What Is AR? And How Augmented Reality Is Transforming the World?
Augmented Reality is no longer a futuristic concept limited to sci-fi movies or experimental tech labs. Today, Augmented Reality is actively transforming how people interact with the digital and physical world blending the two in ways that feel intuitive, useful, and increasingly essential.
From social media filters and interactive shopping to advanced healthcare tools and smart navigation systems, AR is quietly becoming part of everyday life. As devices grow more powerful and user expectations evolve, technologies are shaping a new era of digital experience one where information appears exactly when and where it’s needed.
This guide explores what AR truly is, how it works, and how it’s transforming industries, behaviors, and decision-making across the globe.
What Is Augmented Reality (AR)?

At its core, Augmented Reality is a technology that overlays digital content such as images, animations, sounds, or data onto the real world in real time. Instead of replacing reality, AR enhances it by adding a digital layer to what users already see and experience.
Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which places users inside a completely simulated environment, AR works within the physical world. It enhances existing surroundings rather than disconnecting users from them. This makes AR more accessible, practical, and widely adopted for everyday use.
Common examples of AR include:
- Snapchat or Instagram filters that modify facial features in real time
- Mobile apps that let users preview furniture inside their homes
- Navigation tools that overlay arrows onto real streets
- Educational apps that display 3D models on textbooks
These experiences may feel simple, but they rely on complex systems working together behind the scenes.
How Does AR Work?
To deliver a seamless AR experience, multiple technologies collaborate in real time. The process generally follows three core stages: input, processing, and output.
1. Capturing the Real World
AR-enabled devices such as smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses use cameras and sensors to understand their environment. These tools collect spatial data, detect surfaces, track movement, and recognize objects.
Sensors commonly involved include:
- Cameras for visual input
- GPS for location awareness
- Gyroscopes and accelerometers for motion tracking
- Depth sensors for spatial mapping
This data allows the system to interpret the physical world accurately.
2. Processing and Mapping Data
Once the environment is captured, AR software processes the data using computer vision and advanced algorithms. The system identifies flat surfaces, objects, and depth, then determines where and how digital elements should appear.
This stage is crucial. Proper alignment ensures that virtual objects stay anchored to real-world positions even when users move their devices or change angles.
3. Displaying Digital Overlays
Finally, the processed information is displayed on the user’s screen or AR glasses. Digital elements appear integrated with the real environment, responding dynamically to movement, lighting, and perspective.
This combination of real-time sensing, processing, and visualization creates the immersive experience that defines AR.
Why AR Is Gaining Global Adoption
The rapid adoption of Augmented Reality is not accidental. Several factors are accelerating its growth worldwide.
First, smartphones already equipped with powerful cameras and sensors have made AR widely accessible. Users don’t need specialized hardware to experience it.
Second, improvements in AI, 3D modeling, and cloud computing have made AR more accurate and scalable.
Third, consumer expectations have changed. People now want faster information, interactive experiences, and visual clarity before making decisions.
Together, these factors position AR as a practical solution rather than a novelty.
Real-World Applications of Augmented Reality
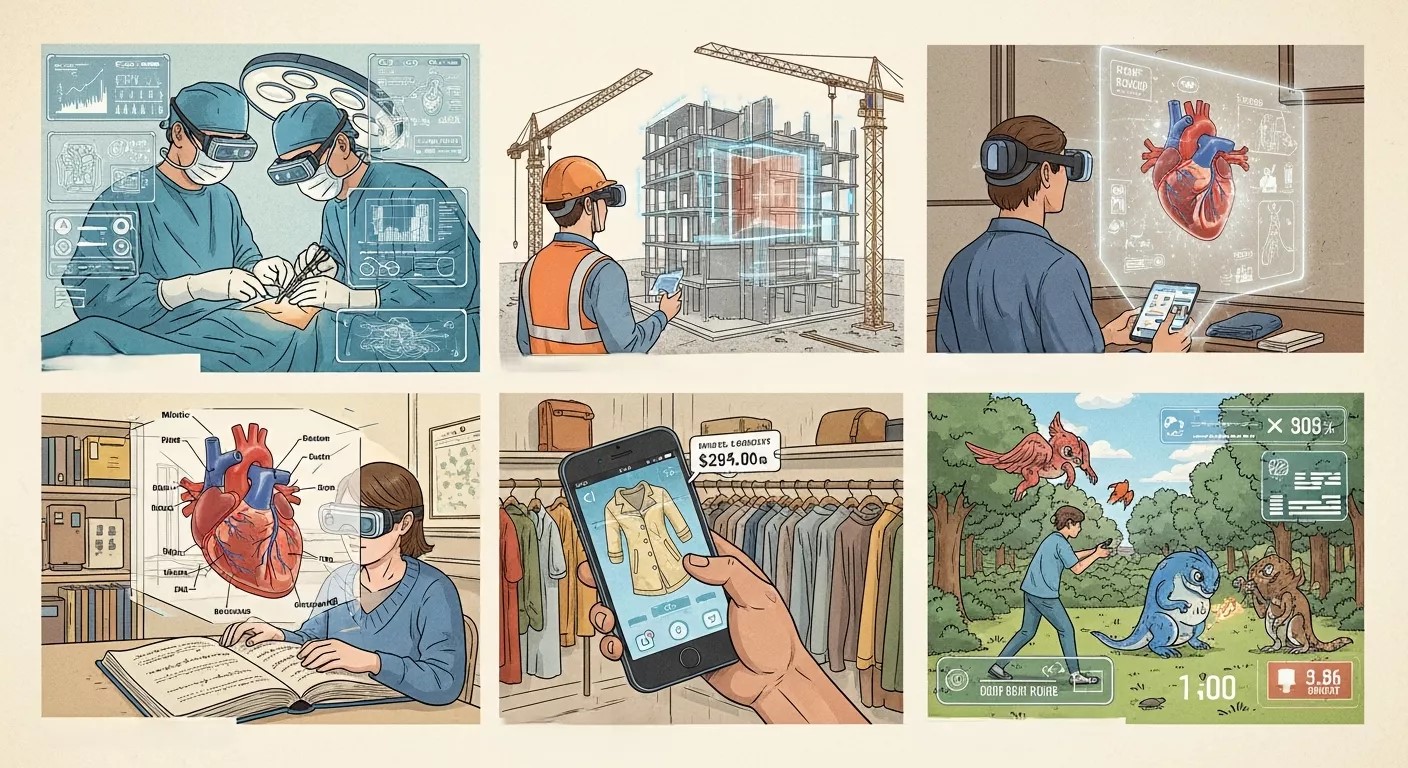

