integrate AR navigation into their premises or customer apps.
Real estate developers emphasize AR-ready infrastructure in new buildings, anticipating widespread adoption of spatial computing and navigation.
The Future of Movement
AR navigation will eventually extend beyond visual cues. Haptic feedback through wearables might provide directional guidance without requiring visual attention.
Integration with autonomous vehicles presents fascinating possibilities. AR could show pedestrians what vehicles “see” and their intended paths, increasing safety and trust.
As 5G networks expand, AR navigation will access richer data streams in real-time, including crowd density information, transportation delays, and environmental alerts.
The ultimate goal is ambient navigation – guidance so natural and unobtrusive we barely notice it’s there, yet it quietly optimizes our movement through increasingly complex spaces.
Conclusion
AR navigation represents a fundamental shift in how we move through and interact with our surroundings. The technology bridges the gap between digital information and physical reality.
For many of us, getting lost might soon become a choice rather than an accident. Our relationship with unfamiliar spaces will transform from anxiety to confident exploration.
The question isn’t whether AR will reshape navigation, but how quickly and thoroughly it will become an essential part of our daily movement through the world.