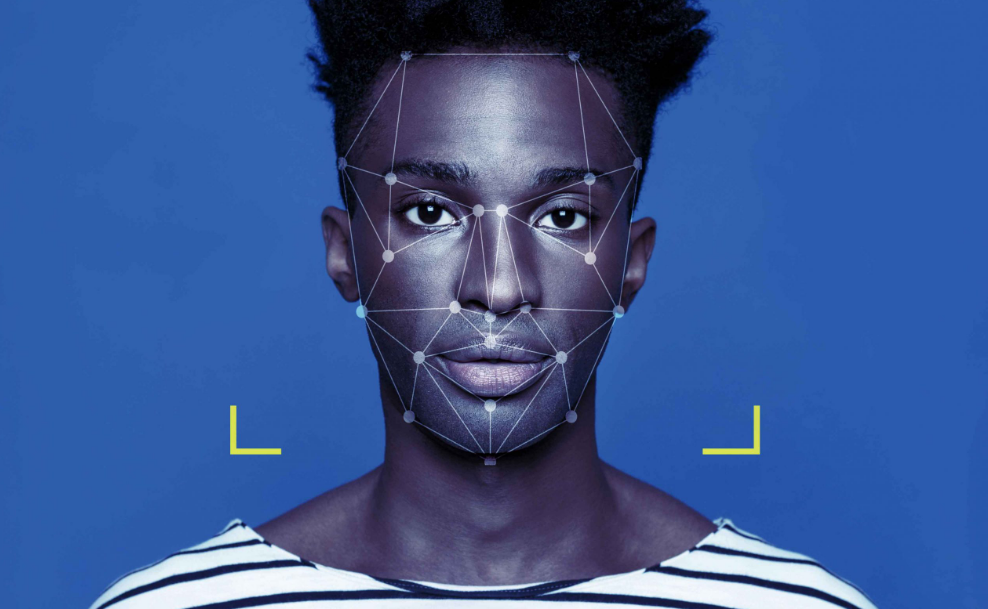
Augmented reality has transformed how we interact with digital content by blending virtual elements with our physical world. Yet something fundamental has been missing from these interactions: emotional intelligence. Traditional AR experiences remain oblivious to our emotional states, responding the same way whether we’re confused, delighted, or frustrated.
This emotional blindness creates a disconnect that limits how natural and intuitive AR experiences feel. After all, human communication isn’t just about words and actions—it’s deeply influenced by emotional cues that guide our responses and shape our connections.
Emotion recognition AI is bridging this gap, enabling AR applications to perceive, interpret, and respond to human emotions in real-time. This technology represents a fundamental shift in how we design AR experiences, moving from static interactions to emotionally intelligent exchanges.
How Emotion Recognition Works in AR
Emotion recognition systems in augmented reality typically analyze multiple data streams to interpret user emotions. Facial expression analysis captures micro-movements in facial muscles, identifying patterns associated with basic emotions like joy, surprise, anger, and confusion.
Voice tone analysis examines speech patterns, detecting emotional states through variations in pitch, rhythm, and vocal intensity. These vocal biomarkers often reveal emotions that facial expressions might conceal.
Biometric sensors in AR headsets or companion devices monitor physiological signals like heart rate variability, skin conductance, and even subtle changes in blood flow revealed through facial imaging. These biological responses provide insight into emotional arousal and stress levels that users themselves might not consciously recognize.
Movement patterns captured through AR headset sensors add another layer of emotional insight. Rapid, jerky movements might indicate excitement or anxiety, while smooth, measured movements suggest confidence or calm.
Most advanced systems combine these inputs using multimodal fusion algorithms, creating a more complete emotional profile than any single analysis method could provide. This approach helps overcome the limitations of individual detection methods and accounts for cultural and individual differences in emotional expression.
Creating Emotionally Responsive AR Experiences
For marketers seeking to leverage emotion recognition in AR campaigns, understanding emotional response becomes invaluable. To explore more innovative AR marketing strategies, visit our comprehensive resource library at ARMarketingTips.com.
When integrated with AR, emotion recognition enables experiences that adapt to users’ emotional states. Virtual characters in AR environments can adjust their behavior based on detected emotions, creating more natural and engaging interactions. A virtual assistant might speak more slowly when confusion is detected or offer encouragement when frustration appears.
Content presentation can automatically adjust to emotional cues. If a user appears overwhelmed, an AR interface might simplify, showing fewer options or providing additional guidance. When excitement is detected, the experience might amplify engaging elements or introduce new features to maintain interest.
Narrative elements in AR experiences can branch based on emotional responses, creating personalized storylines that resonate with individual users. This emotional customization creates deeper engagement than static narratives ever could.
For retail applications, product recommendations can factor in emotional responses to previous items, creating a more intuitive shopping experience. If a customer shows excitement about a particular style, similar items can be highlighted in their AR shopping interface.
Real-World Applications
Emotion-aware AR is finding applications across various industries, each leveraging emotional intelligence to enhance user experiences. In retail environments, AR mirrors equipped with emotion recognition help shoppers find products that evoke positive emotional responses. These systems can detect subtle signs of interest or hesitation that shoppers themselves might not articulate.
