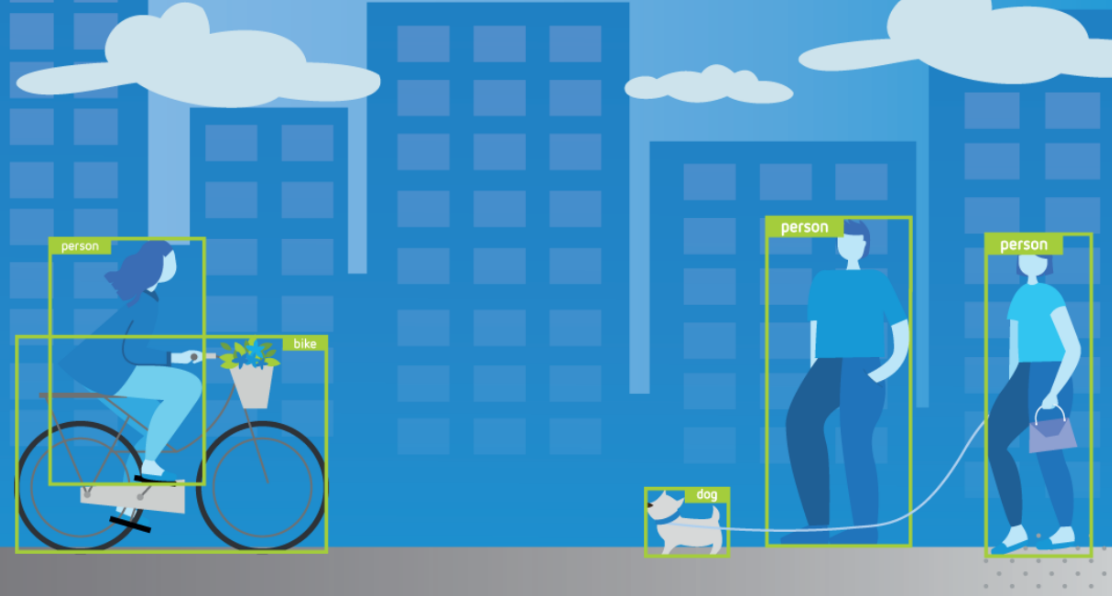
Have you ever wondered how your smartphone can instantly identify objects through its camera? Or how AR applications can place virtual furniture in your living room with perfect positioning?
Behind these technological marvels lies AI-powered object recognition.
What Makes Object Recognition Essential for AR
At its core, augmented reality needs to understand the real world before it can enhance it. This understanding comes from object recognition technology.
Modern AR systems rely on sophisticated AI algorithms to identify real-world objects quickly and accurately. This capability forms the foundation of truly immersive augmented experiences.
Without effective object recognition, AR applications would struggle to place digital content in meaningful ways within our physical surroundings.
The Evolution of Object Recognition in AR
Early AR systems used simple marker-based recognition. They required special QR-like codes to anchor digital content.These systems were limited and inflexible.
Today’s advanced neural networks can identify virtually any object without special markers. This breakthrough has expanded AR’s potential exponentially.
Modern AI can recognize faces, furniture, buildings, foods, and countless everyday items in milliseconds.
This technology continues to improve at a remarkable pace, with recognition accuracy approaching human-level performance in many categories.
How AI Recognition Algorithms Work
Object recognition in AR systems typically involves three key phases:
Detection locates potential objects within a scene. The AI rapidly scans the visual field to identify areas that might contain recognizable items.
Classification determines what the detected object actually is. This process matches visual features against trained models of thousands of object categories.
Tracking maintains awareness of the object’s position even as the camera or object moves. This ensures digital overlays remain properly anchored. These processes happen simultaneously dozens of times per second to create seamless AR experiences.
Real-World Applications Transforming Industries
The impact of AI object recognition in AR spans numerous industries:
Retail customers can visualize products in their homes before purchasing. A sofa, painting, or appliance can be digitally placed in a living space with proper scaling and positioning.
Manufacturing workers receive visual guidance overlaid directly on complex machinery. The system recognizes specific components and provides relevant information precisely where needed.
Healthcare professionals can use AR systems that recognize anatomical structures and overlay crucial medical information during procedures or training.
Education has been revolutionized with AR applications that identify objects in textbooks and bring them to life with interactive 3D models.
Navigation apps now recognize landmarks and buildings to provide intuitive directional guidance through your camera view. Visit our homepage for more insights on leveraging AR technology for business growth.
Challenges and Future Developments
Despite impressive advances, challenges remain in AR object recognition:
Lighting conditions can still impact recognition accuracy. Algorithms continue to improve at functioning in low-light environments.
Processing power limitations affect mobile devices. Developers must balance accuracy with efficiency for smooth performance.
Unusual angles sometimes confuse recognition systems. Next-generation algorithms are addressing this by incorporating 3D understanding rather than relying solely on 2D views.
The future promises even more sophisticated object recognition capabilities. Researchers are developing systems that can: Understand object functions, not just appearances.
Recognize physical properties like material types and textures. Identify subtle state changes in objects, such as whether a device is powered on.
Implementing AI Object Recognition in AR Projects
For developers looking to incorporate object recognition into AR applications:
Pre-trained models offer a solid starting point without extensive AI expertise.
Custom training may be necessary for specialized applications or unique object sets.
Cloud-based solutions can overcome device processing limitations but require internet connectivity.
Edge computing approaches are gaining popularity for applications needing real-time performance without connectivity dependencies.
Conclusion
AI-powered object recognition has transformed augmented reality from a novelty into a powerful tool with practical applications across industries.
As these technologies continue to evolve, we’ll see increasingly seamless integration between digital content and our physical world.
The barrier between virtual and real continues to blur, creating unprecedented opportunities for businesses and developers alike.
The future of AR isn’t just about adding digital elements to our view—it’s about creating intelligent systems that truly understand what they’re seeing.
That understanding begins with object recognition, the foundation upon which the most compelling AR experiences are built.