AR in Entertainment and Gaming
Entertainment was one of the first industries to showcase AR’s potential. Pokémon GO demonstrated how digital content could coexist with physical spaces, encouraging players to explore real locations while interacting with virtual characters.
Since then, AR has expanded across social platforms, mobile games, and live events. Filters, lenses, and effects allow users to transform photos and videos instantly, increasing engagement and creative expression.
AR also enhances live entertainment by adding interactive layers to concerts, sports broadcasts, and theme park attractions.
AR in Retail and E-Commerce
Retail is one of the fastest-growing sectors for Augmented Reality adoption. Shoppers increasingly want confidence before purchasing and AR provides that clarity.
Virtual try-ons allow customers to see how products look on their faces, bodies, or in their homes. Furniture placement apps, for example, eliminate guesswork by showing accurate size, scale, and placement.
This shift is not just improving convenience it’s changing buyer behavior. Brands using AR tools are seeing improved engagement, reduced product returns, and higher customer satisfaction.
These experiences also highlight how AR Marketing to Boost Engagement ROI is becoming a strategic priority rather than a creative experiment.
AR in Education and Learning
Traditional learning often relies on static visuals and abstract explanations. AR changes that by turning concepts into interactive experiences.
Students can explore 3D models of the human body, historical artifacts, or scientific processes directly on their desks. This immersive approach improves comprehension, retention, and curiosity.
In professional training, AR enables hands-on practice without real-world risks. Mechanics, engineers, and medical students can learn complex procedures through guided overlays, reducing errors and improving skill development.
AR in Healthcare
Healthcare is embracing Augmented Reality for both clinical and patient-focused applications.
Surgeons can visualize organs, blood vessels, and anatomical structures before and during procedures. AR-assisted tools improve precision and reduce surgical risks.
Outside operating rooms, AR supports rehabilitation and therapy. Patients can follow guided exercises at home while receiving real-time feedback, making recovery more engaging and effective.
Medical education also benefits from AR simulations, allowing trainees to practice without physical limitations.
AR in Navigation and Smart Mobility
Navigation is becoming more intuitive with AR integration. Instead of interpreting flat maps, users see directions overlaid directly onto real streets.
AR-powered navigation reduces confusion, improves safety, and enhances situational awareness especially in unfamiliar environments.
In automotive technology, AR displays are being developed to show speed, hazard alerts, and route guidance directly on windshields. These advancements signal a future where digital assistance blends seamlessly into daily movement.
AR in Marketing and Advertising
Modern marketing is shifting from passive messaging to interactive experiences. AR plays a central role in this evolution.
Interactive AR campaigns allow users to engage with products before purchasing, creating memorable brand experiences. This is particularly impactful in digital ads, packaging, and in-store displays.
In B2B environments, immersive demos and virtual product walkthroughs are redefining sales presentations. Many organizations now explore How AR Marketing is Transforming B2B by shortening sales cycles and improving understanding of complex solutions.
As competition intensifies, brands are also investing in Advanced AR Marketing Strategies to stand out through personalization and experiential storytelling.
AR in Real Estate and Interior Design
AR has transformed how people visualize spaces. Buyers can tour properties remotely, explore layouts, and view design options without physical visits.