Education platforms use emotion recognition to identify when students struggle with concepts, adjusting lesson difficulty or providing additional support before frustration leads to disengagement. This emotional responsiveness creates more effective learning experiences tailored to individual needs.
Healthcare applications monitor emotional states during therapy or rehabilitation exercises, providing clinicians with valuable insights and adjusting virtual guidance based on patient emotional responses. This emotional awareness can improve adherence to treatment protocols and provide early warning of potential issues.
Entertainment experiences leverage emotional feedback loops to adjust narrative intensity, pacing, and content based on user emotional states. These dynamic adjustments create more immersive and satisfying entertainment experiences that respond to moment-by-moment emotional changes.
Automotive interfaces use AR combined with emotion recognition to detect driver fatigue or distraction, adjusting alerts and information presentation to improve safety. These systems can recognize early signs of emotional states that might impact driving performance.
Ethical Considerations
The power of emotion recognition in AR brings significant ethical responsibilities that developers and marketers must address. Privacy concerns are paramount, as emotion recognition collects deeply personal data about users’ internal states. Clear consent mechanisms and transparent data policies are essential for maintaining user trust.
Emotional manipulation risks must be carefully managed to ensure AR experiences enhance rather than exploit emotional responses. Ethical guidelines should prevent experiences designed to induce negative emotions or exploit psychological vulnerabilities.
Cultural differences in emotional expression can lead to misinterpretation by systems trained on limited cultural datasets. Developers must ensure systems recognize and respect these differences to avoid biased or inaccurate emotional assessments.
Opt-out mechanisms should allow users to disable emotion recognition features without losing core AR functionality. This respect for user autonomy helps build trust in emotion-aware systems.
Data security becomes even more critical when systems collect emotional data. Robust protection measures must safeguard this sensitive information throughout its lifecycle.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing emotion recognition in AR environments presents several technical and practical challenges. Technical limitations include accuracy across diverse user populations, performance constraints on mobile devices, and integration complexity with existing AR frameworks.
Calibration requirements often necessitate personalized baseline measurements to account for individual differences in emotional expression. These calibration processes must be streamlined to avoid disrupting the user experience.
Multi-user scenarios create additional complexity, as systems must track and respond to multiple emotional states simultaneously in shared AR environments. This capability becomes essential for collaborative AR experiences.
Battery consumption increases with the additional processing required for real-time emotion analysis. Developers must optimize algorithms to minimize power impact, especially for wearable AR devices.
User acceptance varies significantly based on cultural factors, technology familiarity, and personal privacy preferences. Thoughtful onboarding experiences can help users understand the benefits of emotion recognition while addressing potential concerns.
Future Directions
As emotion recognition technology matures, several emerging trends will shape its integration with augmented reality. Contextual emotion understanding will move beyond recognizing basic emotions to interpreting emotions within specific situations and environments. This nuanced understanding will enable more appropriate and helpful responses.
Emotional memory systems will track emotional patterns over time, recognizing individual baseline states and detecting meaningful deviations. These historical insights will help systems distinguish between momentary emotions and significant emotional shifts.
Cross-platform emotional profiles will allow emotion-aware AR experiences to maintain consistent emotional intelligence across devices and applications. These unified profiles will create more coherent experiences as users move between different AR environments.
Emotional recommendation engines will suggest content, experiences, or products based not just on explicit preferences but on emotional responses to previous interactions. These systems will better predict what users will find genuinely satisfying rather than just superficially appealing.
Emotional health applications will use AR combined with emotion recognition to support mental wellbeing, helping users visualize and understand their emotional states. These applications represent a promising frontier for therapeutic AR experiences.
Getting Started with Emotion Recognition in AR
Organizations interested in implementing emotion recognition in AR experiences should begin with clearly defined use cases where emotional awareness directly enhances user value. Starting with targeted applications helps manage complexity while demonstrating tangible benefits.
Cross-functional teams combining expertise in AR development, user experience design, and ethical AI implementation will produce more robust solutions than technical teams working in isolation. This collaborative approach helps address both technical and human factors.
User testing becomes especially important when implementing emotion recognition, as emotional responses to these systems vary widely. Iterative testing with diverse user groups helps refine both the technical performance and user acceptance of emotion-aware AR.
Privacy-by-design principles should guide development from the earliest stages, ensuring data minimization, purpose limitation, and user control are built into system architecture. This approach helps prevent privacy issues that might otherwise undermine user trust.
Conclusion
Emotion recognition AI represents the next frontier in augmented reality interaction, moving beyond simple gesture and voice commands to create truly responsive experiences that understand and adapt to human emotions. This evolution makes AR experiences feel more natural, intuitive, and personally relevant.
As this technology matures, it will increasingly differentiate premium AR experiences from basic implementations. Organizations that thoughtfully implement emotion recognition capabilities will create more engaging, effective, and memorable augmented reality interactions.
The future of AR lies not just in what we can see and do in augmented spaces, but in how those spaces understand and respond to our emotional states. By bringing emotional intelligence to digital interactions, we’re creating AR experiences that connect with users on a fundamentally human level.