Interior designers use AR to test color schemes, furniture arrangements, and renovations in real environments. This reduces uncertainty and accelerates decision-making.
For developers and agents, AR adds transparency and engagement to the buying process.
Key Benefits of Augmented Reality
The widespread adoption of AR is driven by clear, measurable advantages.
Enhanced User Experience
AR creates interactive, immersive experiences that feel intuitive and engaging.
Better Decision-Making
Visualizing products, processes, or environments reduces doubt and increases confidence.
Cost Efficiency
Businesses can replace physical prototypes, demos, and training setups with digital alternatives.
Higher Engagement
AR captures attention longer than static content, improving learning outcomes and marketing performance.
Scalability
AR experiences can be deployed globally through mobile devices, making them accessible and adaptable.
Challenges and Limitations of AR
Despite its advantages, AR still faces challenges.
Technical limitations, such as device compatibility and processing power, can affect experience quality. Privacy concerns also arise when AR applications rely heavily on camera data and location tracking.
Content creation remains resource-intensive, requiring skilled designers and developers. However, as tools become more accessible, these barriers are gradually lowering.
The Future of Augmented Reality
The future of Augmented Reality is deeply connected to advancements in hardware, connectivity, and artificial intelligence.
AR glasses are expected to become lighter, smarter, and more affordable. With the expansion of 5G networks, real-time AR experiences will become faster and more immersive.
Industries such as fitness, urban planning, manufacturing, and remote collaboration are already experimenting with next-generation AR use cases.
Major technology companies continue to invest heavily in AR development, signaling long-term commitment rather than short-term experimentation.
Why AR Matters Today
Augmented Reality has evolved beyond novelty. It is now a practical, scalable technology that enhances understanding, improves efficiency, and deepens engagement.
Whether through learning, shopping, healthcare, navigation, or communication, AR is reshaping how people interact with information and the world around them.
As adoption grows, AR and Augmented Reality will become less visible as “technology” and more integrated into everyday experiences quietly improving how people live, work, and decide.
Types of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality can be categorized into different types based on how digital content is triggered and displayed in the real world. Each type serves unique use cases across industries.
Marker-Based AR
This type of AR relies on visual markers such as QR codes, images, or symbols to trigger digital overlays. It is commonly used in print advertising, product packaging, and interactive magazines.
Markerless AR
Markerless AR does not require predefined images. Instead, it uses GPS, cameras, and sensors to understand the environment. This type is widely used in navigation apps, mobile games, and location-based experiences.
Projection-Based AR
Projection-based AR displays digital visuals directly onto physical surfaces. It is often used in manufacturing, exhibitions, and design visualization to guide users through interactive processes.
Superimposition-Based AR
This AR type replaces or enhances parts of real-world objects with virtual elements. It is frequently applied in medical imaging, product visualization, and training simulations.
Core Technologies Powering Augmented Reality

Behind every seamless AR experience lies a combination of advanced technologies working together in real time.
Computer Vision
Enables AR systems to recognize objects, surfaces, and movements within the physical environment.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Enhances object recognition, personalization, and real-time decision-making in AR applications.
3D Modeling and Rendering
Creates realistic and interactive virtual objects that blend naturally with real-world surroundings.
Sensors and Cameras
Track motion, depth, and spatial positioning to ensure accurate alignment of digital content.
AR vs VR vs MR: Understanding the Differences
Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mixed Reality are often confused, but they serve different purposes.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Adds digital elements to the real world
- Virtual Reality (VR): Immerses users in a completely digital environment
- Mixed Reality (MR): Allows real and virtual objects to interact in real time
AR is the most widely adopted because it integrates smoothly into everyday life without isolating users from their surroundings.
Why Businesses Are Investing in Augmented Reality
Businesses are adopting AR not just for innovation, but for measurable performance benefits.
- Increased customer engagement
- Better product understanding and visualization
- Lower return rates in e-commerce
- Faster and more confident purchasing decisions
- Stronger brand recall and customer loyalty
As a result, AR is becoming a strategic business tool rather than a temporary trend.
Challenges and Limitations of AR
Despite its advantages, Augmented Reality still faces several challenges.
- High development costs for advanced AR experiences
- Device compatibility and performance limitations
- Privacy and data security concerns
- Need for skilled developers and designers
However, continuous technological advancements are gradually reducing these barriers.
Preparing for an AR-Driven Future
To stay competitive, businesses and individuals can begin preparing for broader AR adoption.
- Develop AR-ready digital content
- Integrate AR into customer journeys
- Track AR performance and user behavior
- Stay updated on emerging AR tools and platforms
Early adoption of AR can provide a long-term competitive advantage as the technology becomes more mainstream.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality has moved beyond innovation hype to become a powerful, practical technology shaping everyday experiences. By blending digital information with the physical world, AR is transforming industries, improving decision-making, and redefining how people interact with products, services, and information. As technology continues to evolve, AR will play an even greater role in creating smarter, more immersive, and more meaningful digital experiences across the world.